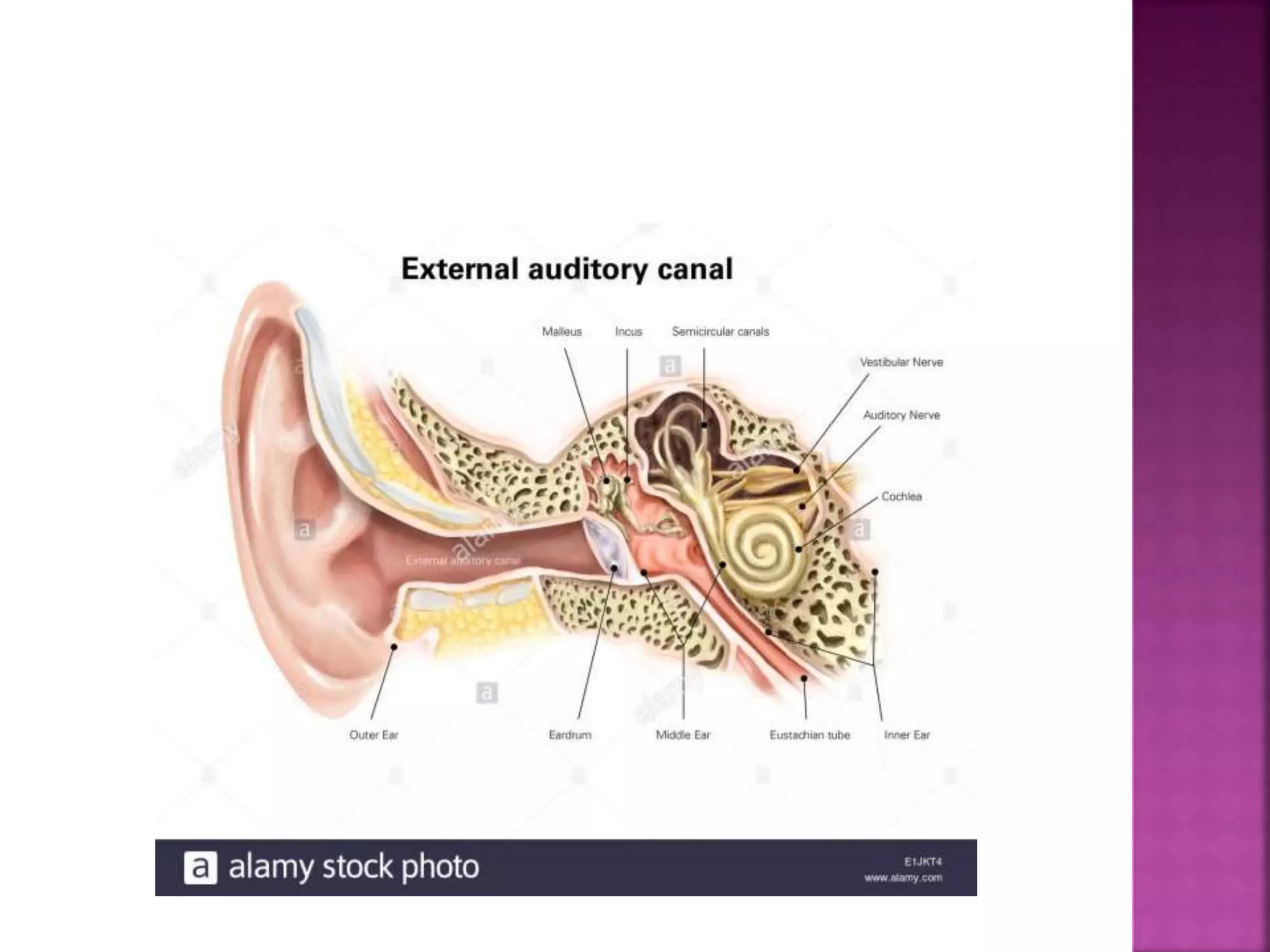
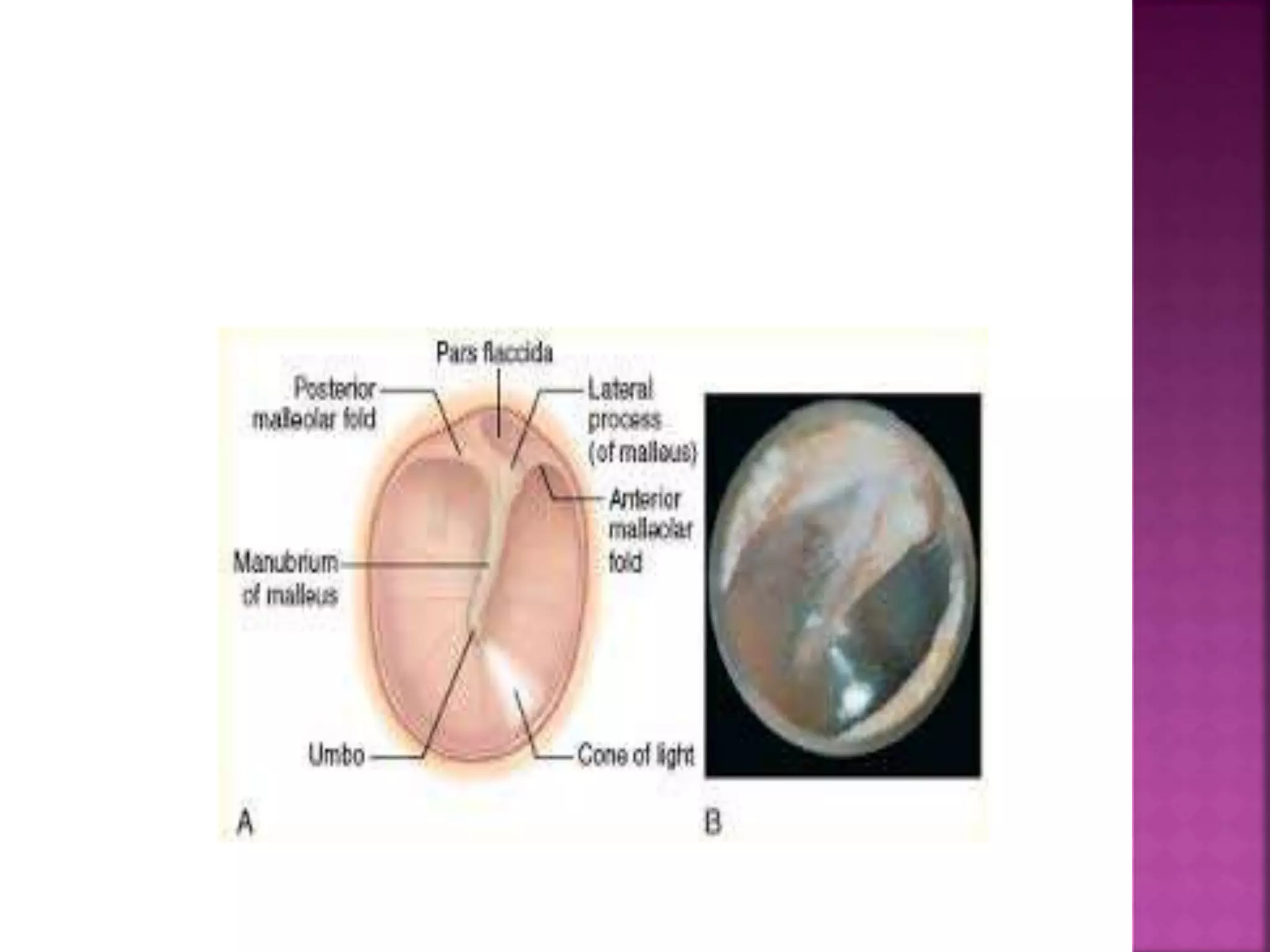
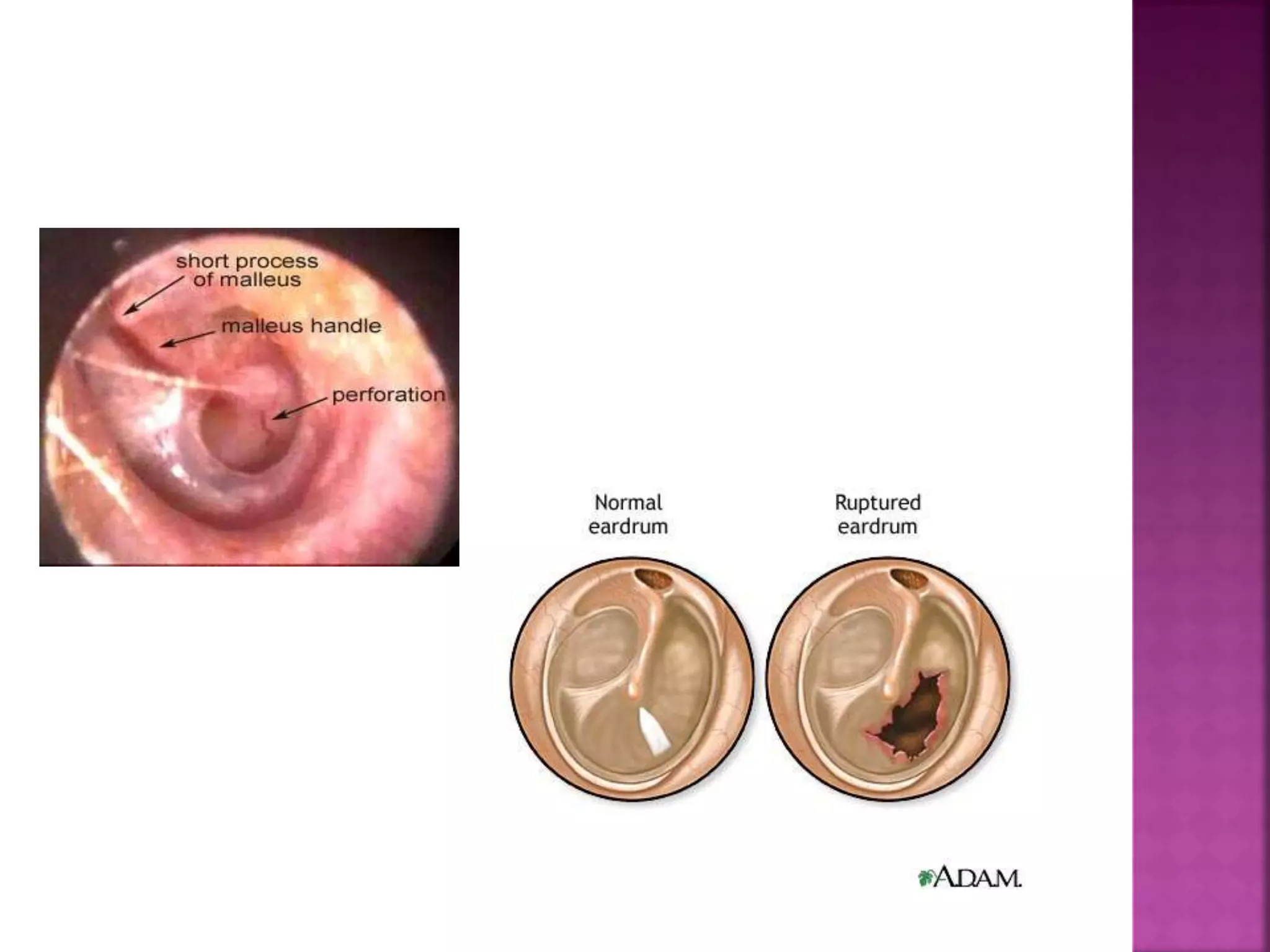
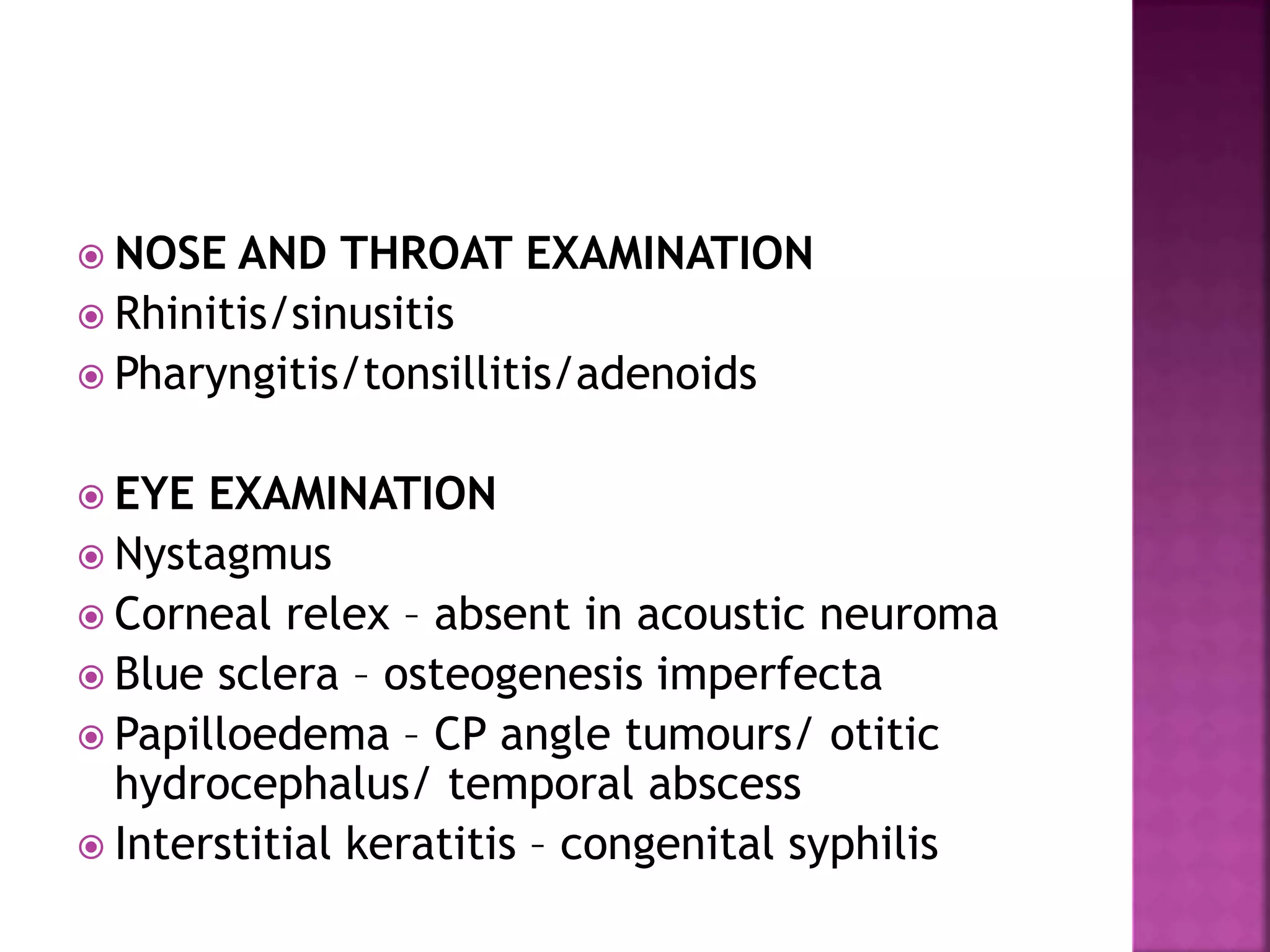
This document provides guidance on performing a thorough examination of the ear, including inspection, palpation, and various tests. It describes how to examine the external ear, ear canal, tympanic membrane, mastoid region, and surrounding areas. Examination findings are outlined for various normal and abnormal conditions. The document also mentions examining related structures like the nose, throat, eyes, respiratory and cardiovascular systems as part of a full ear examination.