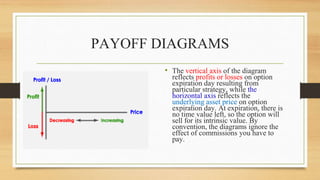
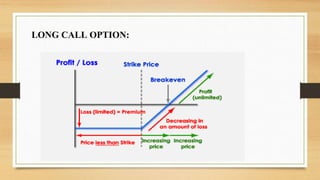
This document provides an overview of payoff diagrams for options. It defines a payoff diagram as a graphical representation of potential profits and losses from an options strategy based on the price of the underlying asset. The document explains that the vertical axis shows profits/losses and the horizontal axis shows the underlying asset price. It then gives an example of a long call option, which profits if the asset price rises above the strike price. In summary, the document defines payoff diagrams, explains how they illustrate options strategy outcomes, and provides an example for a long call option.