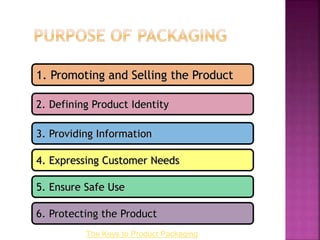
Packaging and labeling serve several important purposes. Packaging protects products during shipping and storage, prevents tampering, and aids in product promotion and sales. Labeling provides key information to customers about product contents and use. Effective labels feature graphics and fonts that attract attention, communicate the brand, and describe the product through colors, shapes, and clearly presented contact and contents information. Together, packaging and labeling are an essential part of marketing strategy and ensuring safe and appropriate product use.