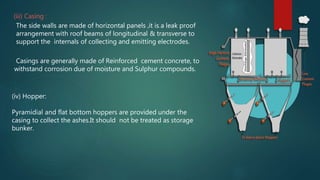
The document provides information on electrostatic precipitators (ESPs) including their purpose, construction, working principle, types, performance factors, advantages, and disadvantages. ESPs are large industrial emission control units that use electric charges to remove dust particles from exhaust gases. They apply high voltage to generate corona discharge which charges particles negatively, allowing them to be attracted to and collected by positively charged plates. Wet ESPs are better for removing fine particles and addressing issues with dry ESPs like re-entrainment and dust cake resistivity. Despite their high costs, ESPs are necessary due to their high removal efficiency even for nano-scale particles.