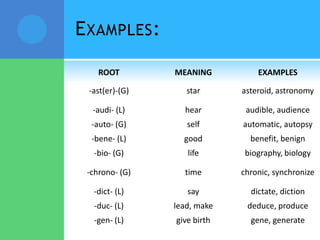
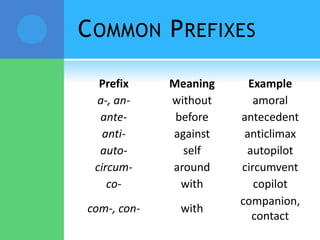
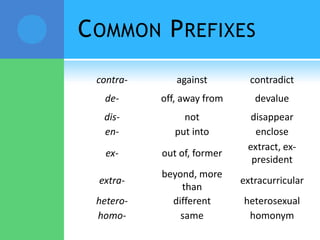
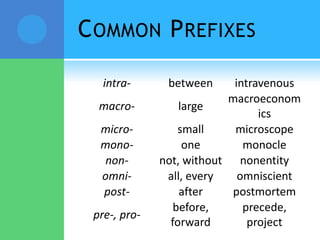
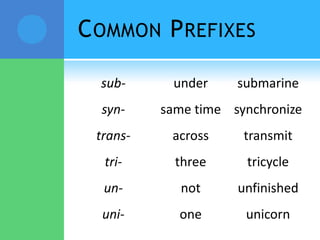
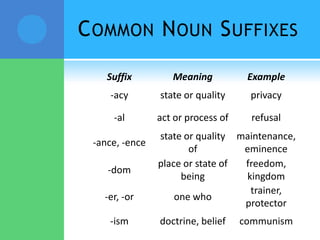
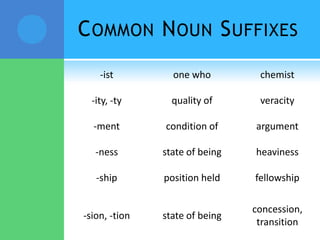
A root is a word element that forms the base of a word and can have prefixes or suffixes added to derive new words. Roots often come from Latin or Greek and carry a specific meaning. Examples provided describe common roots such as "voc" meaning word/name and "audi" meaning hear. Common prefixes and suffixes are also described, including how they can change a word's meaning or class. Prefixes are added to the beginning of a word while suffixes are added to the end.