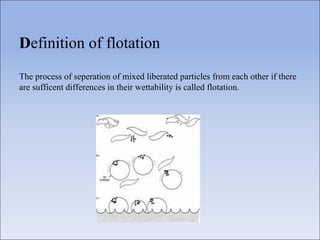
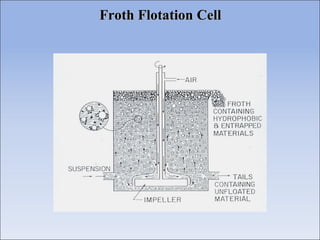
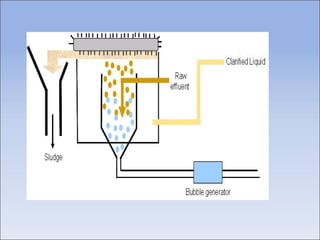
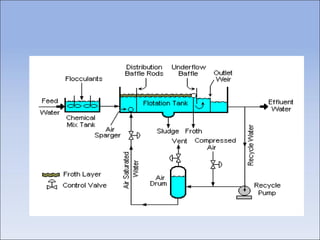
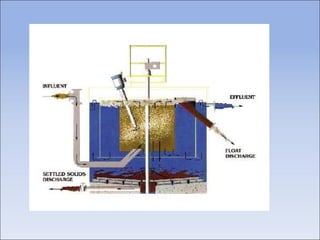
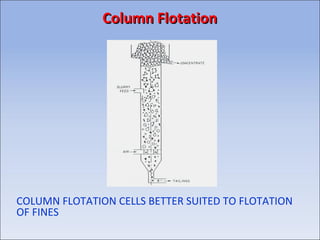
Flotation is a process used to separate minerals from gangue by taking advantage of differences in the abilities of minerals to wet or adhere to air bubbles. It involves grinding ore to liberate particles, rendering the desired mineral hydrophobic using surfactants, and introducing air bubbles. Hydrophobic minerals attach to the bubbles and are carried to the surface, forming a froth layer that is skimmed off. Reagents called collectors, frothers, and modifiers are used to control the selectivity and efficiency of the separation. Flotation is widely used in the mining industry to concentrate ores for further processing.