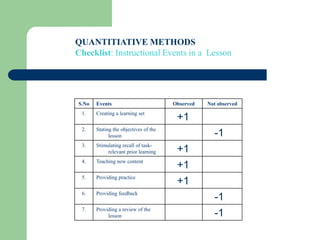
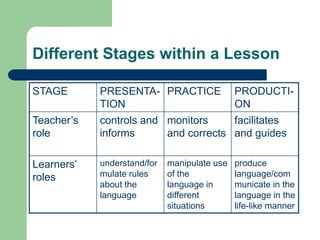
The document discusses the importance of reflective teaching practices for professional development in English language teaching (ELT). It defines reflective practice as critically analyzing one's own experiences and attempting to generalize lessons from that reflection. The document outlines that reflective teaching involves reflecting on areas like content knowledge, understanding learners, teaching approaches, and lesson effectiveness. Both qualitative and quantitative methods of reflection are presented, like journals, feedback forms, and checklists. An example of a retrospective teaching report is provided, and readers are asked to reflect on how they would analyze the report. Overall, the document argues that reflective practice helps teachers structure problems, question their approaches, and improve their instruction over time through self-analysis.