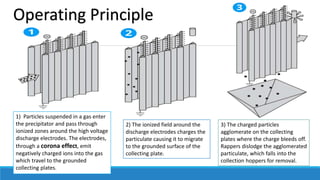
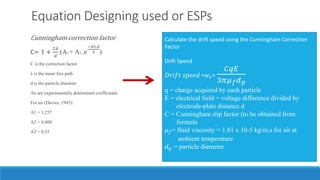
Electrostatic precipitators remove dust particles from gas exhaust by charging particles with a high-voltage charge and collecting them on oppositely charged plates. They operate by ionizing particles in the gas which migrate to grounded collection plates. Particles agglomerate on plates and are removed periodically. Electrostatic precipitators can be single or two-stage, dry or wet, and plate or tubular design. They are commonly used to control emissions from industries like oil refining, power plants, and food processing.