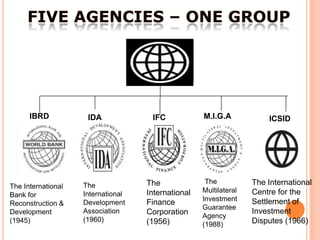
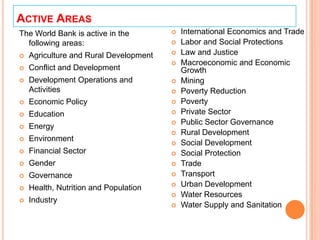
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and technical assistance to developing countries. It was established in 1944 and is headquartered in Washington D.C. with over 7,000 employees worldwide. The World Bank aims to reduce poverty and promote sustainable development through loans, guarantees, risk management, and advisory services. It has over 180 member countries and is governed by the Board of Governors and Executive Directors. The World Bank Group consists of five institutions that provide financial and technical assistance to developing countries in areas such as health, education, infrastructure, agriculture and economic development.