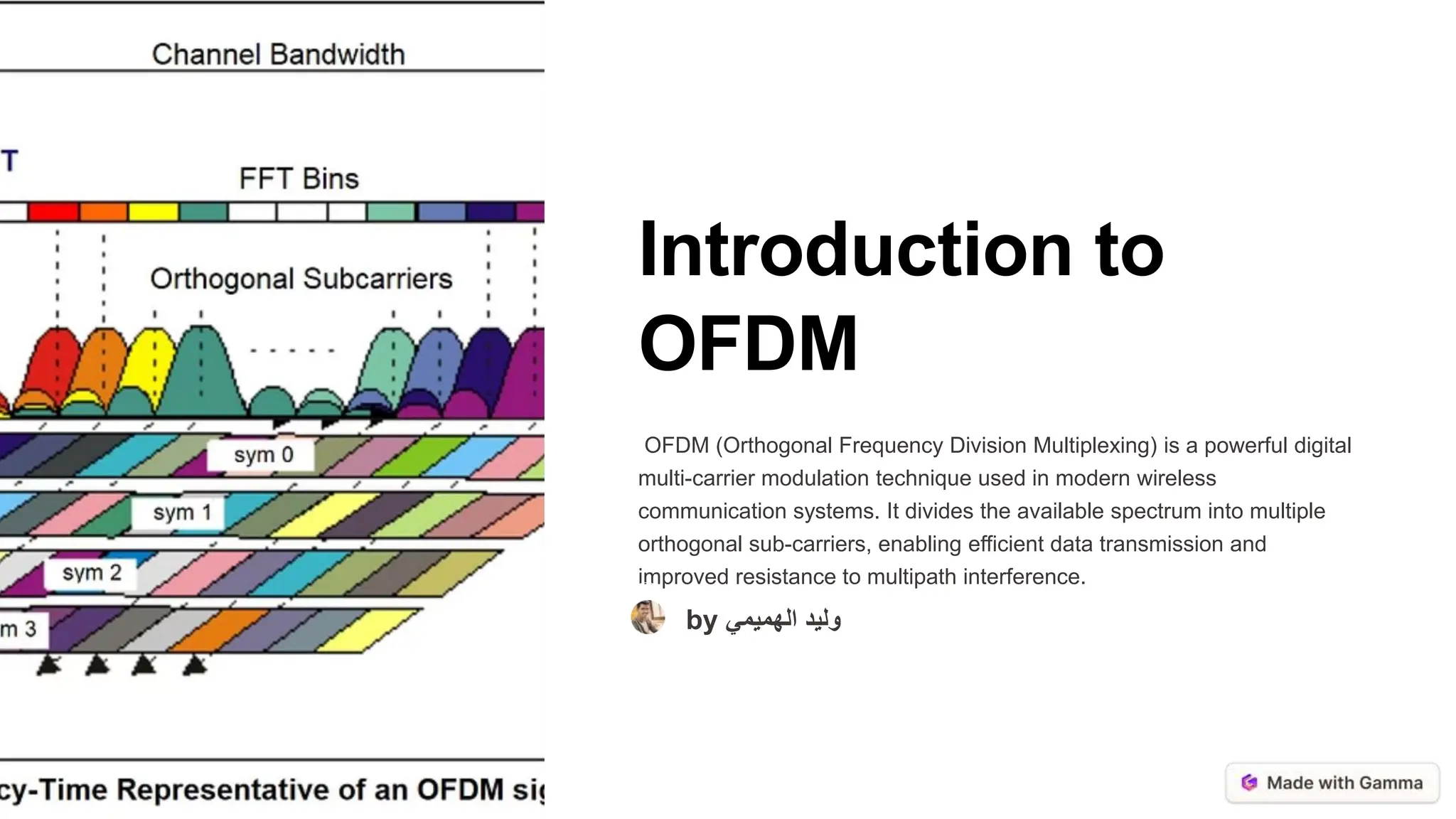
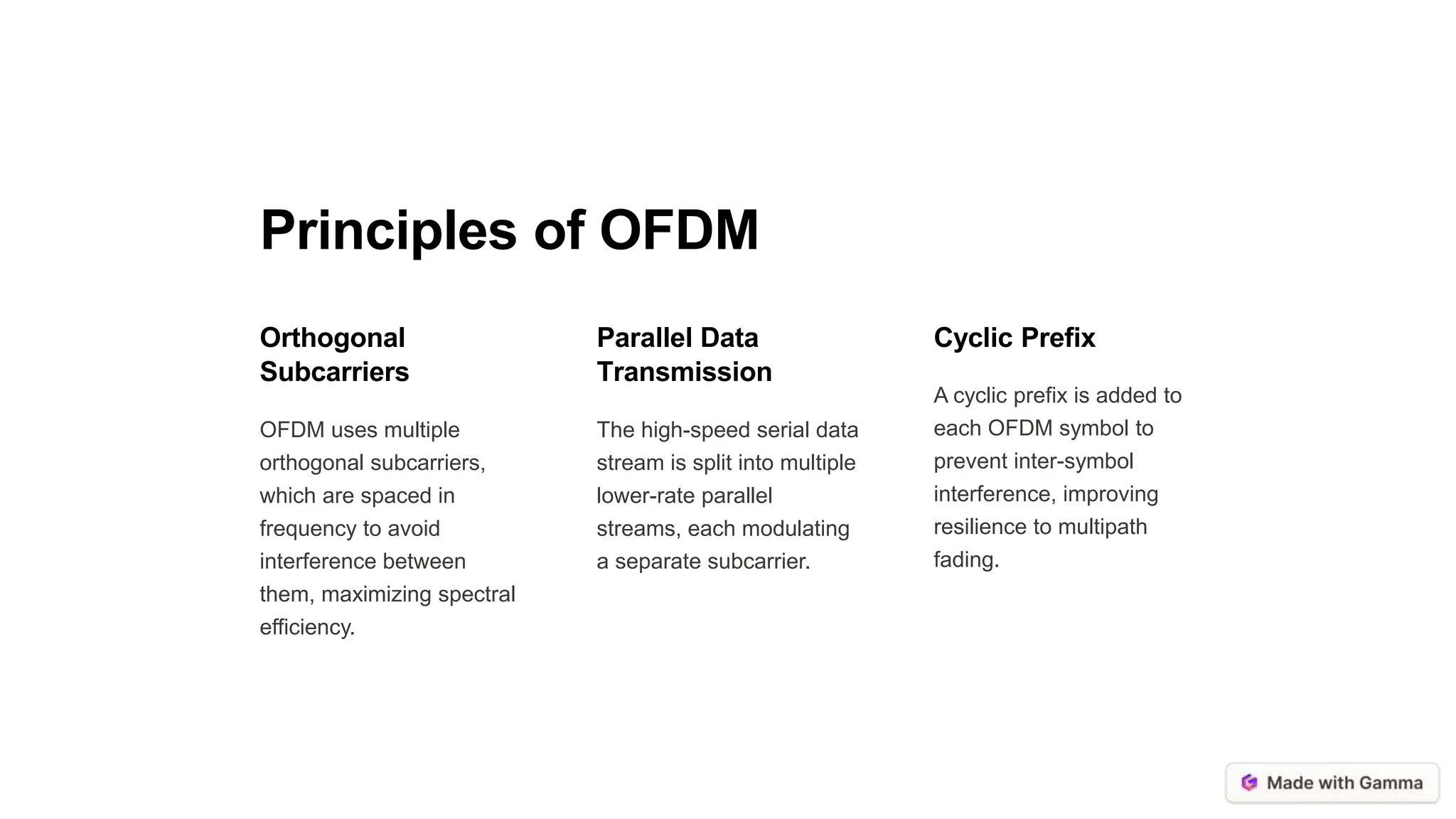
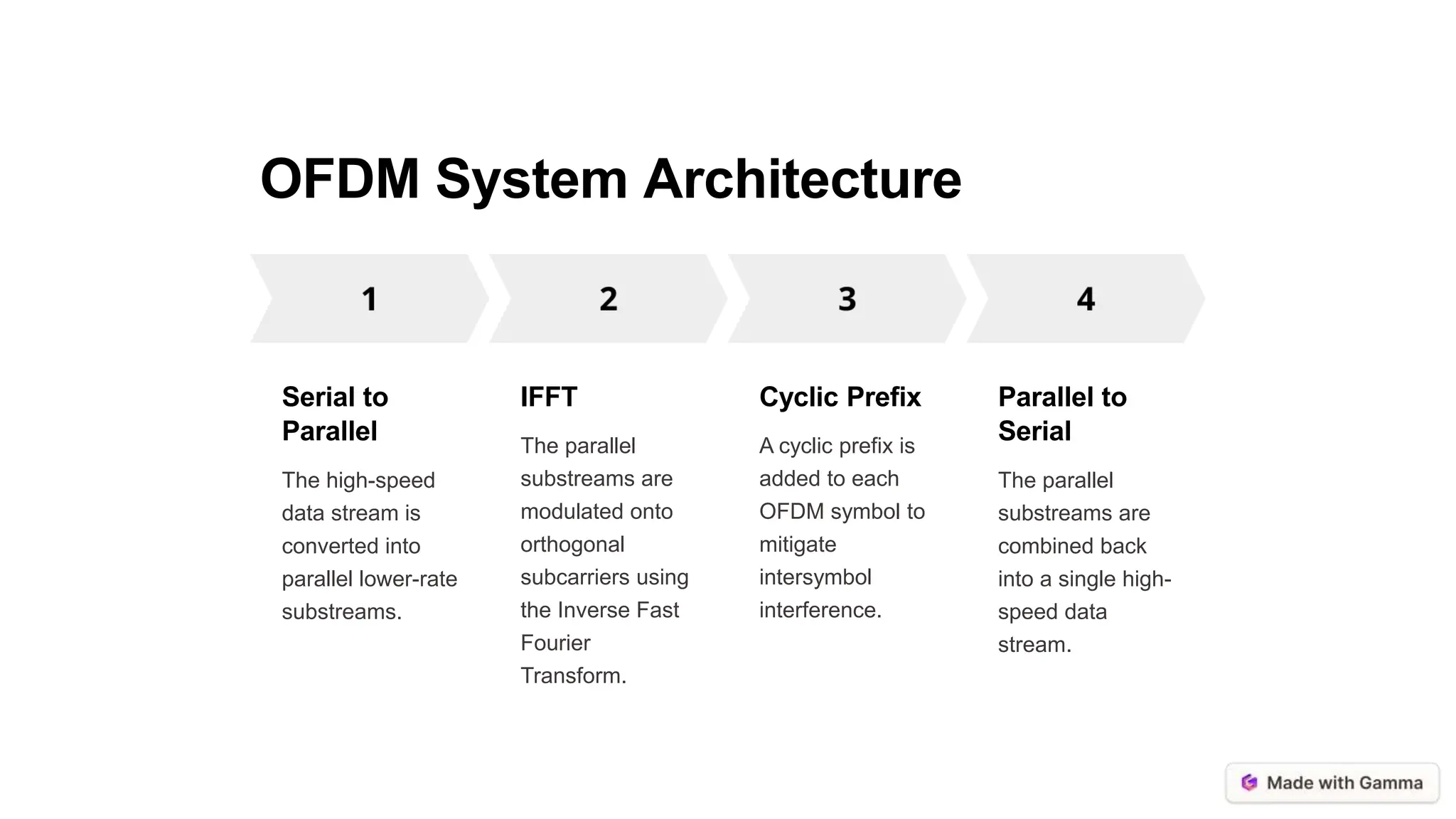
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) is a digital multi-carrier modulation technique that enhances data transmission in wireless communication by dividing the spectrum into orthogonal sub-carriers. It offers advantages such as high spectral efficiency, resilience to multipath interference, and flexibility in resource allocation, making it suitable for various applications including Wi-Fi and cellular networks. However, OFDM faces challenges like high peak-to-average power ratio and synchronization sensitivity, which need to be addressed for future advancements.