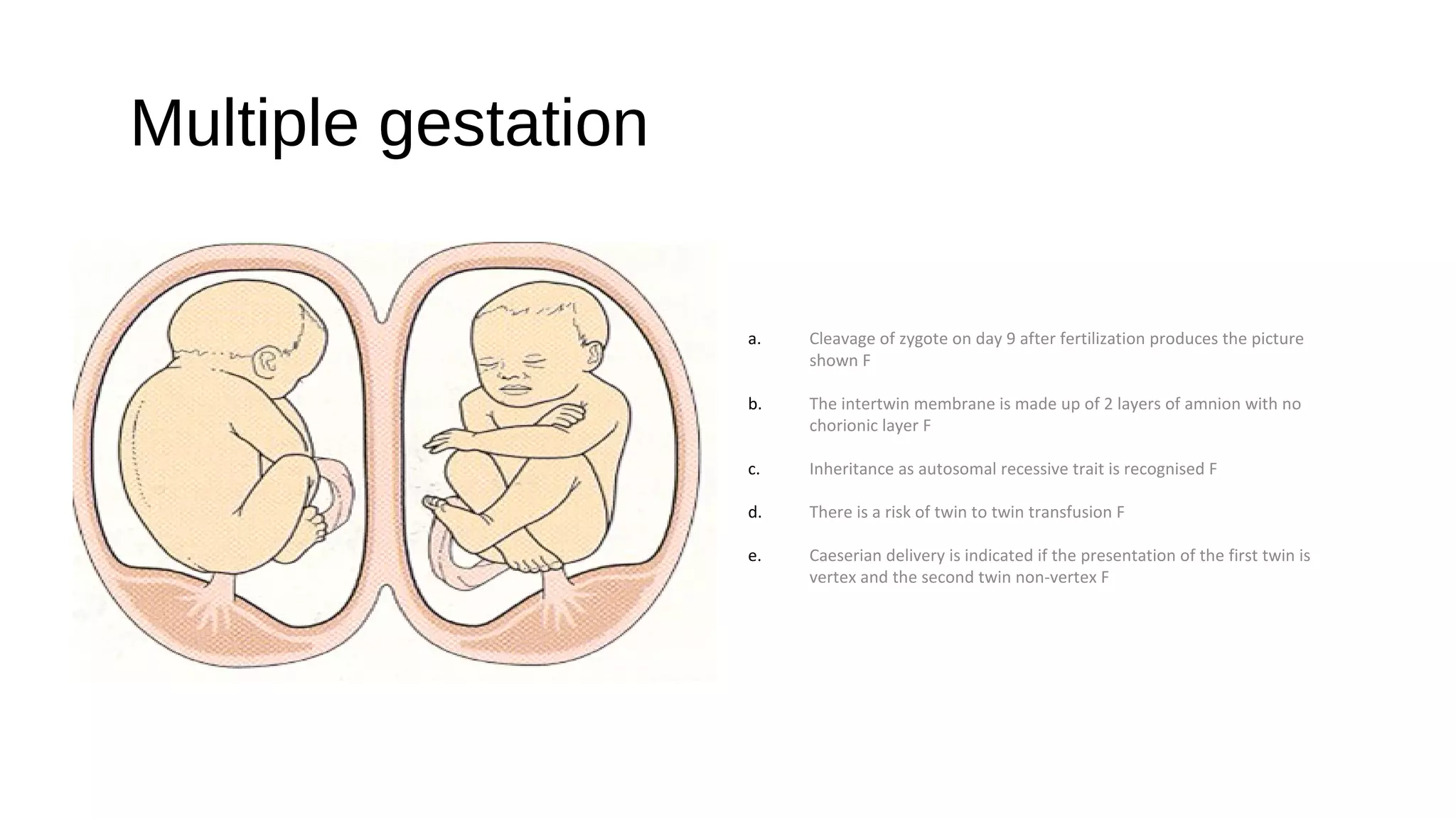
1. This document contains multiple choice questions about obstetrics and gynecology instruments, procedures, and conditions.
2. It addresses topics like risk factors for ureteric injury during surgery, features of delayed ureteric injury post-operatively, and characteristics of different obstetric instruments and their appropriate usage.
3. The questions test knowledge about prevention of complications, identifying high-risk patients, and selecting the best management approach in different clinical scenarios.