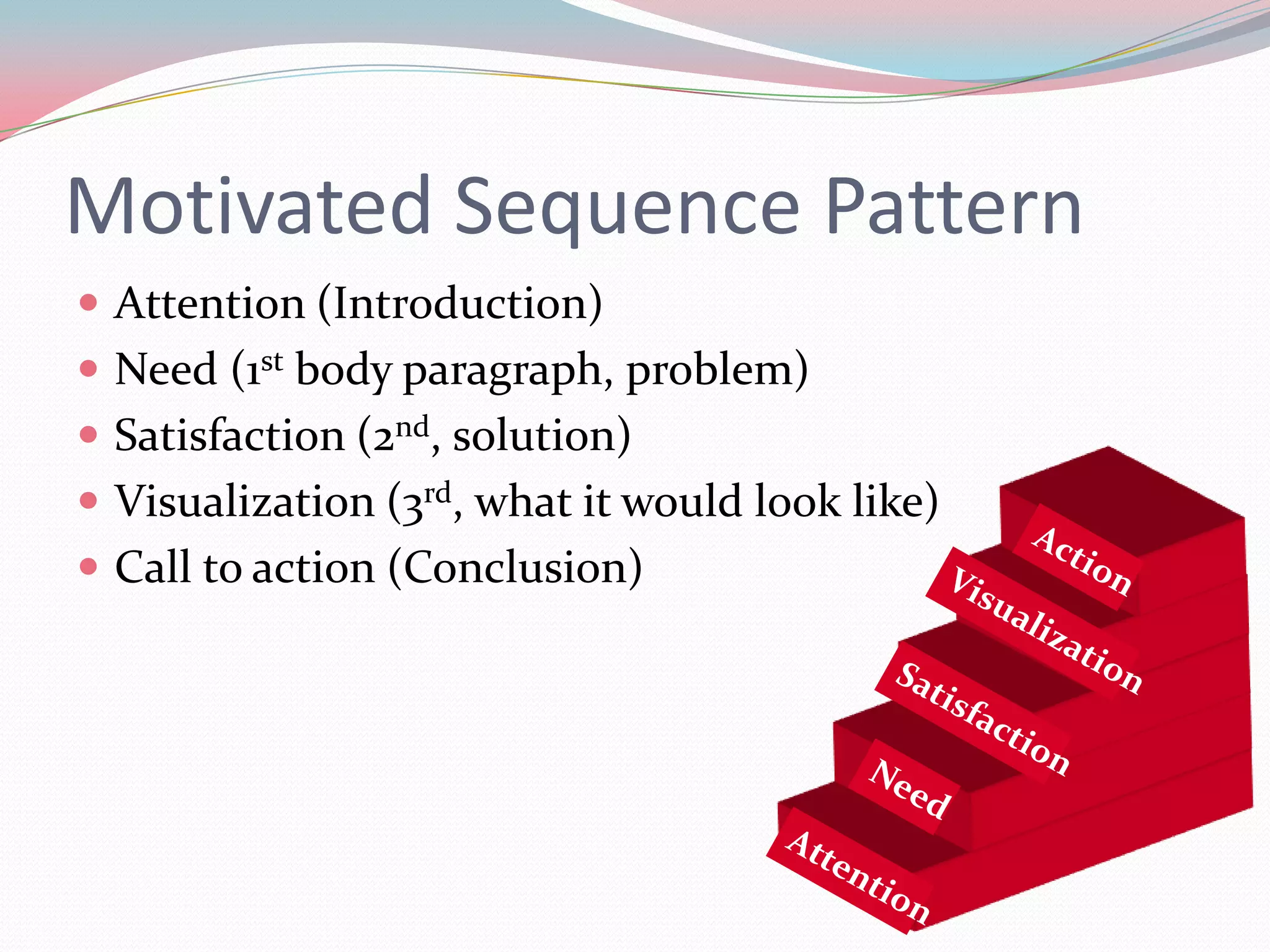
This document discusses strategies for organizing the main points of informative and persuasive speeches. It describes common patterns such as chronological order, categories/topics, geographical order, cause and effect, problem and solution, claims, refutation, and the motivated sequence. The key difference between informative and persuasive speeches is that persuasive speeches call the audience to take some kind of action.