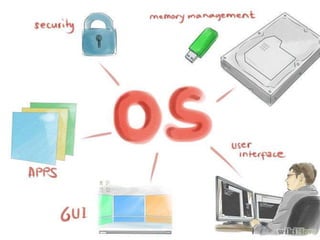
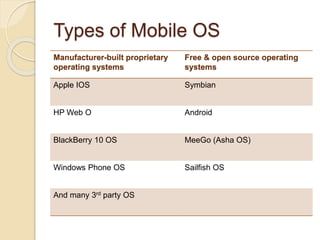
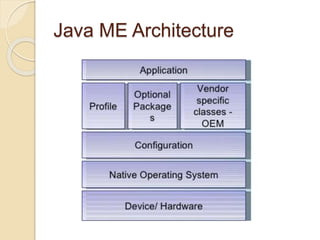
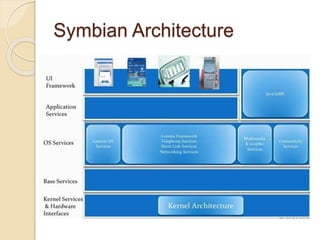
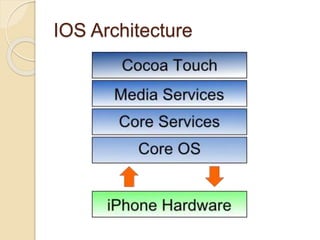
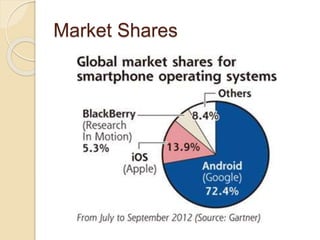
The document discusses mobile operating systems, detailing their evolution, types, advantages, disadvantages, and applications. It highlights the differences between mobile and smartphone operating systems and emphasizes the need for a balance between design, hardware, and software for optimal user experience. The future of mobile OS, including emerging platforms like Firefox OS, Tizen, and Ubuntu Touch, is also addressed, suggesting that success depends on user requirements.