This document provides an introduction to OpenGL with code samples. It discusses the history and overview of OpenGL, versions, philosophy, functionality, usage, conventions, basic concepts like the rendering pipeline and primitives. It also covers environment setup for using OpenGL with Windows SDK and GLUT as well as providing code samples. The document serves as a high-level overview of OpenGL for developers.






![Part01 : Convention
Constants:
prefix GL + all capitals (e.g. GL_COLOR_BUFER_BIT)
Functions:
prefix gl + capital first letter (e.g. glClearColor)
returnType glCommand[234][sifd] (type value, ...);
returnType glCommand[234][sifd]v (type *value);
Many variations of the same functions
glColor[2,3,4][b,s,i,f,d,ub,us,ui](v)
[2,3,4]: dimension
[b,s,i,f,d,ub,us,ui]: data type
(v): optional pointer (vector) representation
Example:
glColor3i(1, 0, 0)
or
glColor3f(1.0, 1.0, 1.0)
or
GLfloat color_array[] = {1.0, 1.0, 1.0};
glColor3fv(color_array)
10 Part 01 - Introduction February 13, 2013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opengltraining-130213070214-phpapp01/75/OpenGL-Introduction-10-2048.jpg)
![Part01 : Basic Concepts
OpenGL as a state machine (Once the value of a
property is set, the value persists until a new value is
given).
Graphics primitives going through a “pipeline” of
rendering operations
OpenGL controls the state of the pipeline with many state
variables (fg & bg colors, line thickness, texture
pattern, eyes, lights, surface material, etc.)
Binary state: glEnable & glDisable
Query: glGet[Boolean,Integer,Float,Double]
Coordinates :
XYZ axis follow Cartesian system.
11 Part 01 - Introduction February 13, 2013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opengltraining-130213070214-phpapp01/75/OpenGL-Introduction-11-2048.jpg)
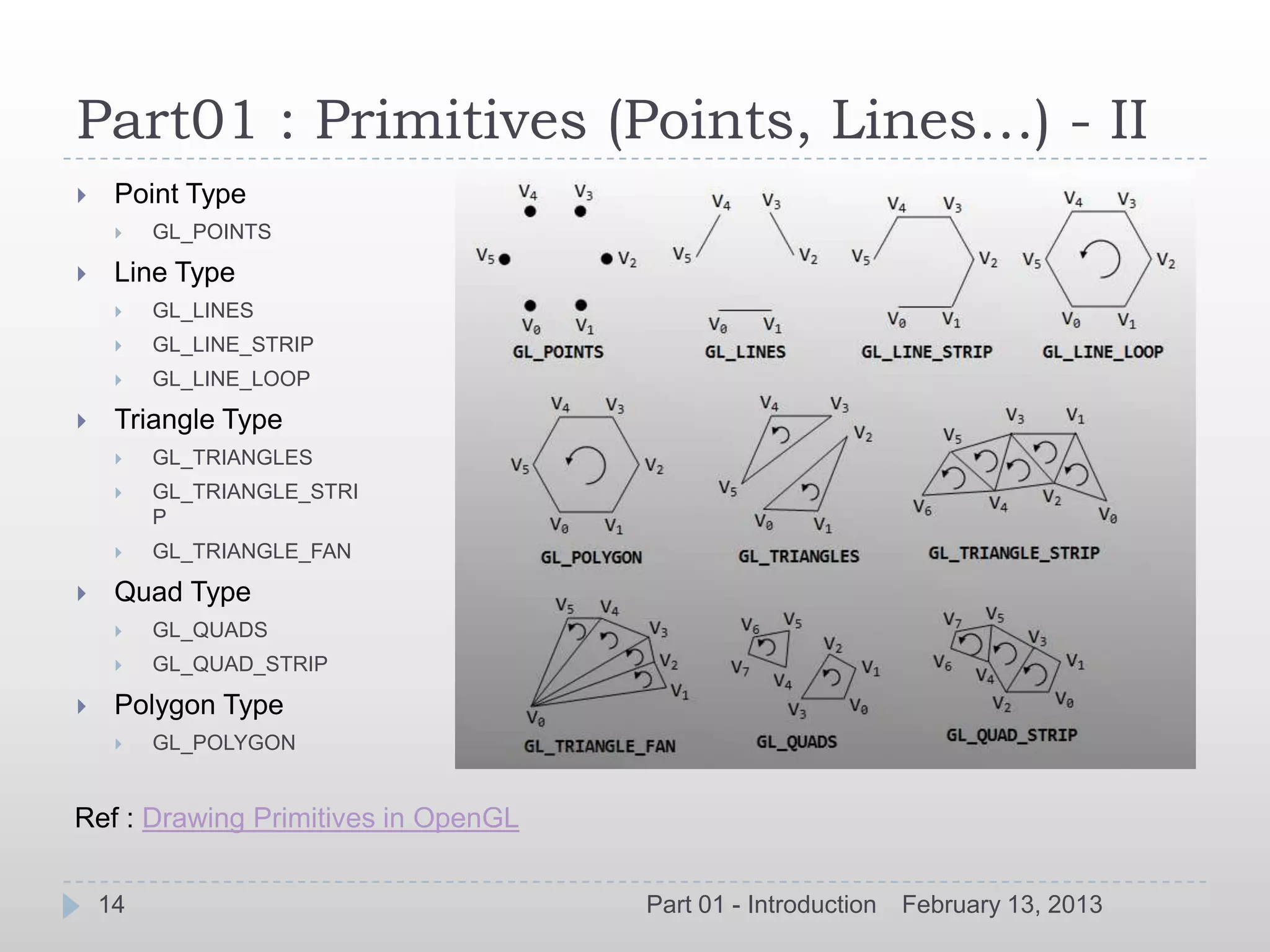
![Part01 : Primitives (Points, Lines…) - I
All geometric objects in OpenGL are created from a set of basic
primitives.
Certain primitives are provided to allow optimization of geometry for
improved rendering speed.
Primitives specified by vertex calls (glVertex*) bracketed by
glBegin(type) and glEnd()
Specified by a set of vertices
glVertex[2,3,4][s,i,f,d](v) (TYPE coords)
Grouped together by glBegin() & glEnd()
glBegin(GLenum mode)
glBegin(GL_POLYGON) mode includes
GL_POINTS
glVertex3f(…) GL_LINES, GL_LINE_STRIP, GL_LINE_
LOOP
glVertex3f(…) GL_POLYGON
glVertex3f(…) GL_TRIANGLES, GL_TRIANGLE_STRI
P
glEnd GL_QUADS, GL_QUAD_STRIP
13 Part 01 - Introduction February 13, 2013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opengltraining-130213070214-phpapp01/75/OpenGL-Introduction-13-2048.jpg)




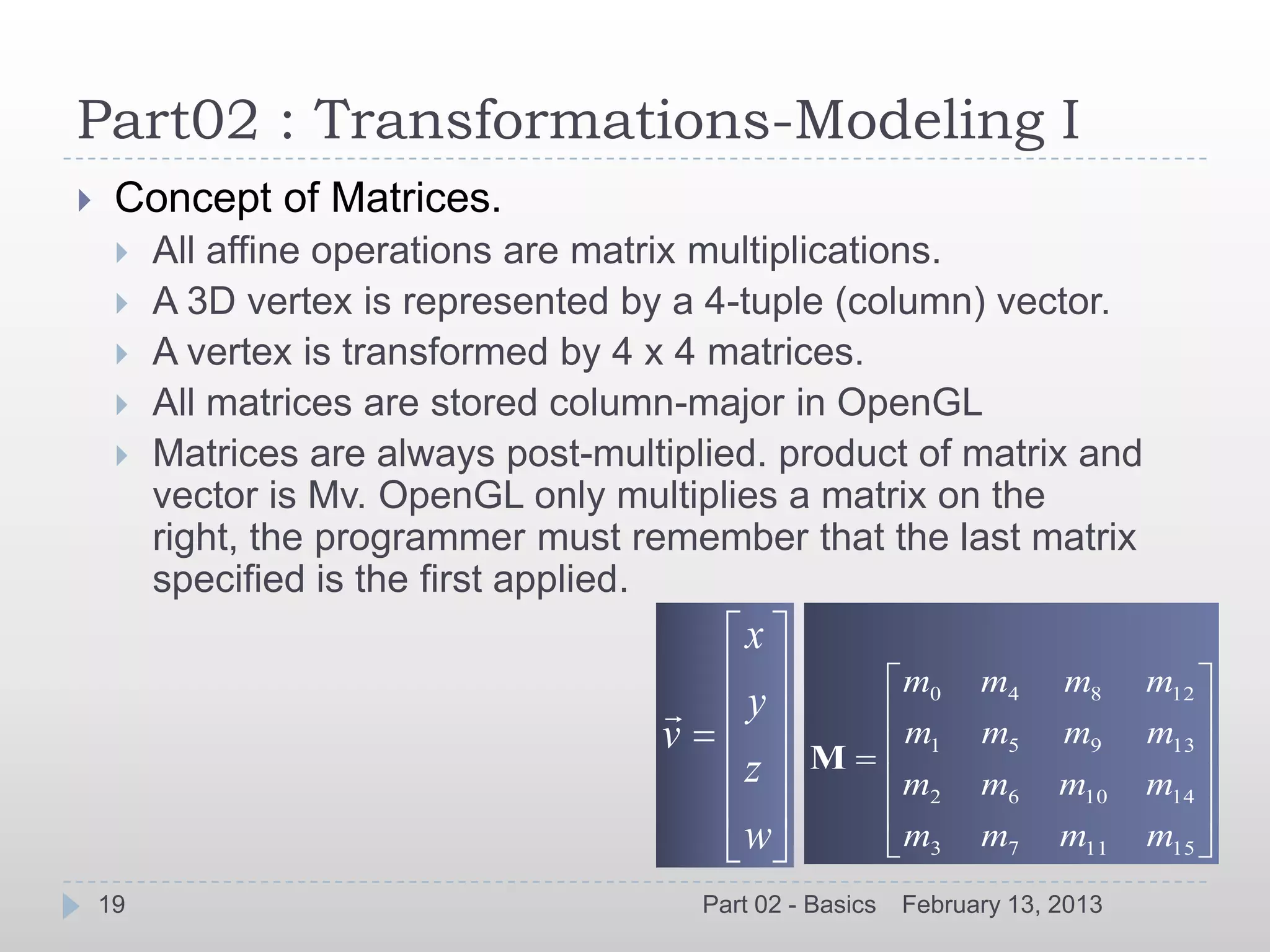

glMatrixMode(GLenum mode) glRotate[f,d](angle,x,y,z)
Initialize current Matrix glScale[f,d](x,y,z)
glLoadIdentity(void) Order is important
glLoadMatrix[f,d](const TYPE
*m)
Concatenate current Matrix
glMultMatrix(const TYPE *m)
20 Part 02 - Basics February 13, 2013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opengltraining-130213070214-phpapp01/75/OpenGL-Introduction-20-2048.jpg)