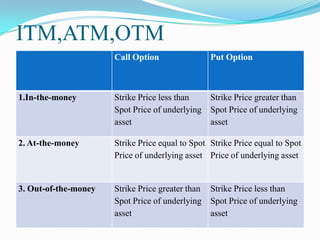
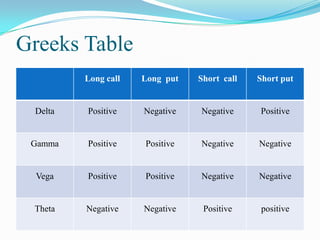
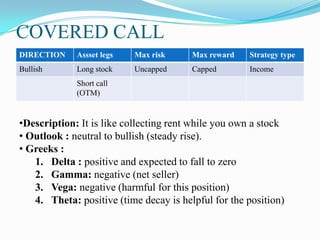
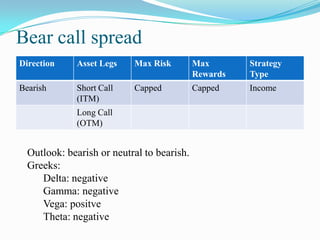
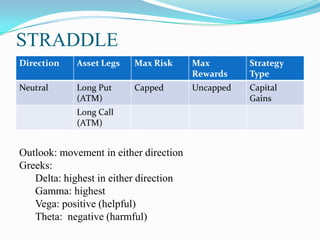
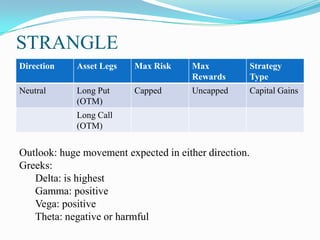
The document defines derivatives and describes the key characteristics of different types of derivatives like forwards, futures, options, and swaps. It also discusses derivatives markets, types of traders, option strategies like covered calls and bull put spreads, and volatility strategies like straddles and strangles. The key details covered include how derivatives derive their value from underlying assets, the difference between exchange-traded and over-the-counter derivatives, Greeks like delta and gamma, and using different option positions for income generation or playing volatility.