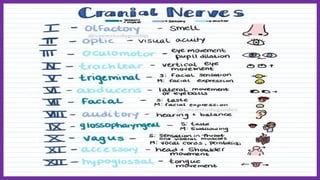
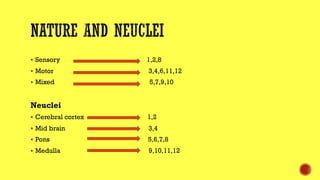
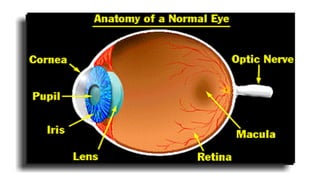
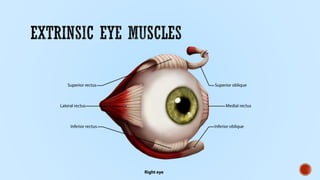
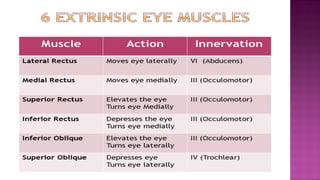
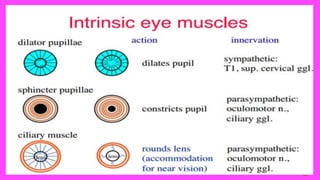
This document provides information about cranial nerves 3, 4, and 6 which innervate eye muscles. It lists the names and functions of the extraocular and intrinsic eye muscles. Cranial nerve 3 innervates most of the extraocular muscles as well as the intrinsic muscles. Cranial nerve 4 innervates the superior oblique muscle and cranial nerve 6 innervates the lateral rectus muscle. The effects of lesions to each of these cranial nerves are described, including paralysis of specific eye movement and pupil abnormalities.