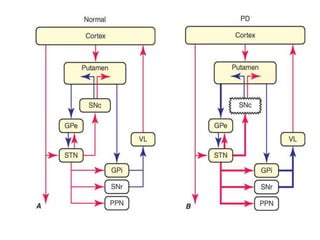
Parkinson's disease is characterized by tremors, rigidity, bradykinesia and postural instability. It is caused by degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra, reducing striatal dopamine. The basal ganglia circuitry is disrupted, affecting movement planning and execution. Levodopa is the most effective treatment but has long term side effects; it is often combined with carbidopa to reduce peripheral effects and dosage. Differential diagnoses include conditions with similar parkinsonian symptoms but different causes or presentations.