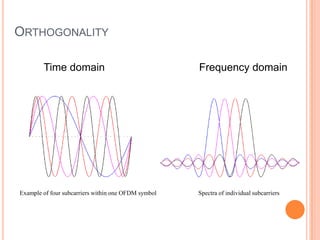
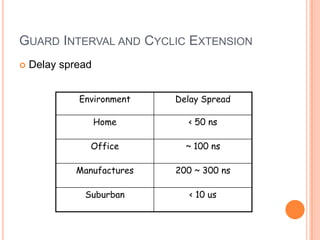
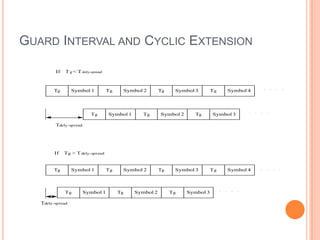
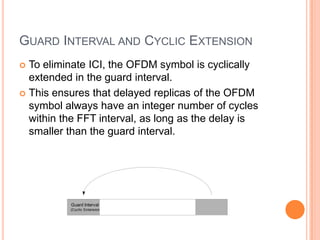
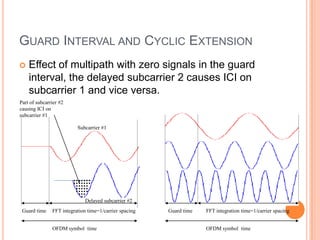
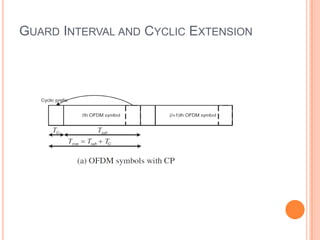
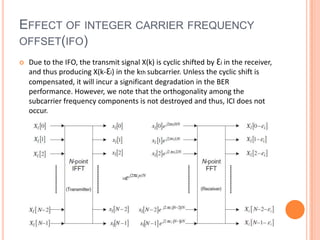
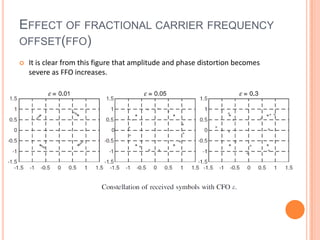
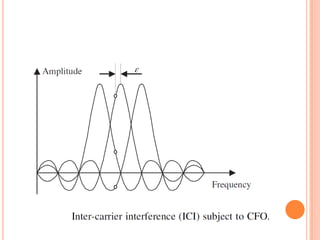
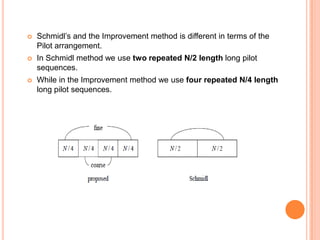
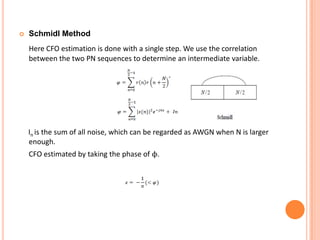
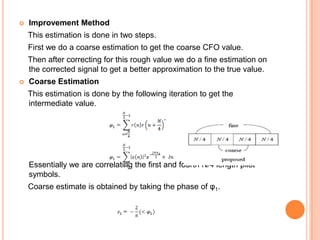
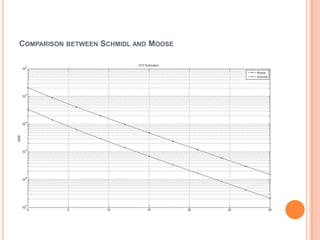
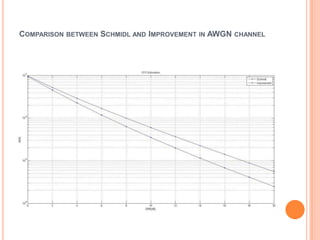
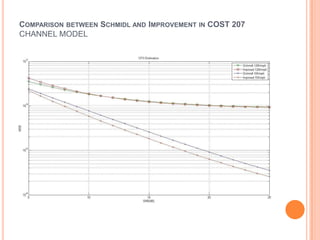
OFDM is a digital multi-carrier modulation technique that divides the available spectrum into several narrowband channels or subcarriers. It allows for high data rates by transmitting multiple digital signals over different subcarriers that are spaced closely together. The data is divided into several parallel data streams or channels, with each subcarrier modulated with a conventional modulation scheme like QAM at a low symbol rate. OFDM has become popular for applications like wireless networking due to its ability to combat multipath fading and its high spectral efficiency. It implements the orthogonal subcarriers using the inverse fast Fourier transform (IFFT) and fast Fourier transform (FFT) to generate the signal and decode it.

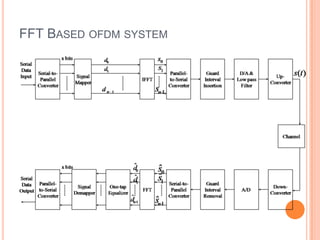
![OFDM IMPLEMENTATION
x bits
x1 d1 s1
Serial
D/A
Data Serial-to- x2 Signal d2 s2 Parallel- Guard
&
Input Parallel Mapper IFFT to-Serial Interval
Lowpass
Converter x n 1
(QPSK)
dn 1 sn 1
Converter Insertion
Filter
x= [1,0,1,1,0,0…] x1=[1,0] d1=[-1]
x2=[1,1] d2=[-i]
x3=[0,0] d3=[1]
…….. ……..](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ofdmfinal-111125032200-phpapp01/85/Ofdm-final-5-320.jpg)
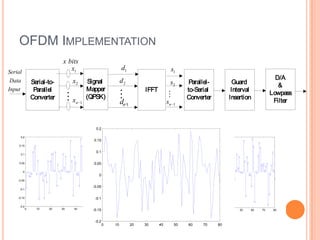
![HOW?
Discrete Fourier transform (DFT) and inverse DFT (IDFT) processes are
useful for implementing these orthogonal signals.
Note that DFT and IDFT can be implemented efficiently by using fast
Fourier transform (FFT) and inverse fast Fourier transform (IFFT),
respectively.
In the OFDM transmission system, N-point IFFT is taken for the transmitted
symbols , so as to generate , the samples for the sum
of N orthogonal subcarrier signals.
Let y[n] denote the received sample that corresponds to x[n] with the
additive noise w[n] (i.e., y[n] =x[n]+w[n]).
Taking the N-point FFT of the received samples, , the noisy
version of transmitted symbols can be obtained in the receiver.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ofdmfinal-111125032200-phpapp01/85/Ofdm-final-7-320.jpg)