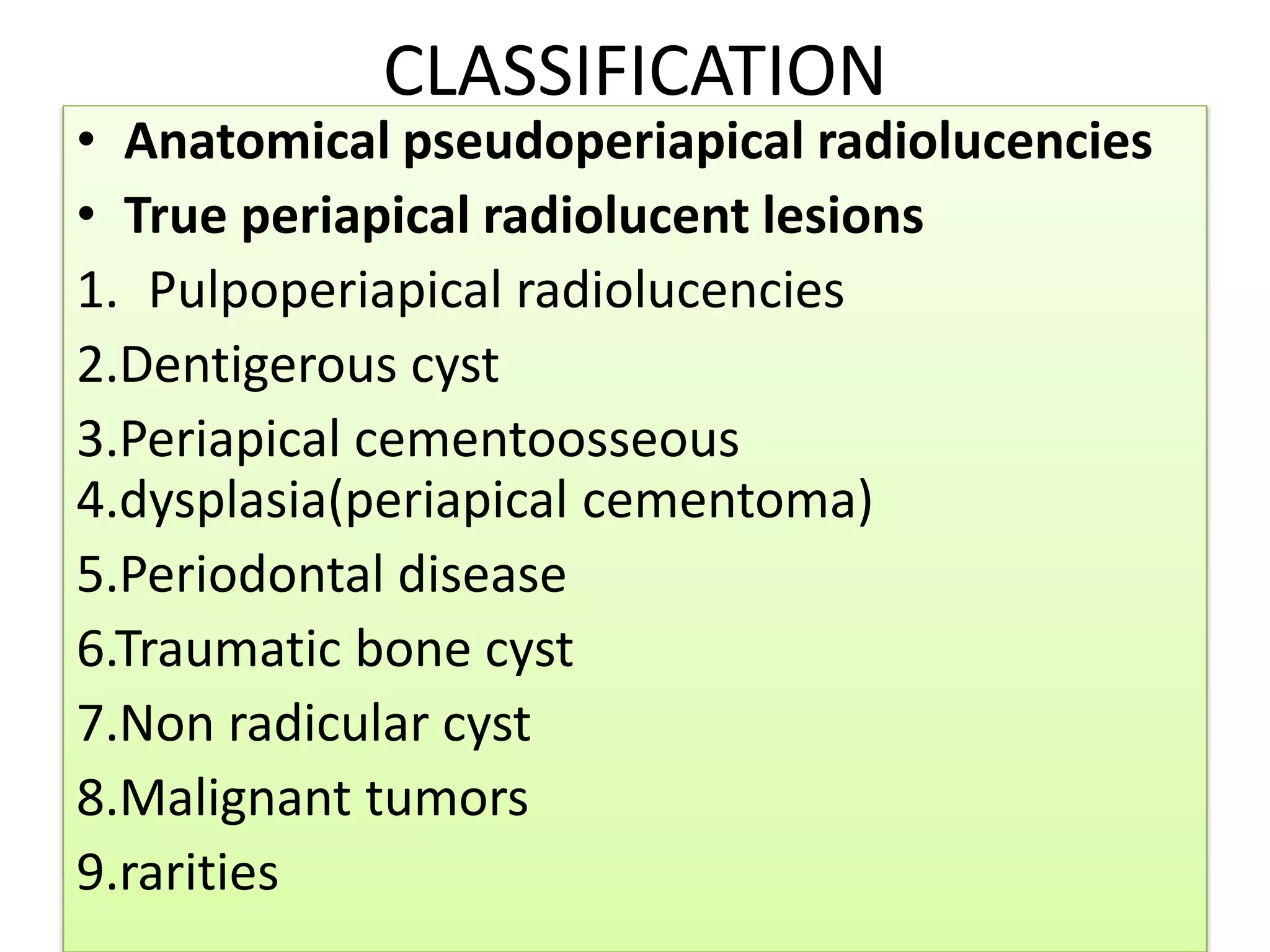
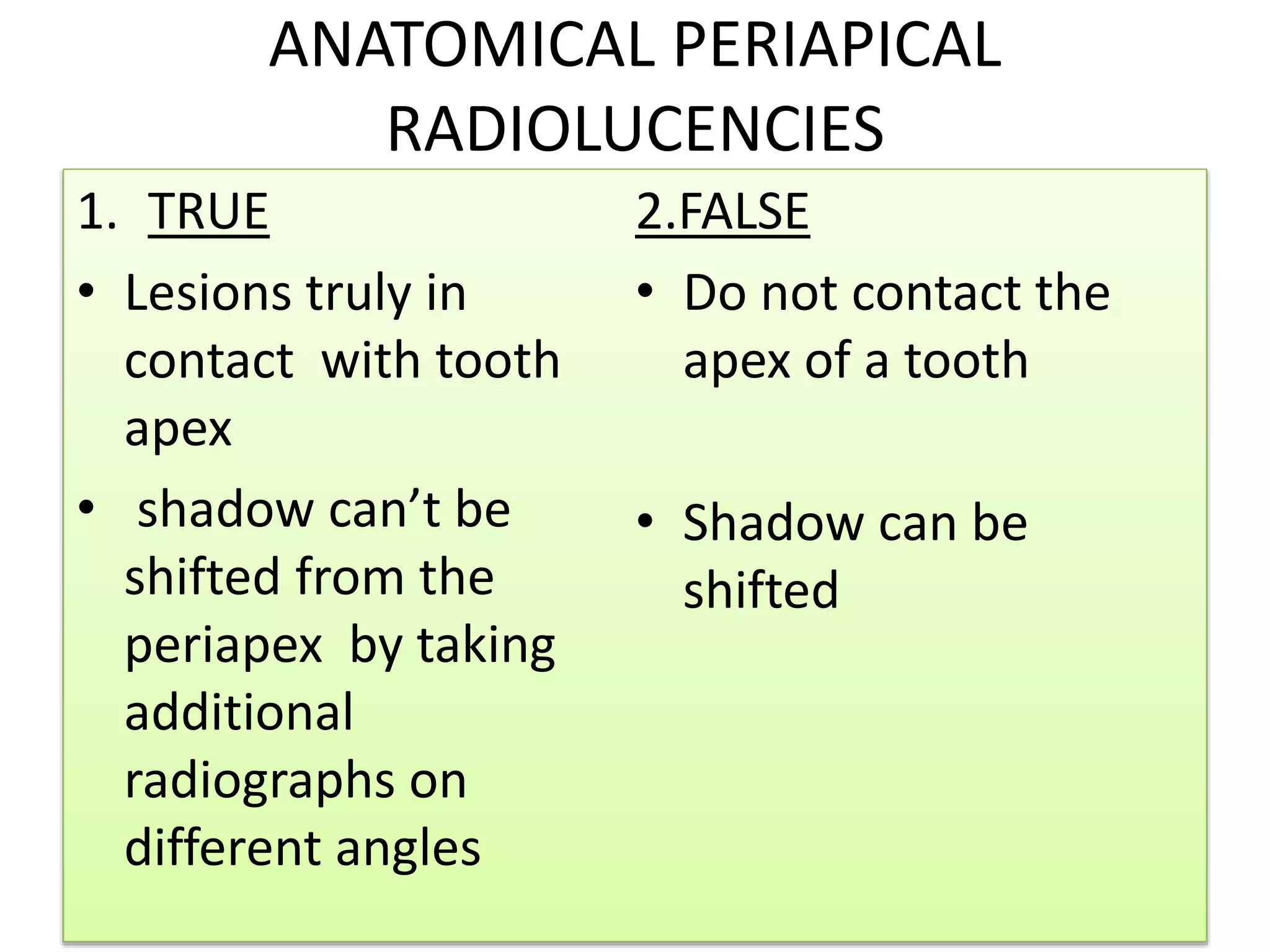
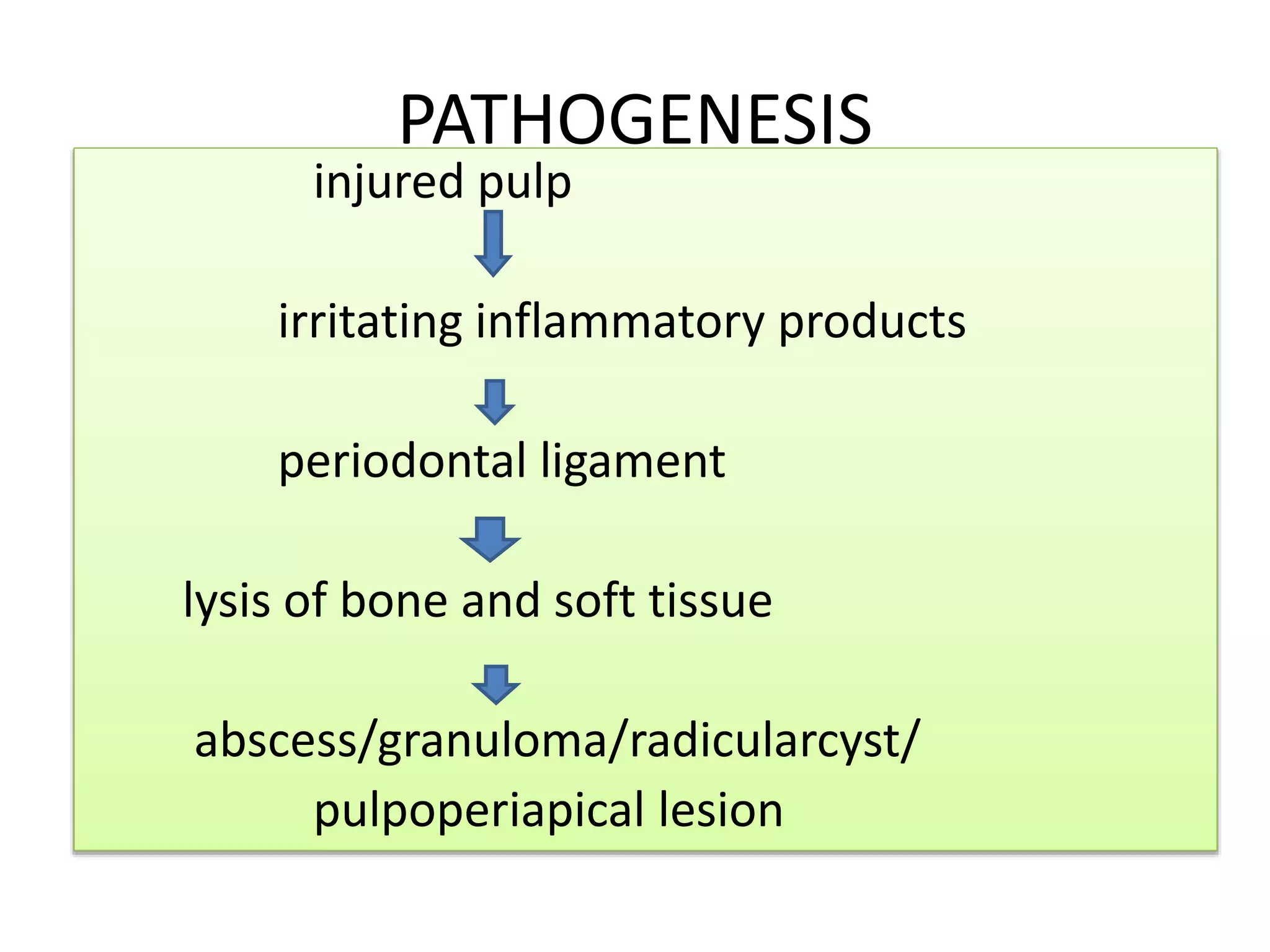
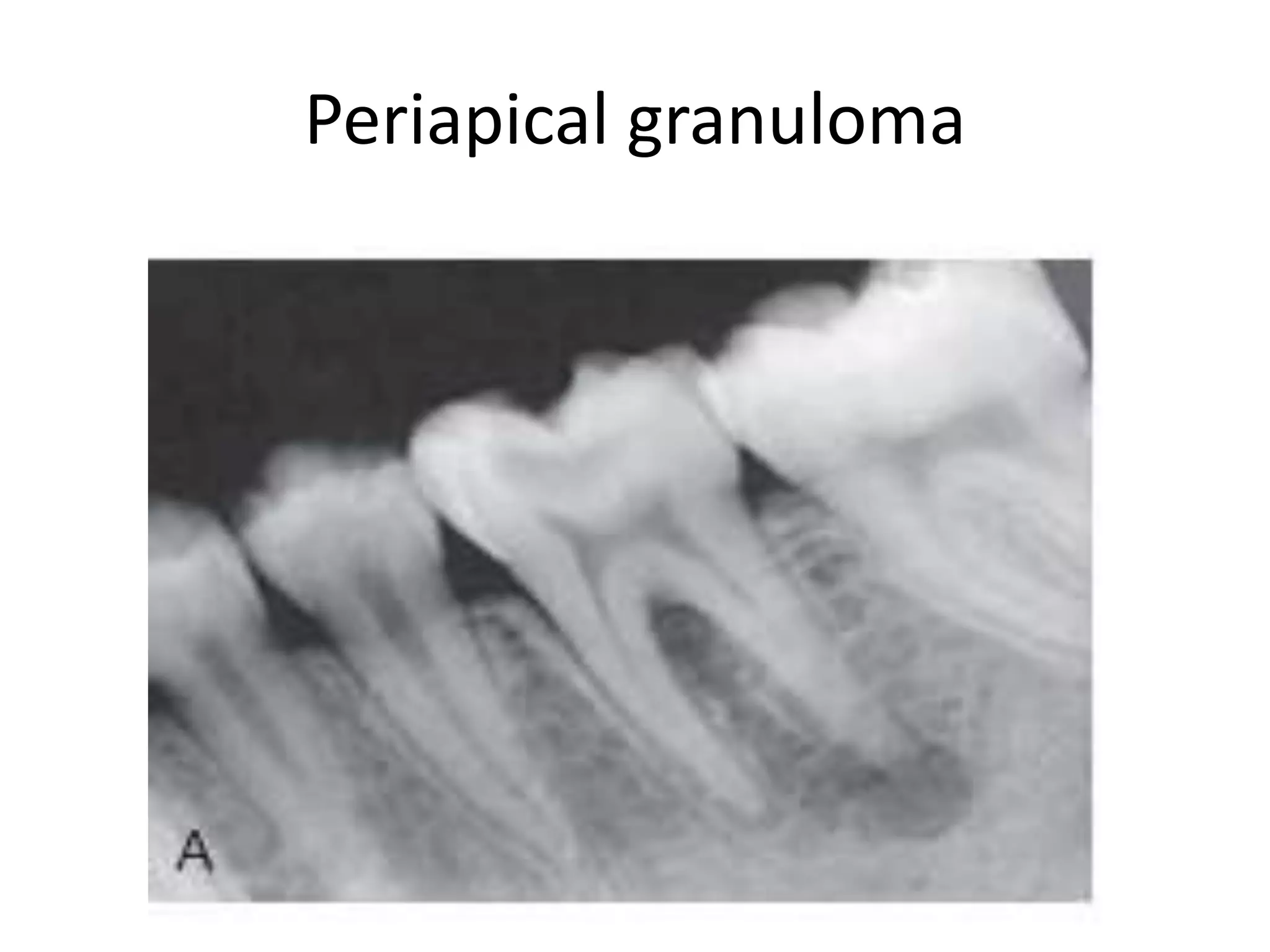
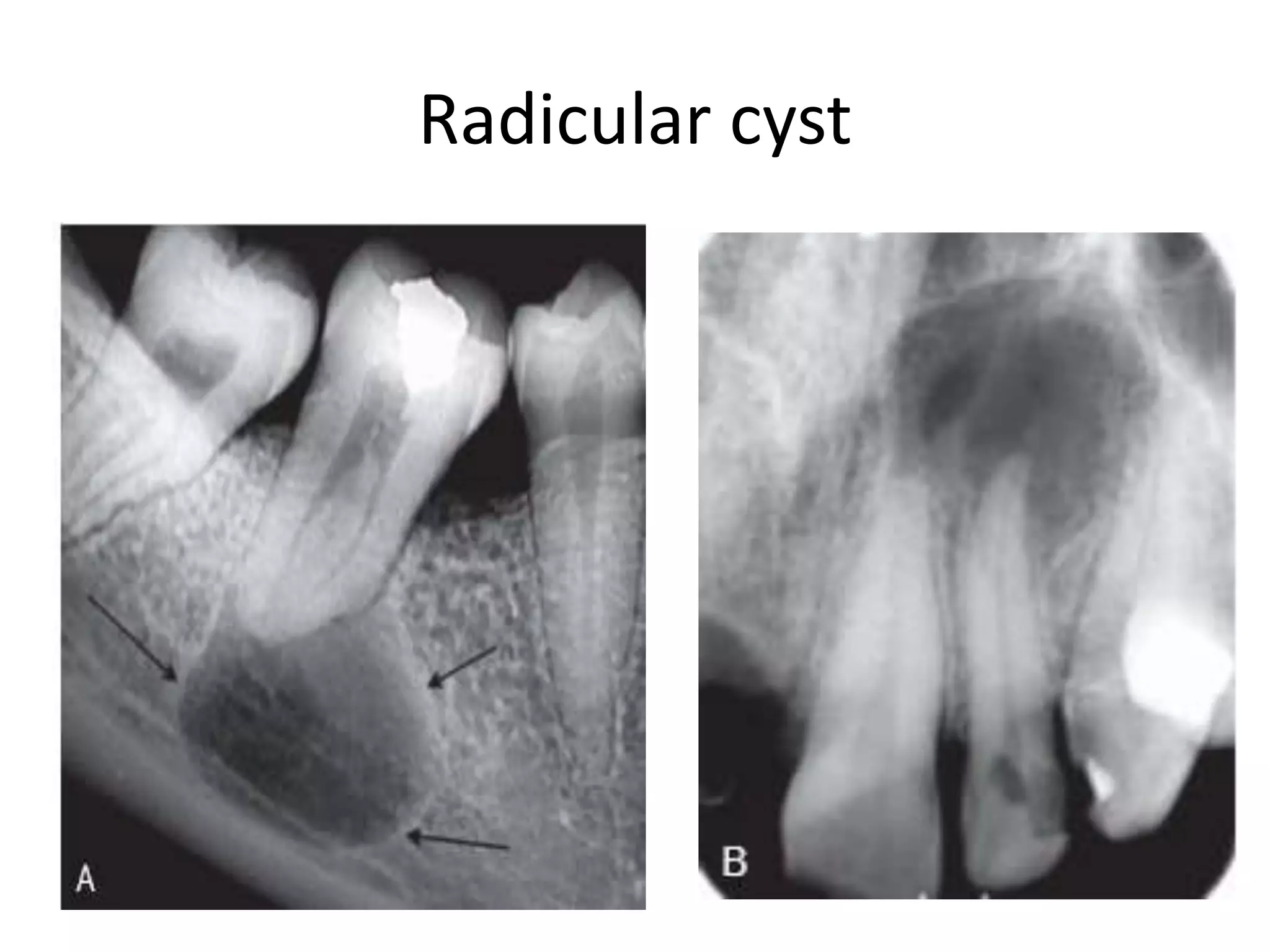
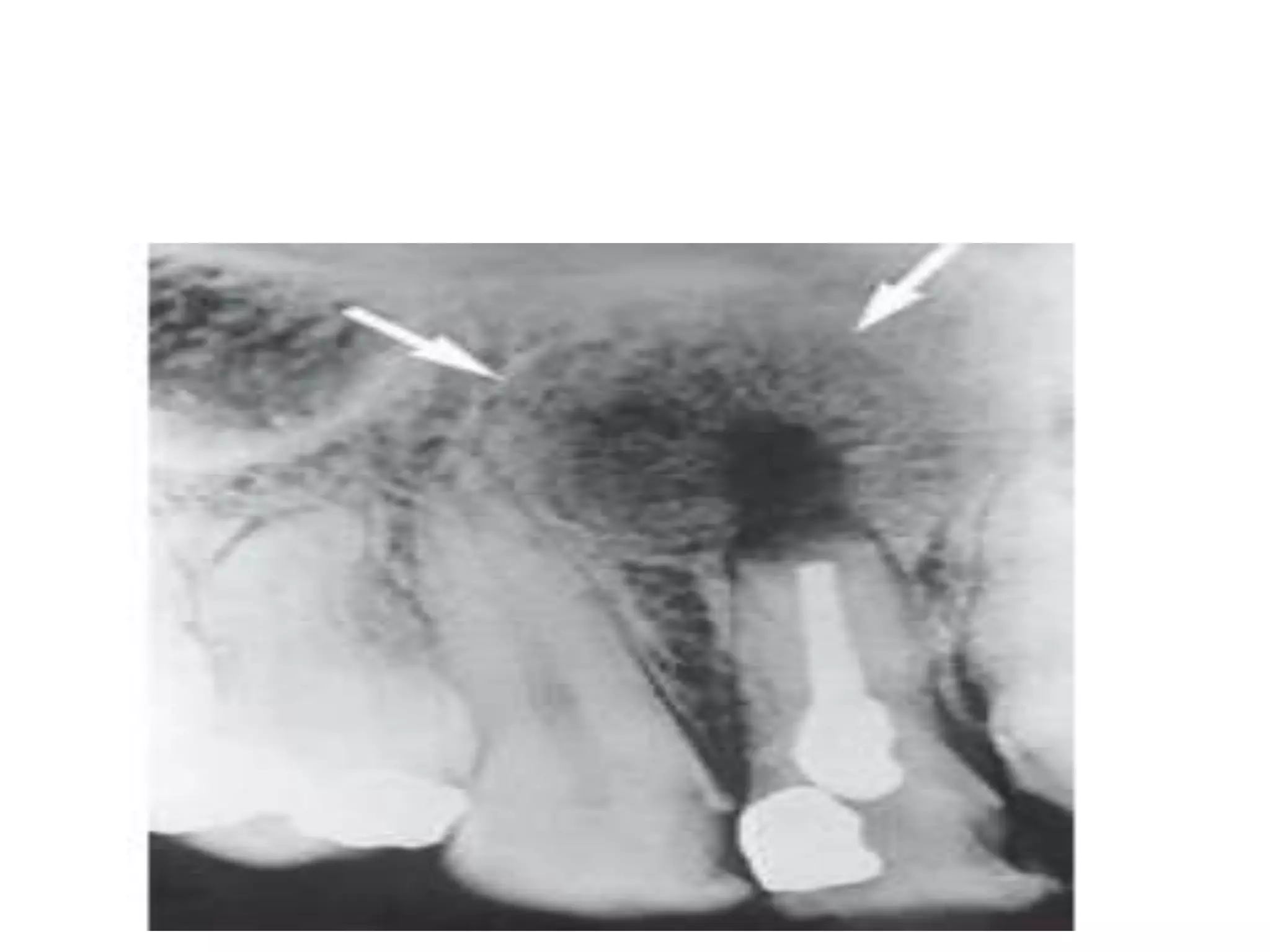
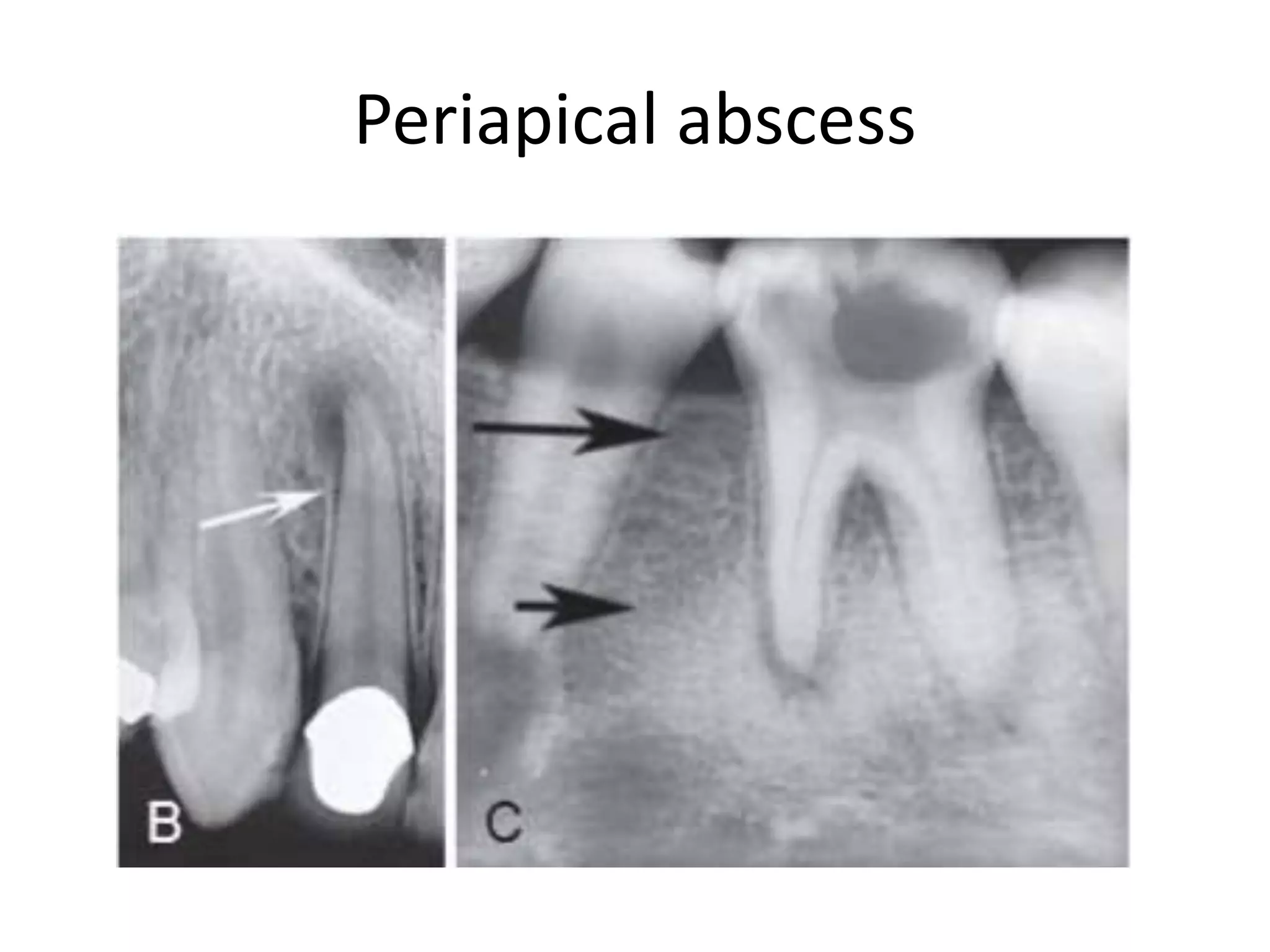
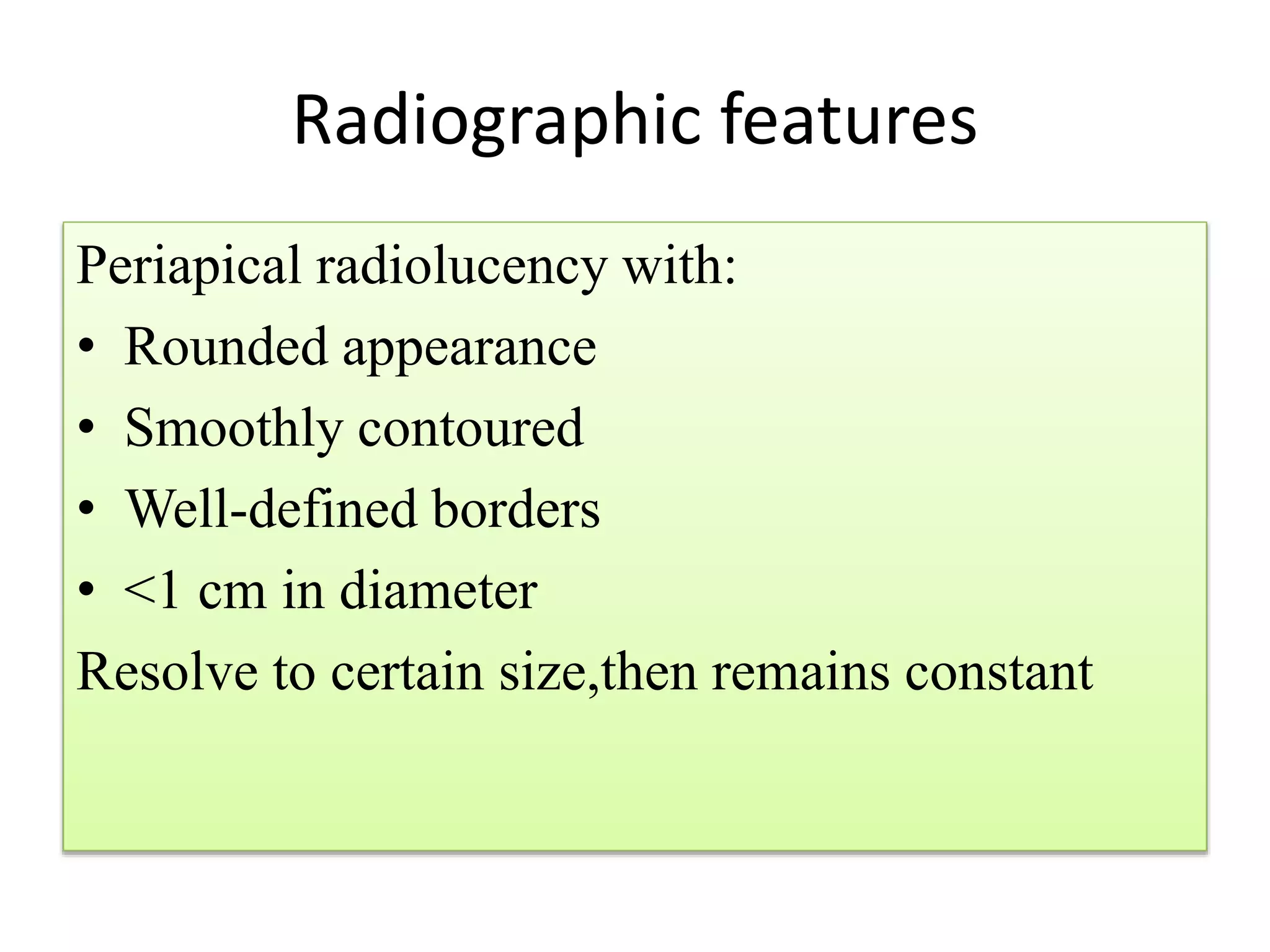
Periapical radiolucencies can have many causes, both benign and malignant. They are often classified as either anatomical pseudoperiapical radiolucencies, which do not contact the tooth apex, or true periapical radiolucent lesions, which do. Common true lesions include periapical granulomas, radicular cysts, and periapical abscesses. Periapical granulomas appear as well-defined radiolucencies, while radicular cysts can cause tooth displacement if left untreated. Management depends on the diagnosis and may involve root canal treatment, extraction, or surgery. Differential diagnosis considers conditions like osteomyelitis, dentigerous cysts,