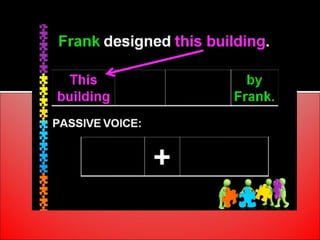
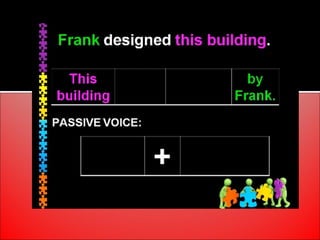
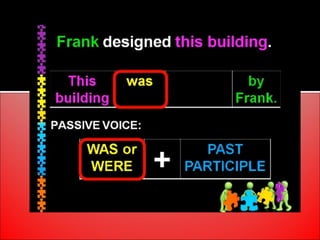
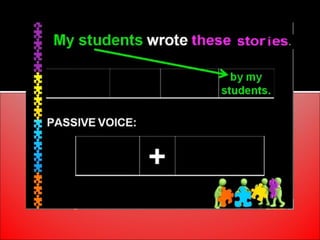
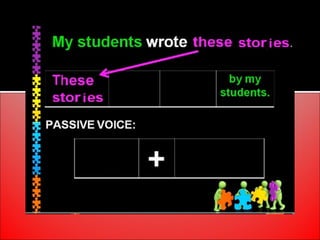
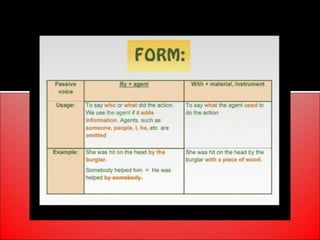
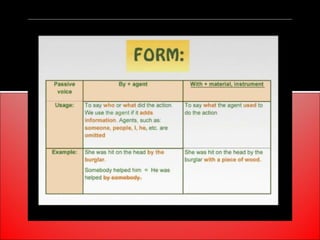
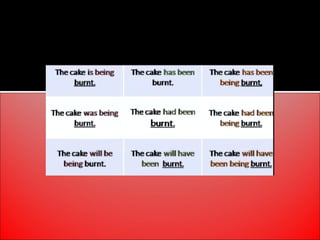
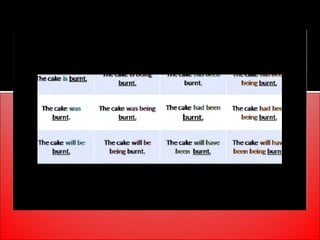
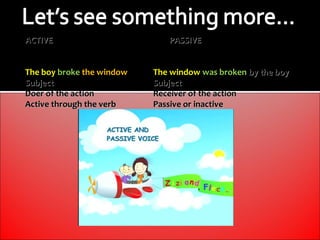
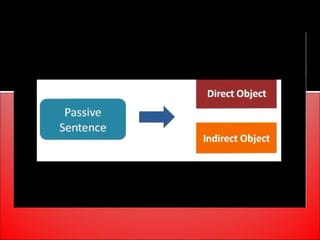
The document provides an overview of active and passive voice in English grammar, defining both and explaining their functions. It includes examples, exercises, and guidelines on how to recognize and use each voice appropriately. The lesson aims to equip learners with the ability to differentiate between active and passive voice, as well as apply their knowledge in practice.