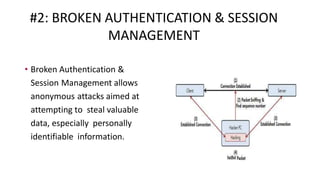
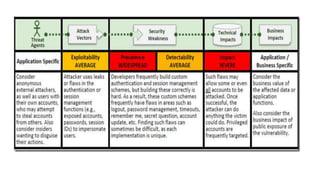
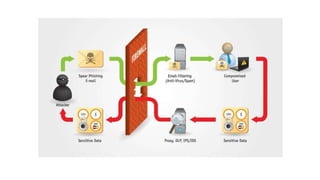
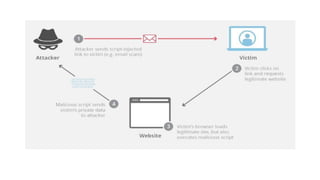
The document outlines the top 10 vulnerabilities according to OWASP: 1) Injection, 2) Broken Authentication & Session Management, 3) Sensitive Data Exposure, 4) XML External Entities, 5) Broken Access Control, 6) Security Misconfiguration, 7) Cross-Site Scripting, 8) Insecure Deserialization, 9) Using Components with Known Vulnerabilities, and 10) Insufficient Logging & Monitoring. Each vulnerability is briefly described, with Injection being the most common issue that allows hostile data to execute unintended commands. Broken Authentication, Sensitive Data Exposure, and Cross-Site Scripting are also major risks. Proper logging and monitoring is important to detect attacks.