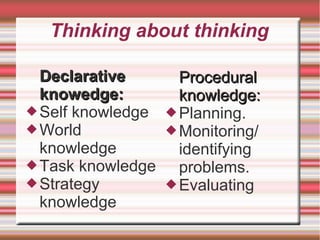
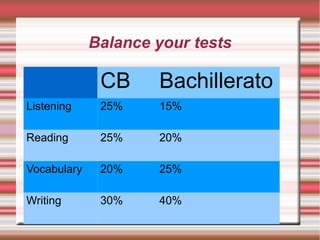
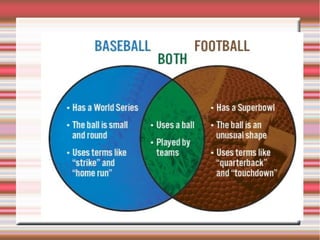
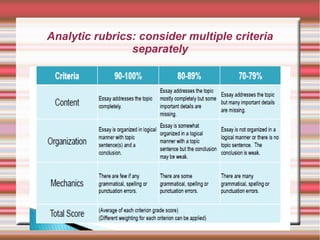
The document provides strategies for accelerating academic learning for English learners. It discusses identifying students' academic needs, describing an instructional model, and identifying learning strategies. Academic needs include developing vocabulary, reading to acquire information, understanding oral presentations, participating in discussions, and writing to communicate knowledge. The document also discusses the role of academic content, input texts, the teacher's role, thinking strategies, metacognitive strategies, and assessing student writing.