Embed presentation
Downloaded 12 times



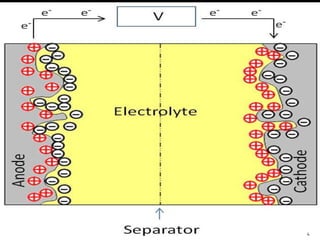
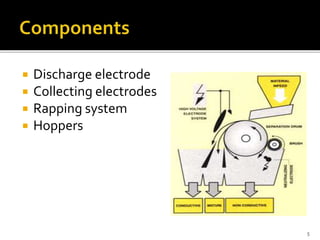


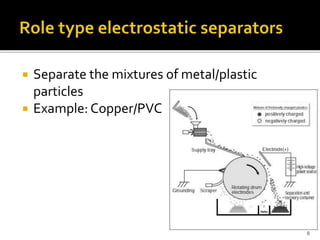
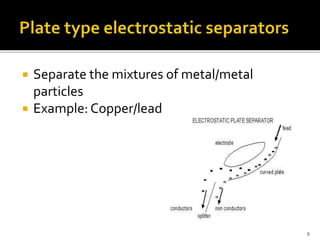
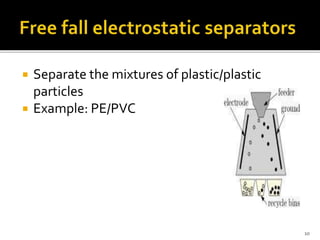



An electrostatic separator uses electrostatic forces to selectively sort solid particles based on their charge. It works by inducing a charge on particles in a gas stream using discharge electrodes, then collecting the charged particles on oppositely charged collecting electrodes. Key components include discharge electrodes, collecting electrodes, a rapping system to remove collected particles, and hoppers to contain the separated particles. Electrostatic separators can separate mixtures of different metal, plastic, or metal and plastic particles, and operate either dry or wet.












