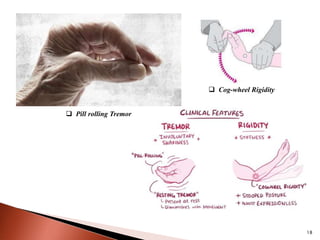
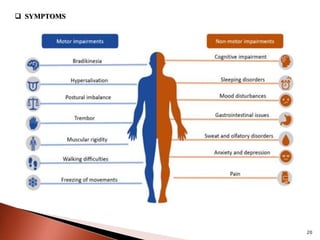
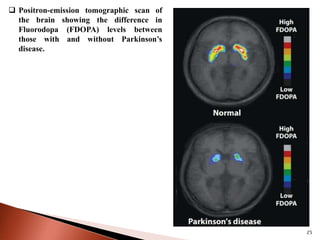
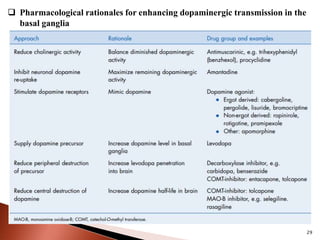
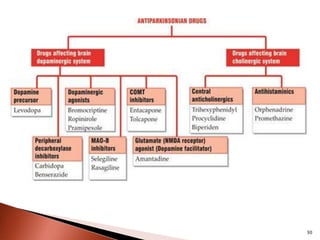
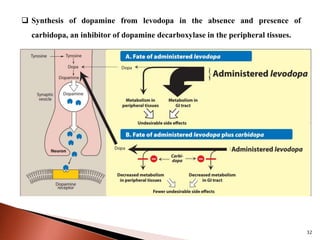
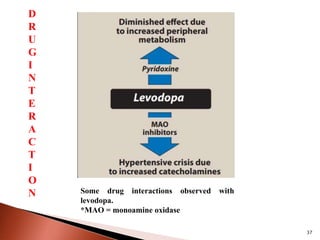
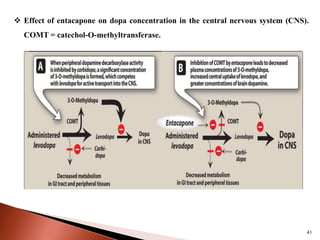
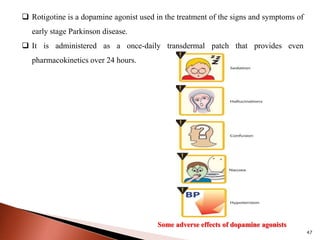
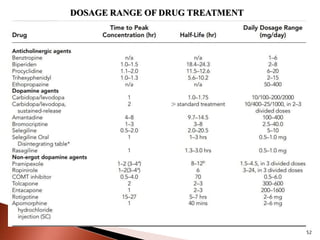
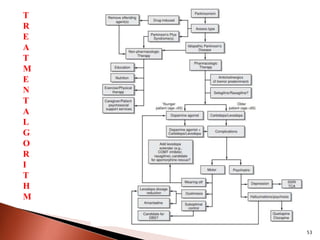
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by motor symptoms such as tremors, rigidity, and bradykinesia, primarily due to the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra. It affects approximately 1% of the population over 65 and has both primary (idiopathic) and secondary causes, with drug-induced parkinsonism being noteworthy as it can often be reversed upon cessation of the offending medication. Current treatment aims to enhance dopaminergic activity through pharmacological means, primarily with levodopa and carbidopa to manage symptoms, alongside non-pharmacological interventions like exercise and nutrition.