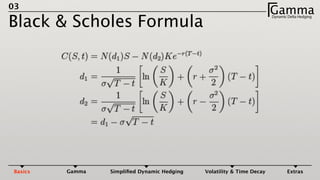
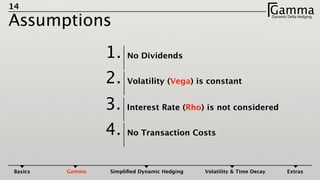
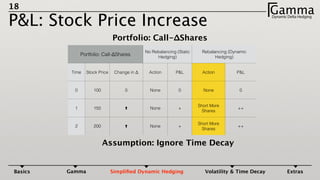
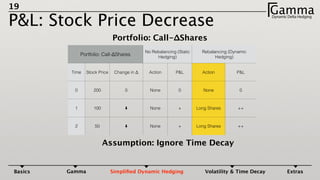
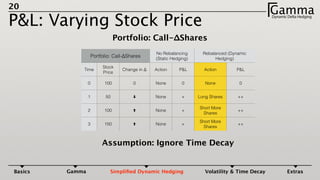
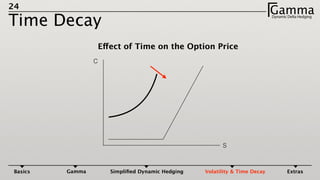
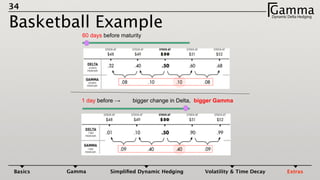
1) Dynamic delta hedging involves frequently adjusting a portfolio to maintain a hedge against changes in the underlying asset price. It accounts for the fact that an option's delta is not constant and changes with the price of the underlying.
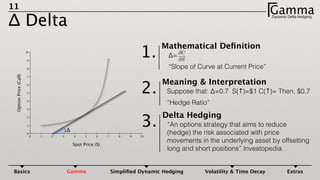
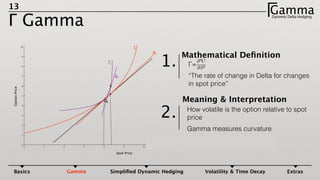
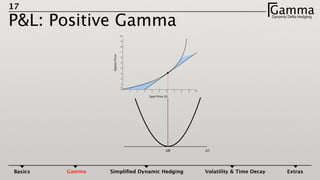
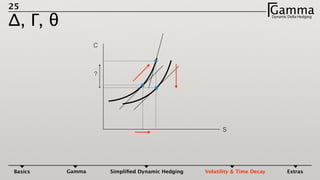
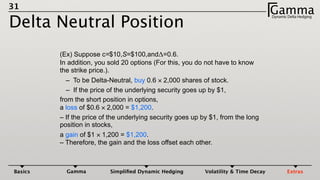
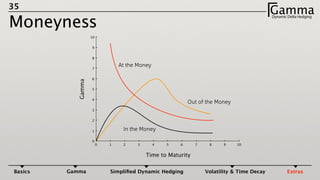
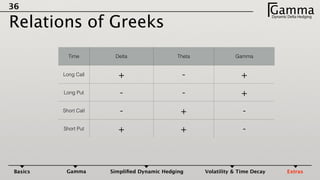
2) Gamma measures how much an option's delta changes given a small change in the underlying price. Maintaining a gamma hedge in addition to a delta hedge helps protect profits in the portfolio as the underlying price fluctuates.
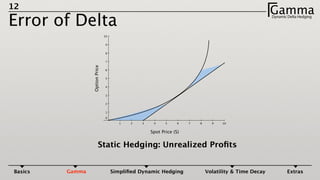
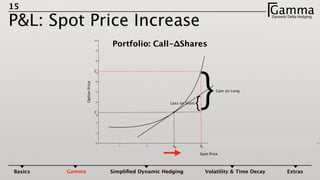
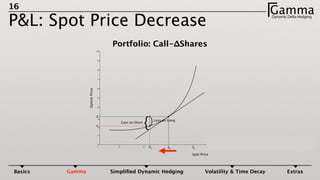
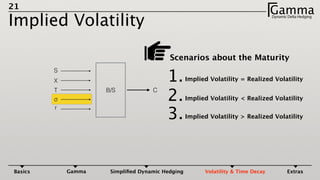
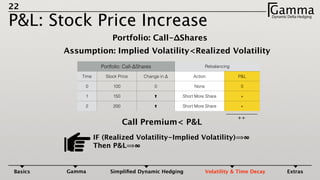
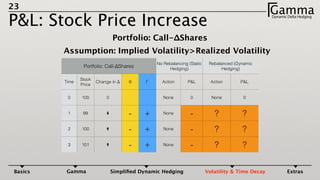
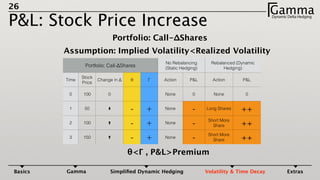
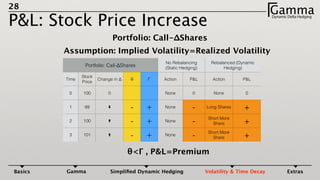
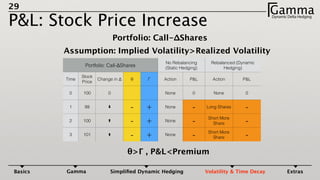
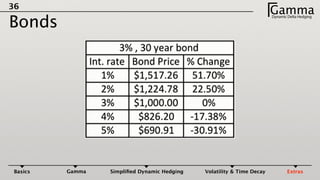
3) The profit and loss of a delta hedged portfolio depends on factors like realized versus implied volatility. If realized volatility is higher than implied, the portfolio gains. If realized equals implied, the portfolio breaks even. If realized is lower, the portfolio loses money