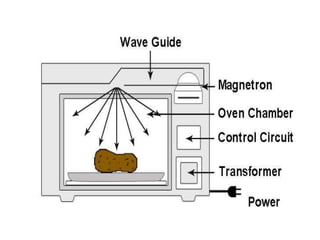
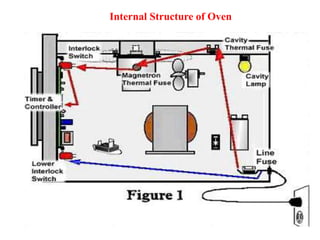
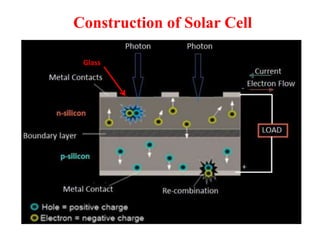
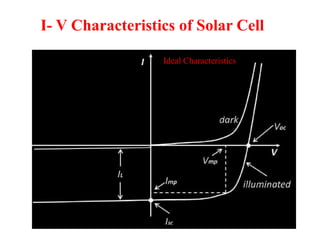
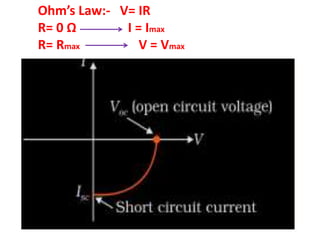
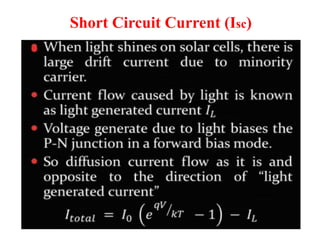
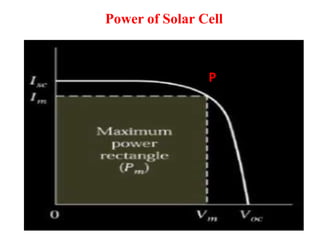
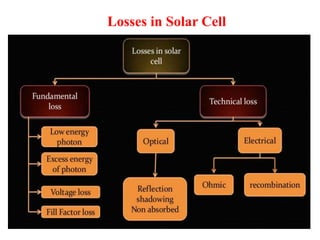
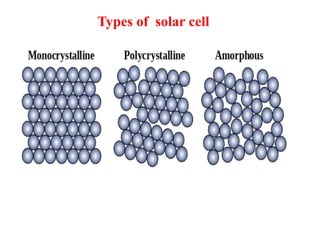
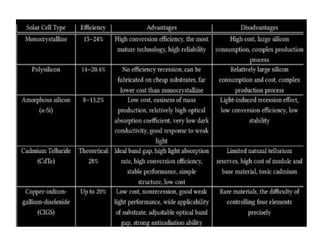
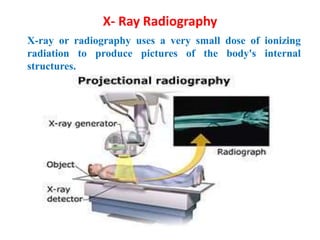
A microwave oven heats and cooks food by exposing it to electromagnetic waves in the microwave frequency range, which induces molecules in the food to rotate and produce thermal energy. It works by passing microwave radiation through food, which is absorbed by water, fat, and other substances, causing the molecules to rotate and collide with other molecules to disperse energy. The microwaves are produced by a magnetron and transferred through a waveguide to the cooking chamber, where a stirrer distributes them and they are absorbed by the food. Microwave cooking may retain more nutrients than conventional cooking.