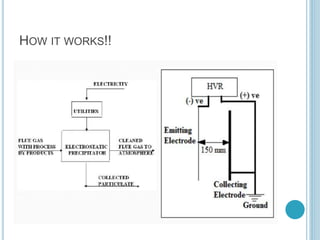
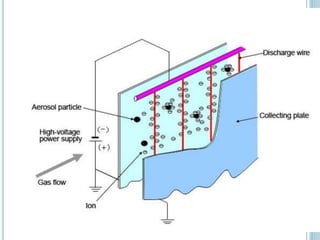
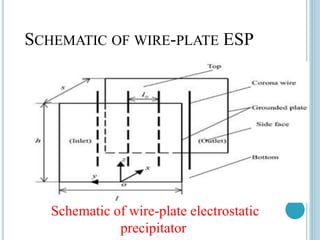
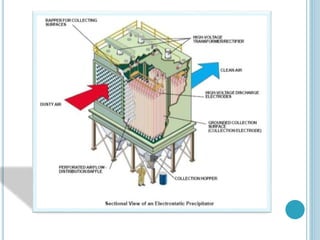
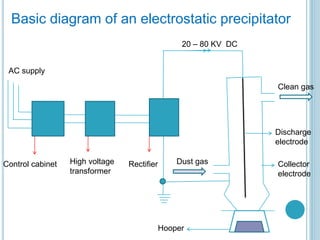
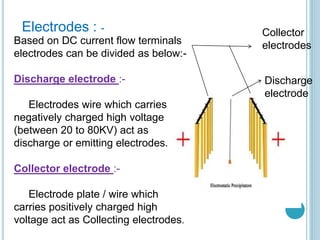
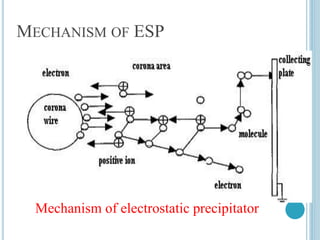
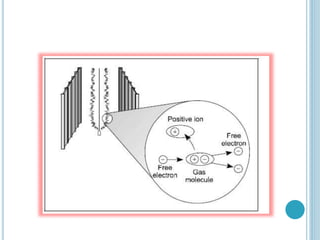
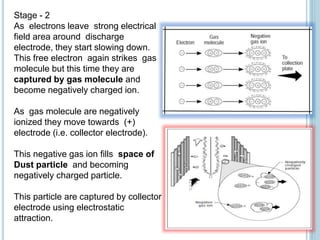
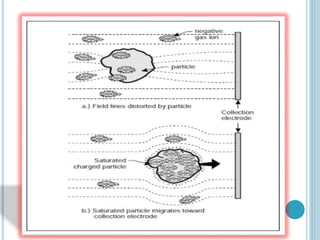
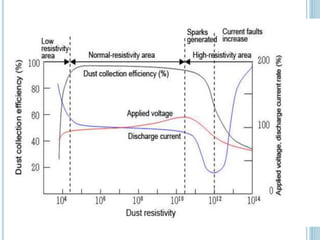
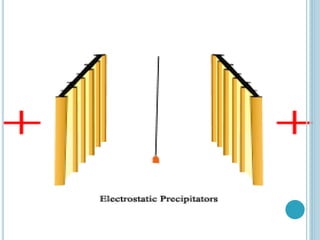
An electrostatic precipitator (ESP) removes dust particles from gas streams like air using electrostatic attraction. It has high-voltage discharge electrodes that ionize gas molecules, and positively charged collection electrodes that attract the ionized dust particles. The ESP operates in three stages: particle charging by corona discharge from the electrodes, transport of charged particles towards the collection plates, and collection of particles on the positively charged collection plates. ESPs are highly efficient filtration devices that allow gases to flow through while removing fine particulate matter like dust and smoke.