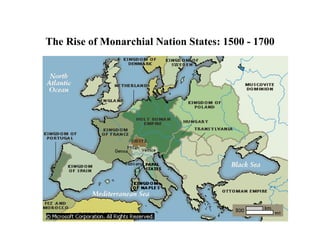
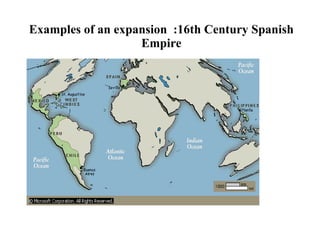
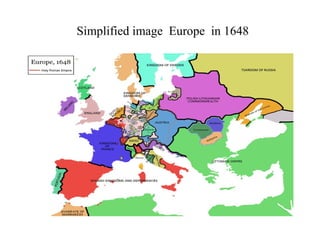
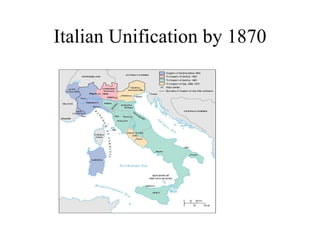
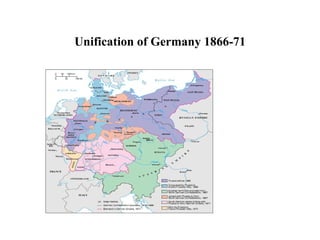
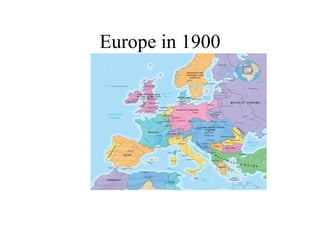
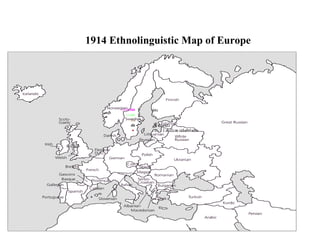
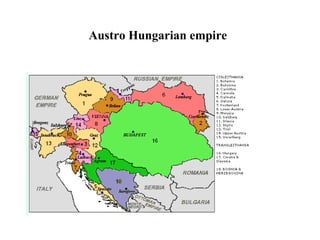
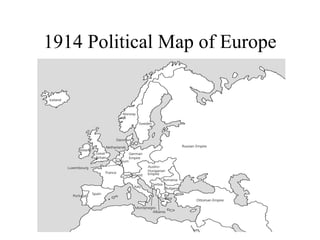
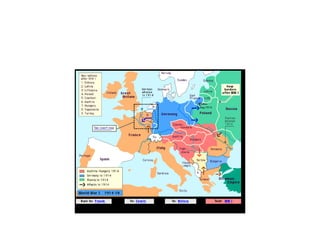
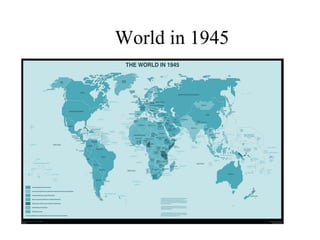
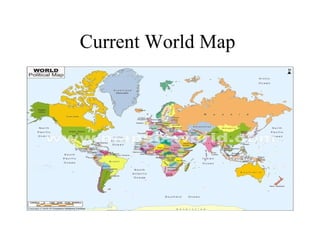
The document traces the origin and development of the nation state system from the 16th century to present day. It discusses the rise of early nation states in Europe like Portugal, Spain, Britain and France. Key events and agreements that shaped the nation state system include the Treaty of Westphalia (1648), Utrecht Treaty (1713), Congress of Vienna (1815), and the two World Wars (1914-1918 and 1939-1945) which led to the dissolution of old empires and emergence of new nation states. The modern nation state is characterized by territoriality, a sense of nationality, sovereignty, and equal recognition under international law.