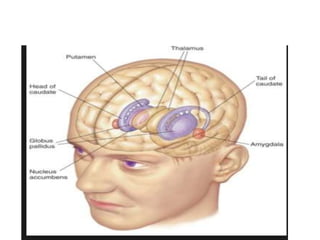
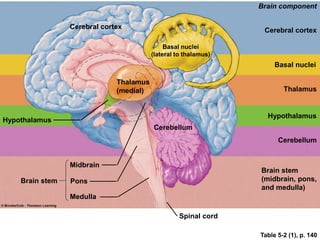
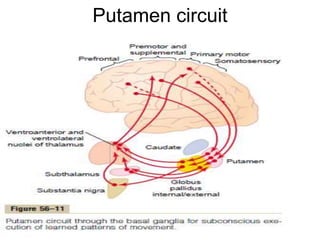
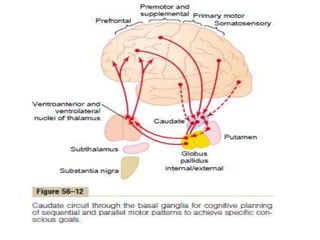
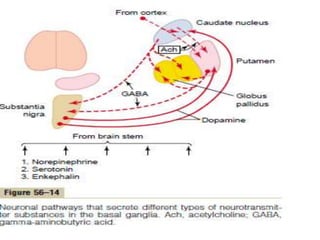
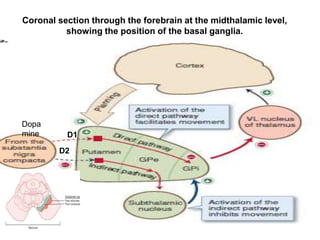
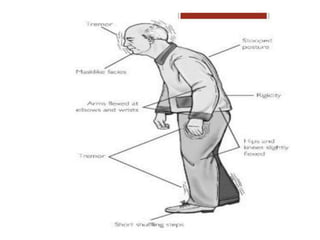
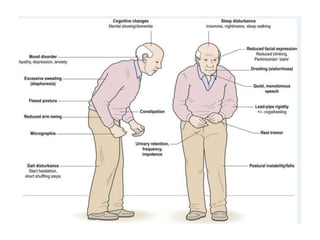
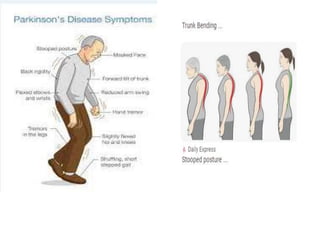
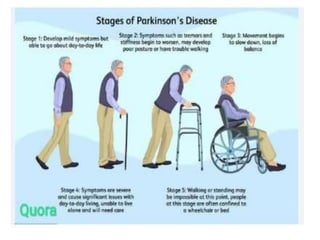
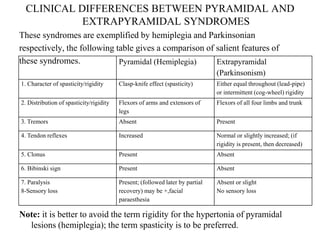
This document discusses Parkinsonism, a motor system disease caused by damage to the basal ganglia, specifically the substantia nigra, resulting in dopamine deficiency. The key features are akinesia, rigidity, tremors, and changes to posture and gait. Pathophysiologically, there is an imbalance between excitation and inhibition in the basal ganglia circuitry due to less dopaminergic inhibition of the putamen. Treatment involves replacing dopamine using L-Dopa or inhibiting its breakdown with monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Other treatments include deep brain stimulation to disrupt dysfunctional circuits. The document contrasts features of Parkinsonism versus those of pyramidal system diseases like hemiplegia.