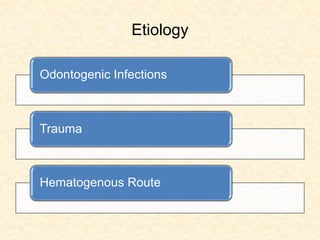
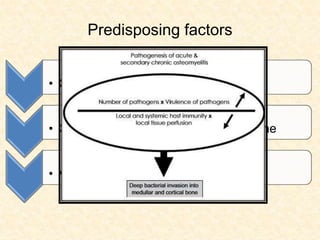
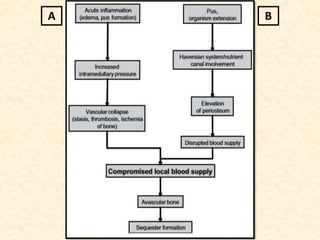
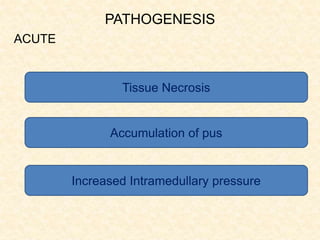
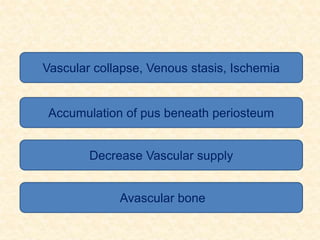
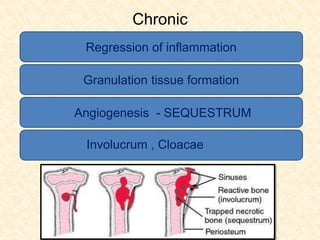
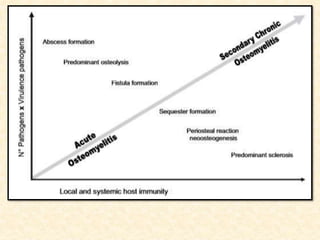
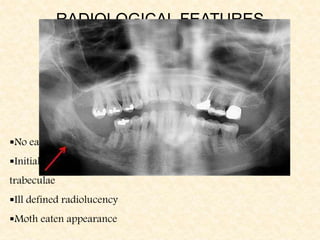
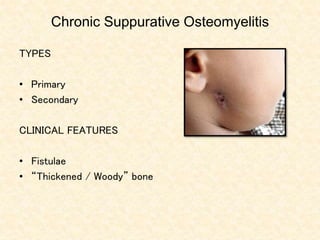
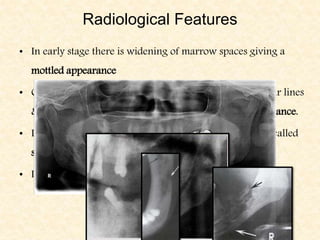
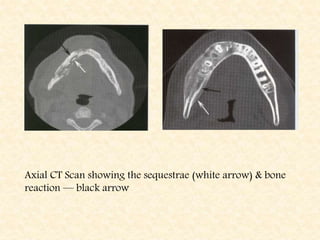
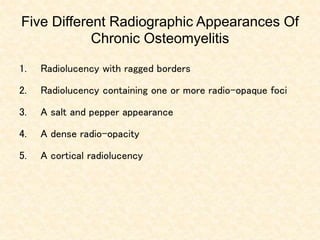
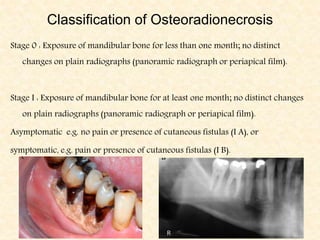
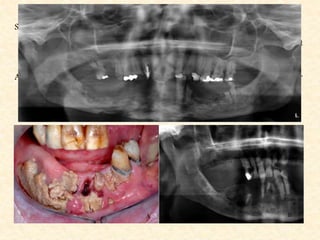
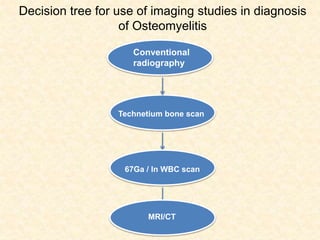
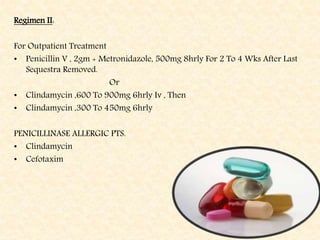
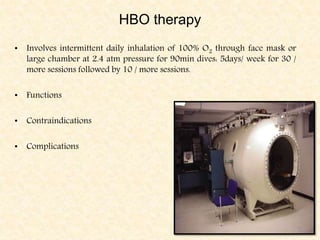
The document provides a comprehensive overview of osteomyelitis, particularly focusing on its definition, classification, causes, pathogenesis, clinical features, and treatment options. It covers both acute and chronic forms of the disease, detailing various predisposing factors and microbiological agents involved. The text emphasizes the importance of early recognition and appropriate management to prevent significant morbidity related to the condition.