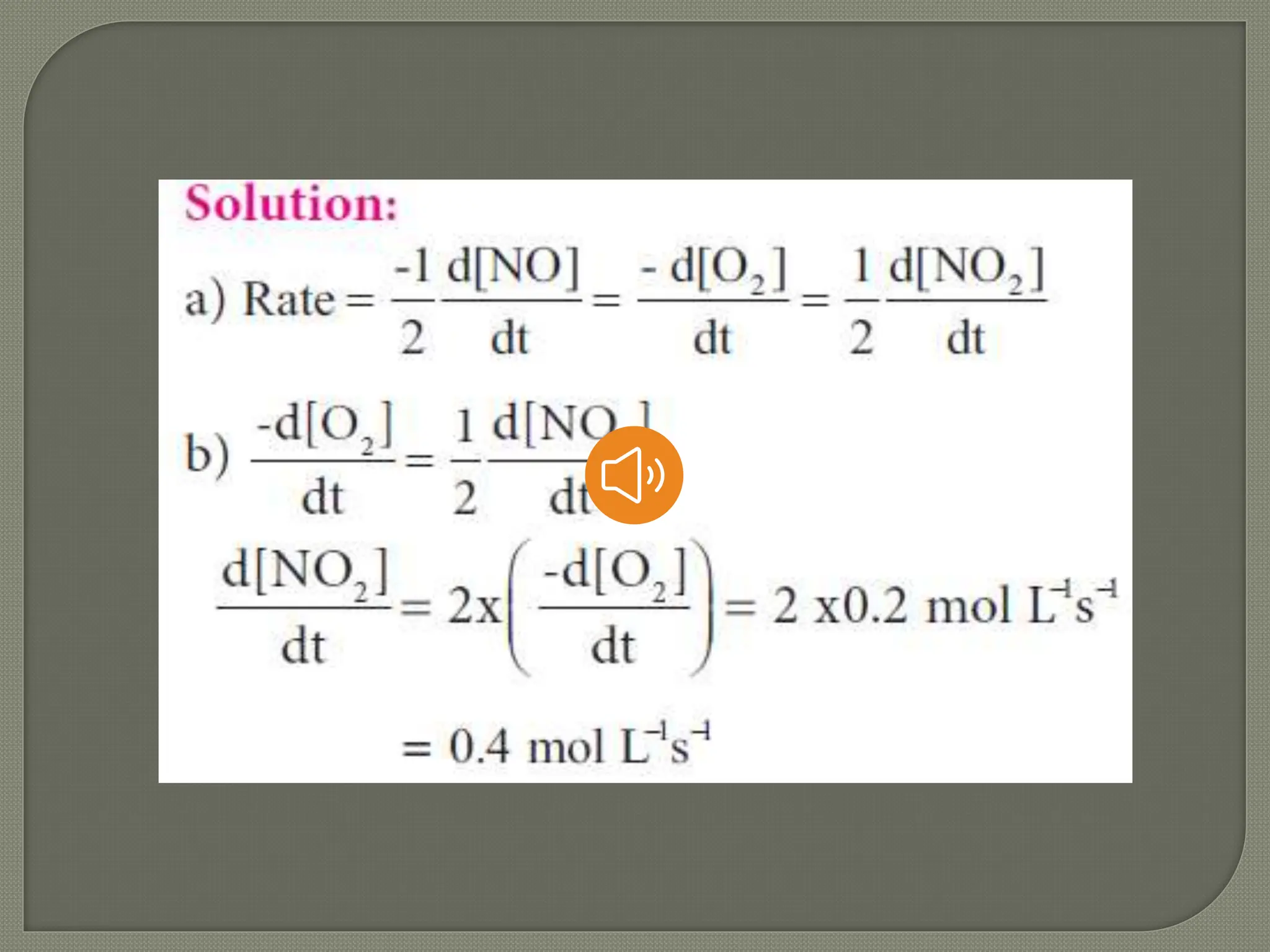
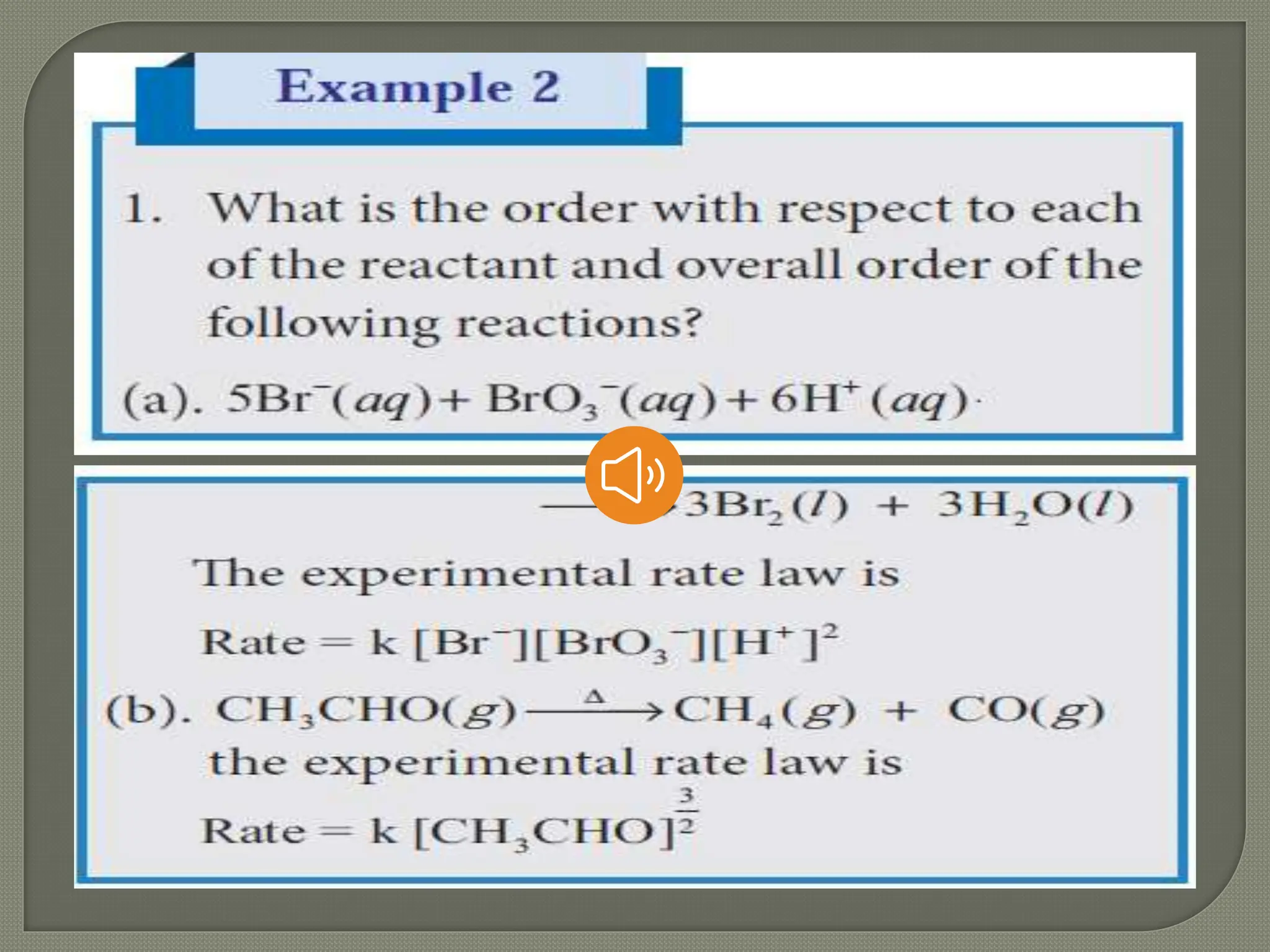
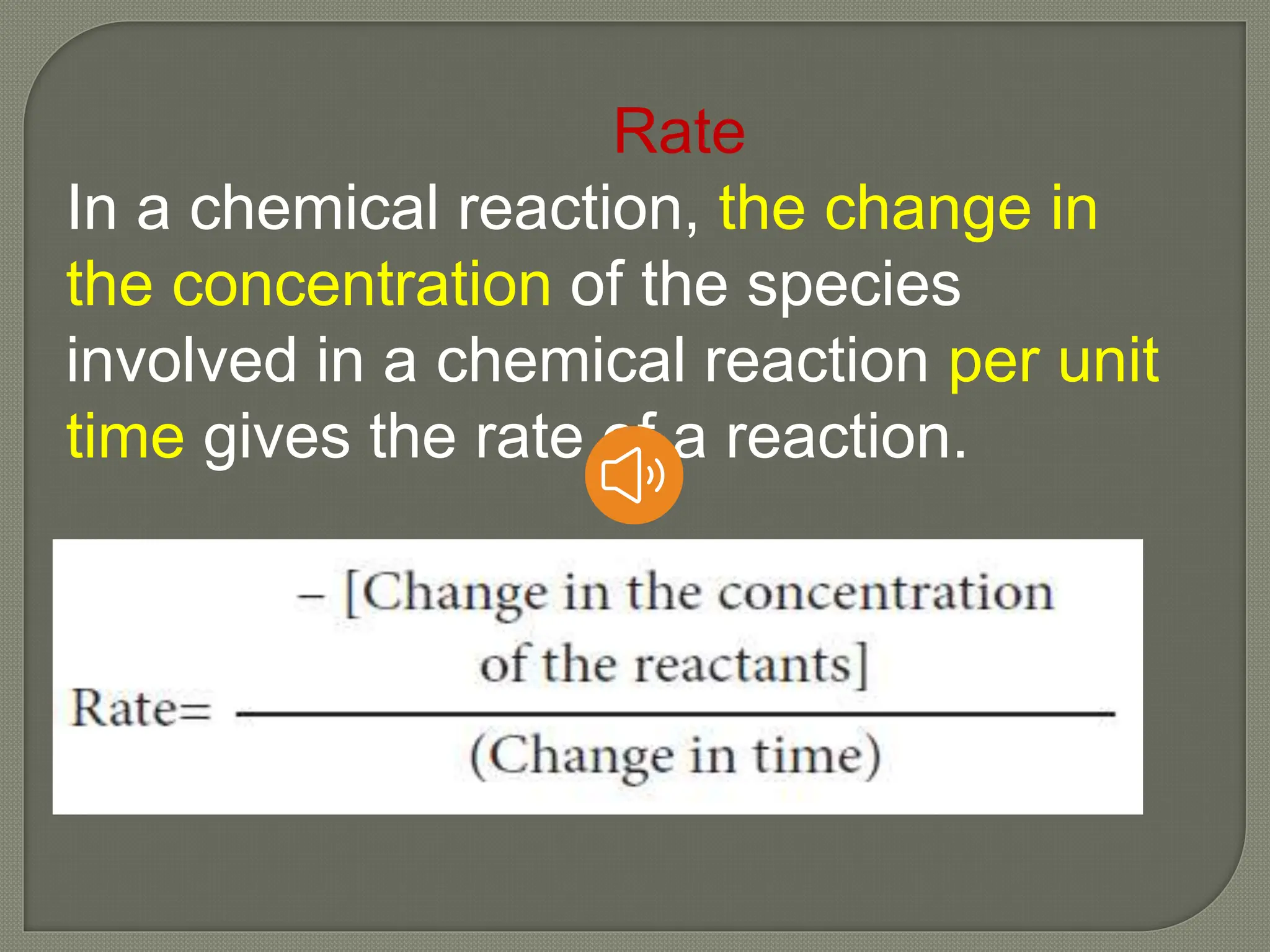
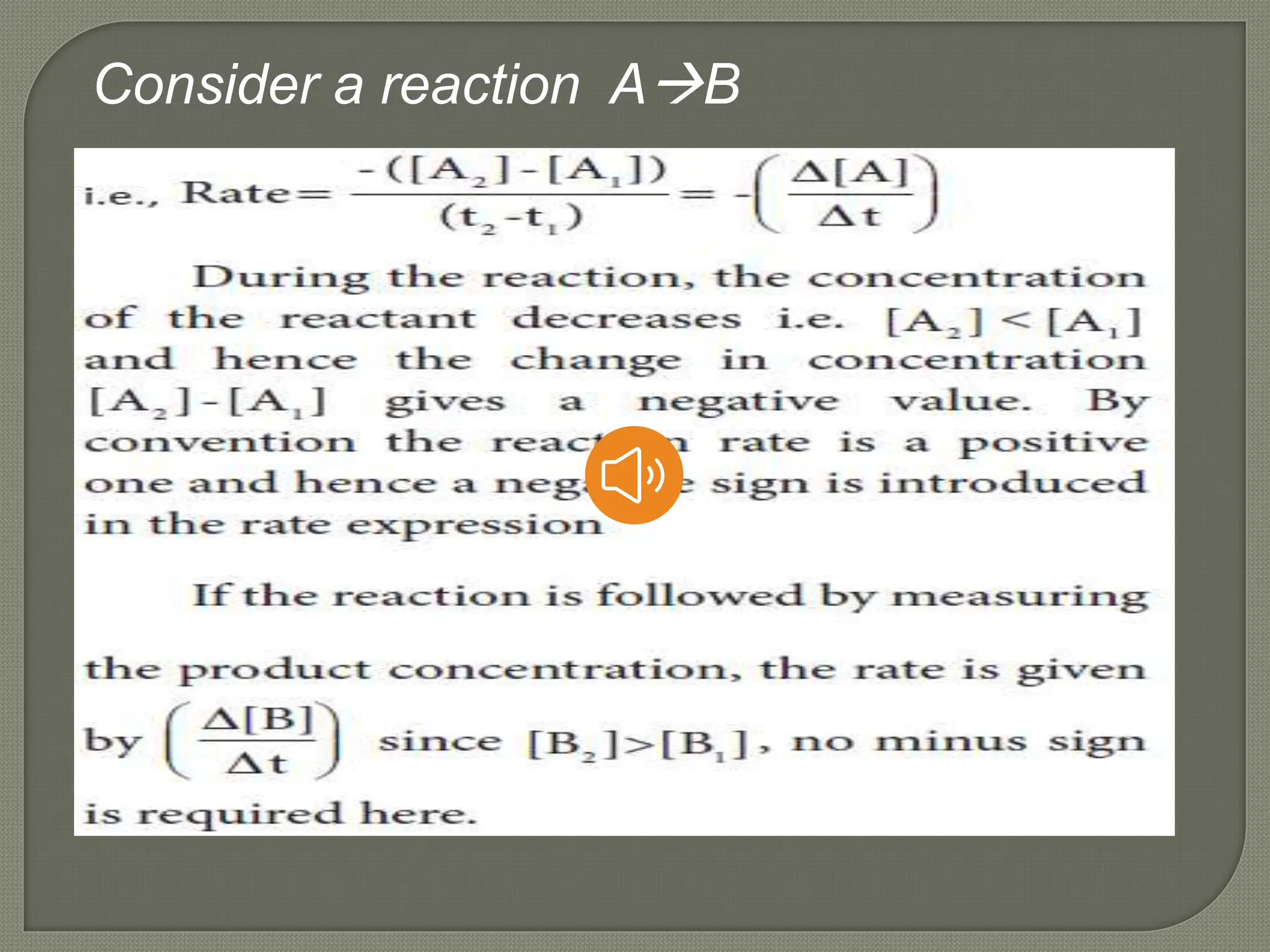
Chemical kinetics is the study of the rate and mechanism of chemical reactions under specific conditions such as temperature and pressure. It helps in determining reaction rates and optimizing industrial processes. Key concepts include average and instantaneous rates, rate laws, order of reaction, molecularity, and the rate-determining step.


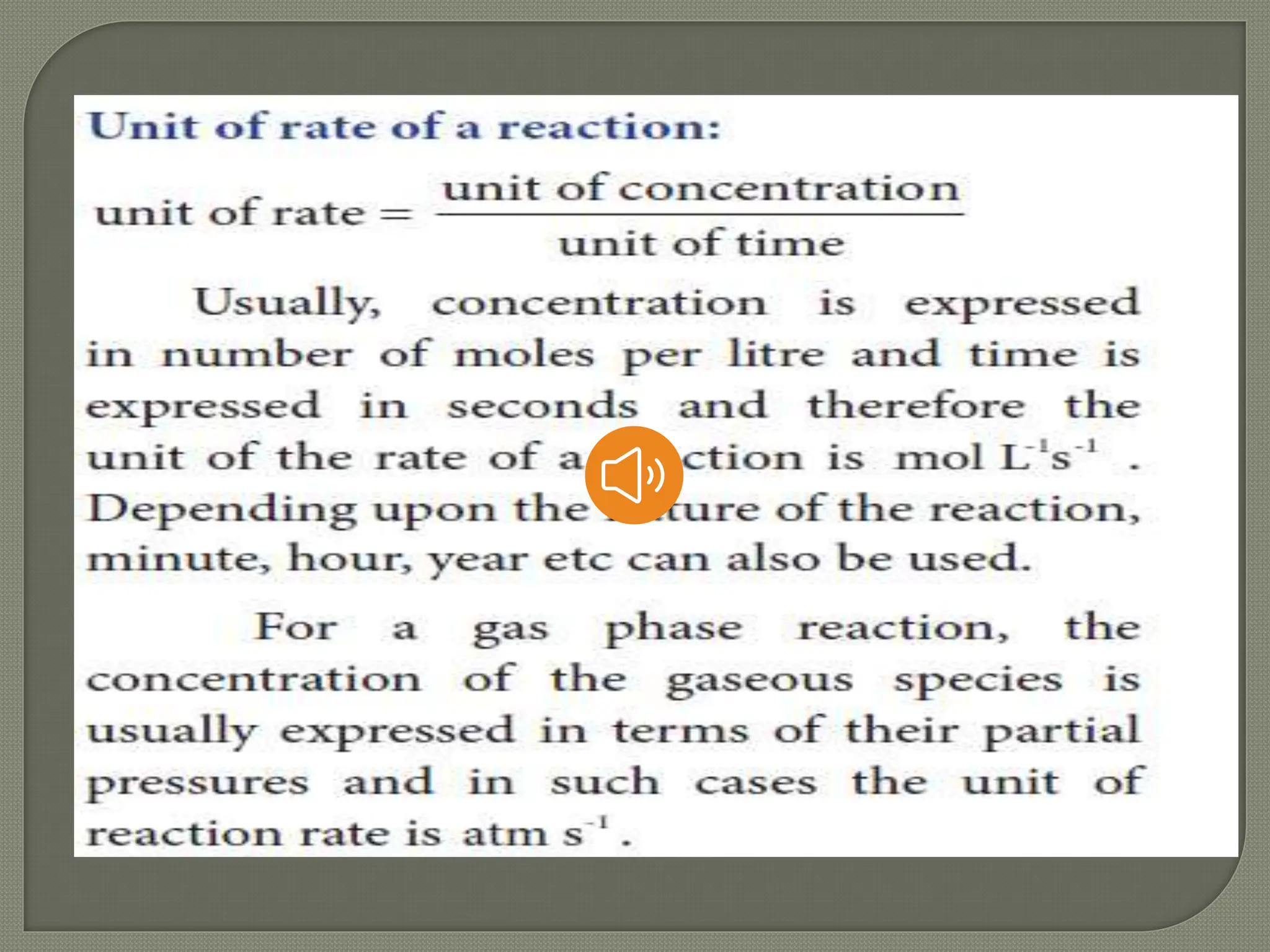


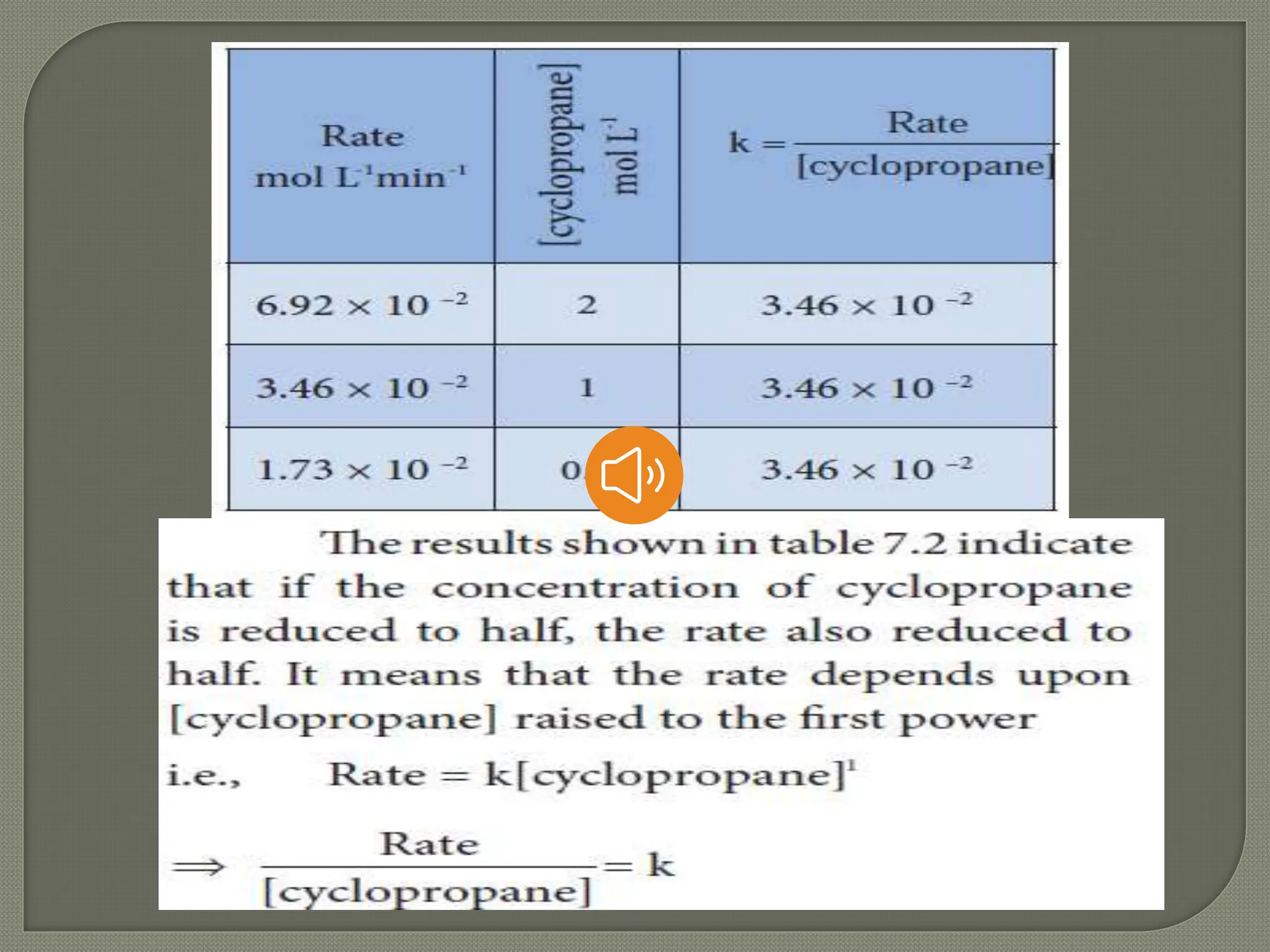
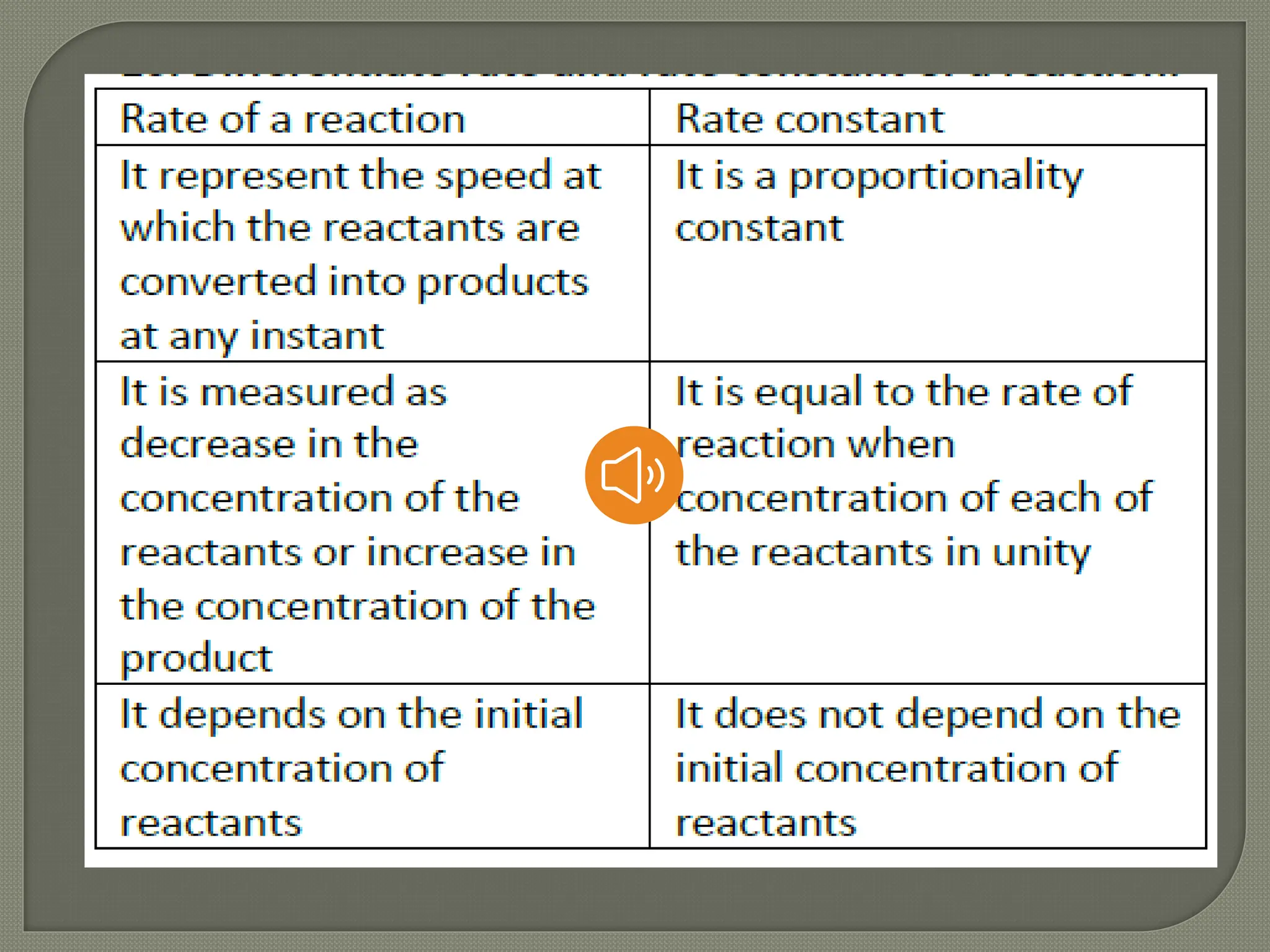
![Rate law and Rate constant.
Rate law which relate rate of a reaction
with rate constant and concentration of
reactant.
Ex. A+B --> c ; For this reaction rate law is
written as r = k [A] [B]
Rate constant is equal to rate of the
reaction when concentration of all the
reactants kept unity.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chemicalkinetics1-240513004634-eb4fae98/75/CHEMICAL-KINETICS-Part-1-Slide-show-Presentation-8-2048.jpg)
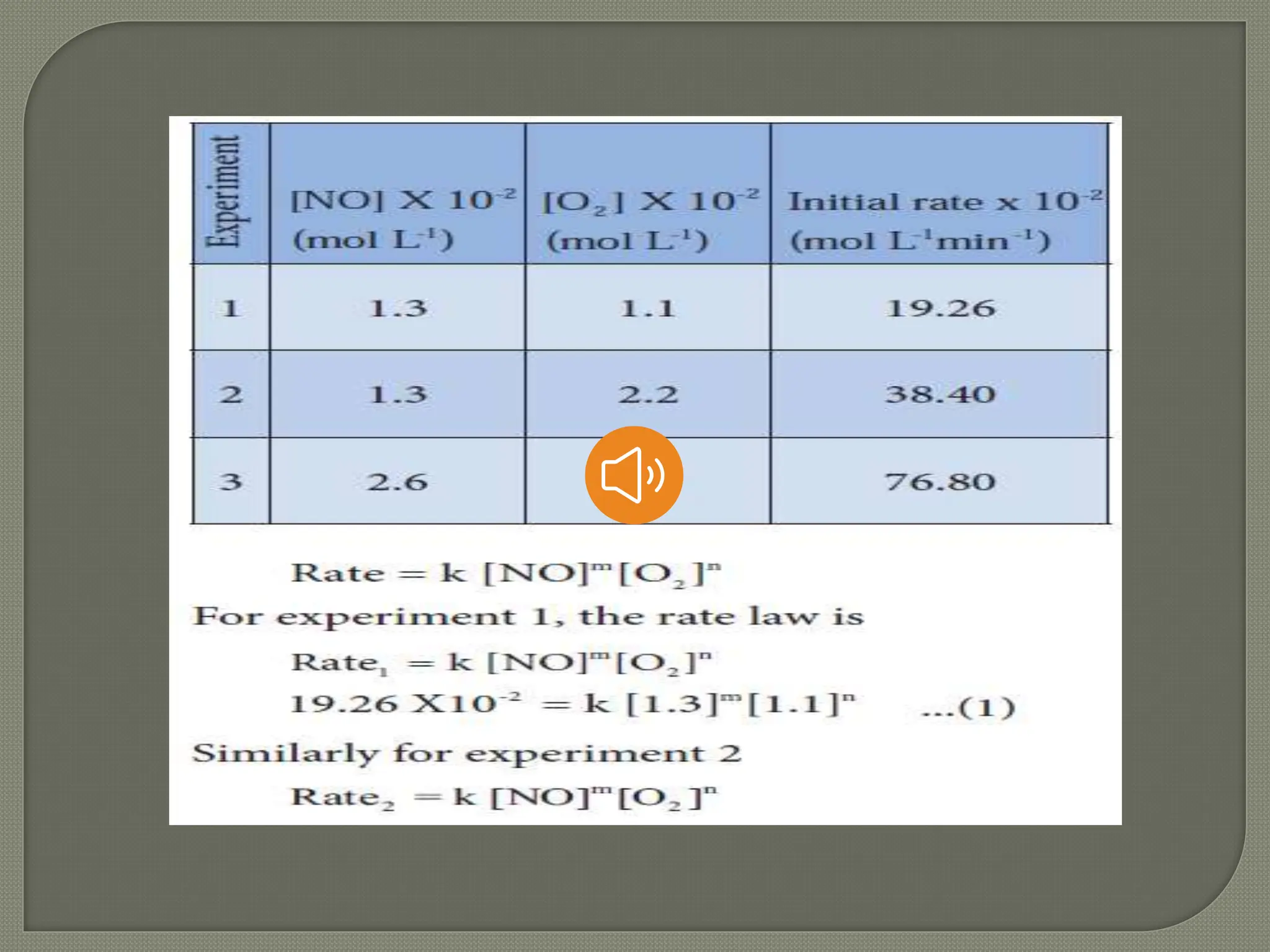
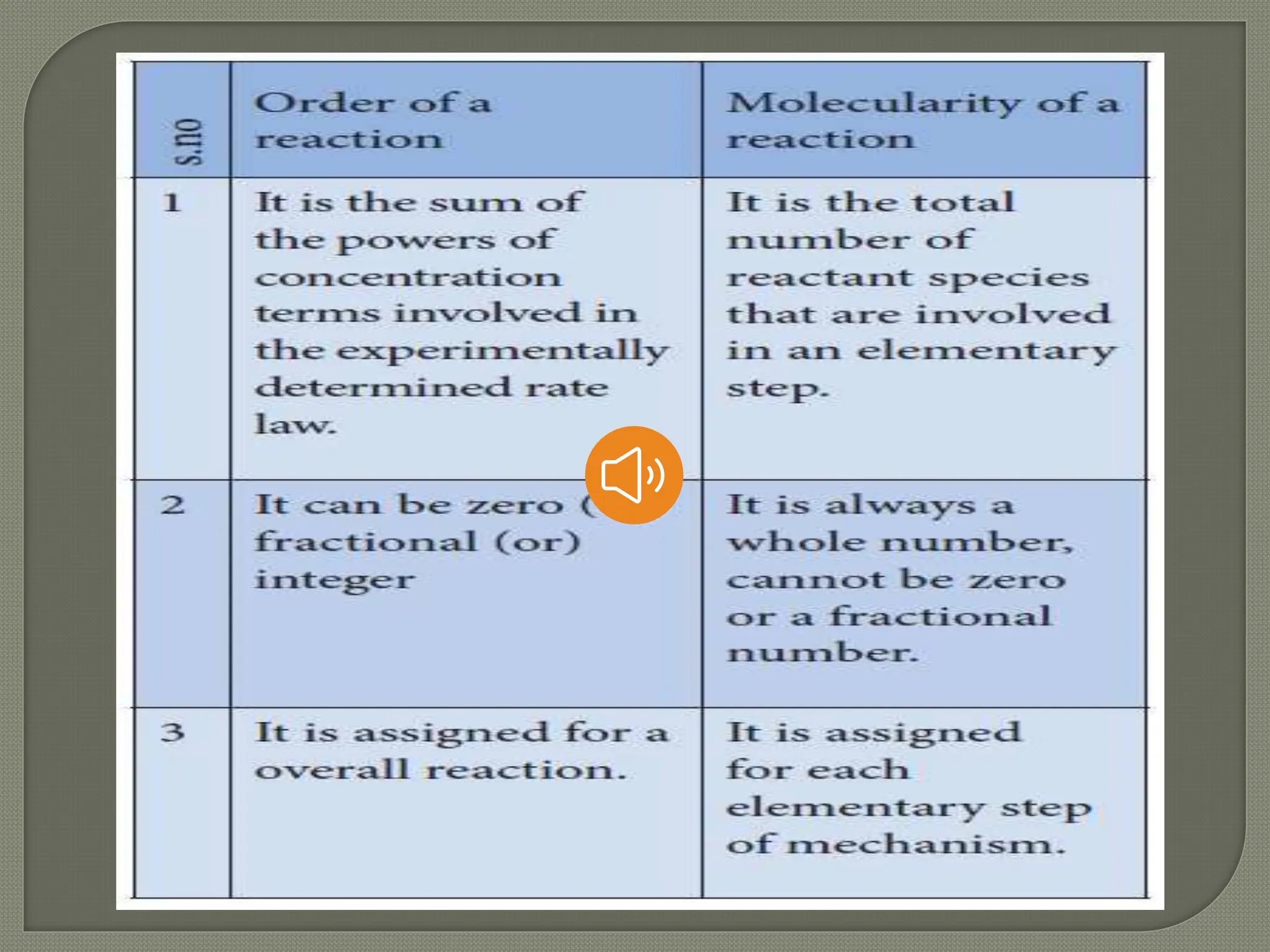
![order
It is defined as sum of the power of
concentration term that involved in rate
equation.
The rate law for the reaction
aA + bB----> Product
Rate = K [ A ]a [ B ]b
Order = a + b](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chemicalkinetics1-240513004634-eb4fae98/75/CHEMICAL-KINETICS-Part-1-Slide-show-Presentation-9-2048.jpg)