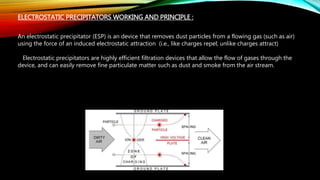
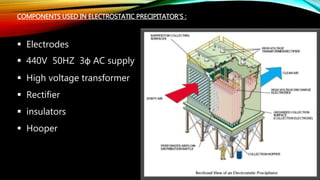
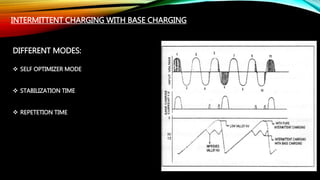
An electrostatic precipitator removes dust from flue gases using the attraction between charged dust particles and oppositely charged plates. It works by first charging the dust particles using a corona discharge near discharge electrodes, which creates ions that charge the particles. The charged particles are then attracted to nearby grounded or positively charged collecting electrodes, where they accumulate and are later removed. Electrostatic precipitators use components like electrodes, high voltage transformers, rectifiers, and insulators to generate a strong electrostatic field and separate dust from the flue gas into a hopper for disposal. Controllers help regulate the voltage applied to maximize the dust collection rate over time.