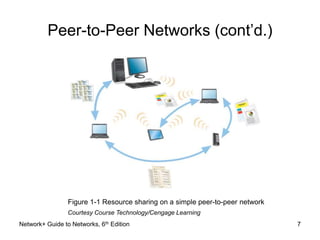
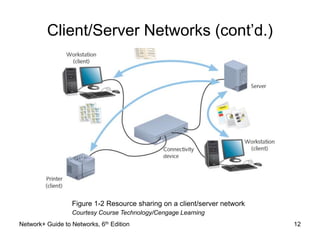
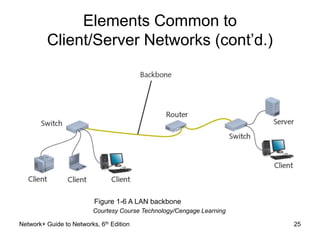
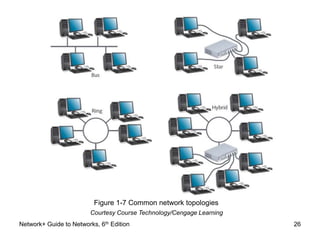
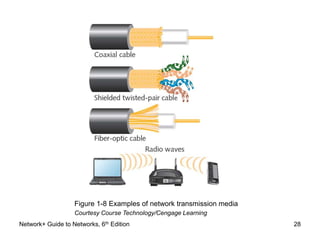
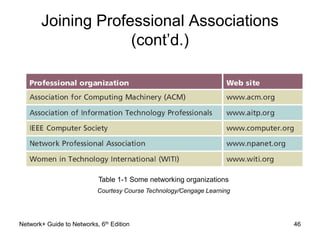
This document provides an overview of chapter 1 from the Network+ Guide to Networks, 6th Edition. It introduces networking concepts such as peer-to-peer and client/server networks. Peer-to-peer networks allow direct communication between equal nodes, while client/server networks use a centralized server to manage shared resources. The document also discusses common network types like LANs, MANs, and WANs and elements of client/server networks including clients, servers, network cards, and protocols. Finally, it outlines several common uses for networks such as file and print sharing, remote access services, and email communication.