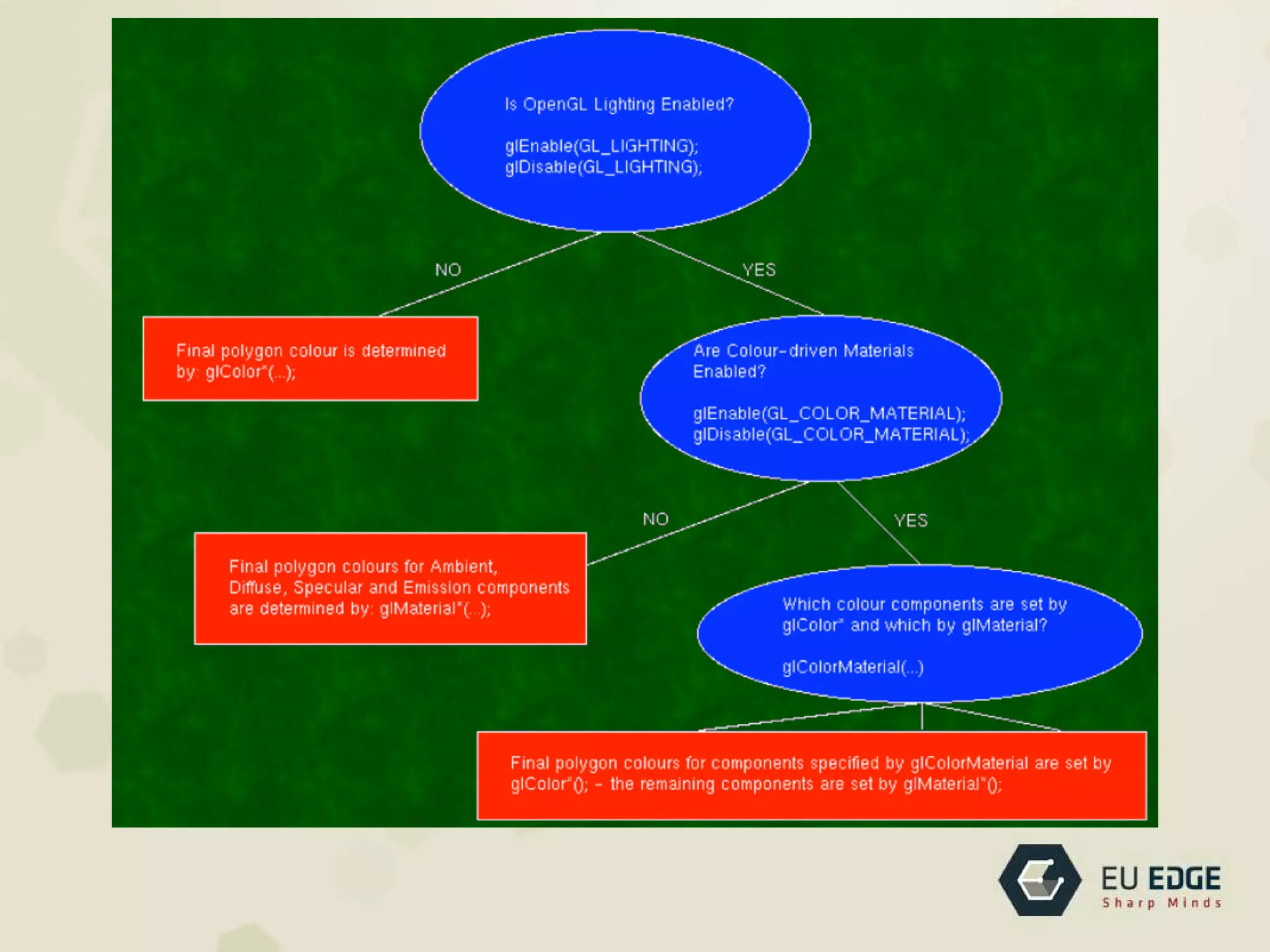
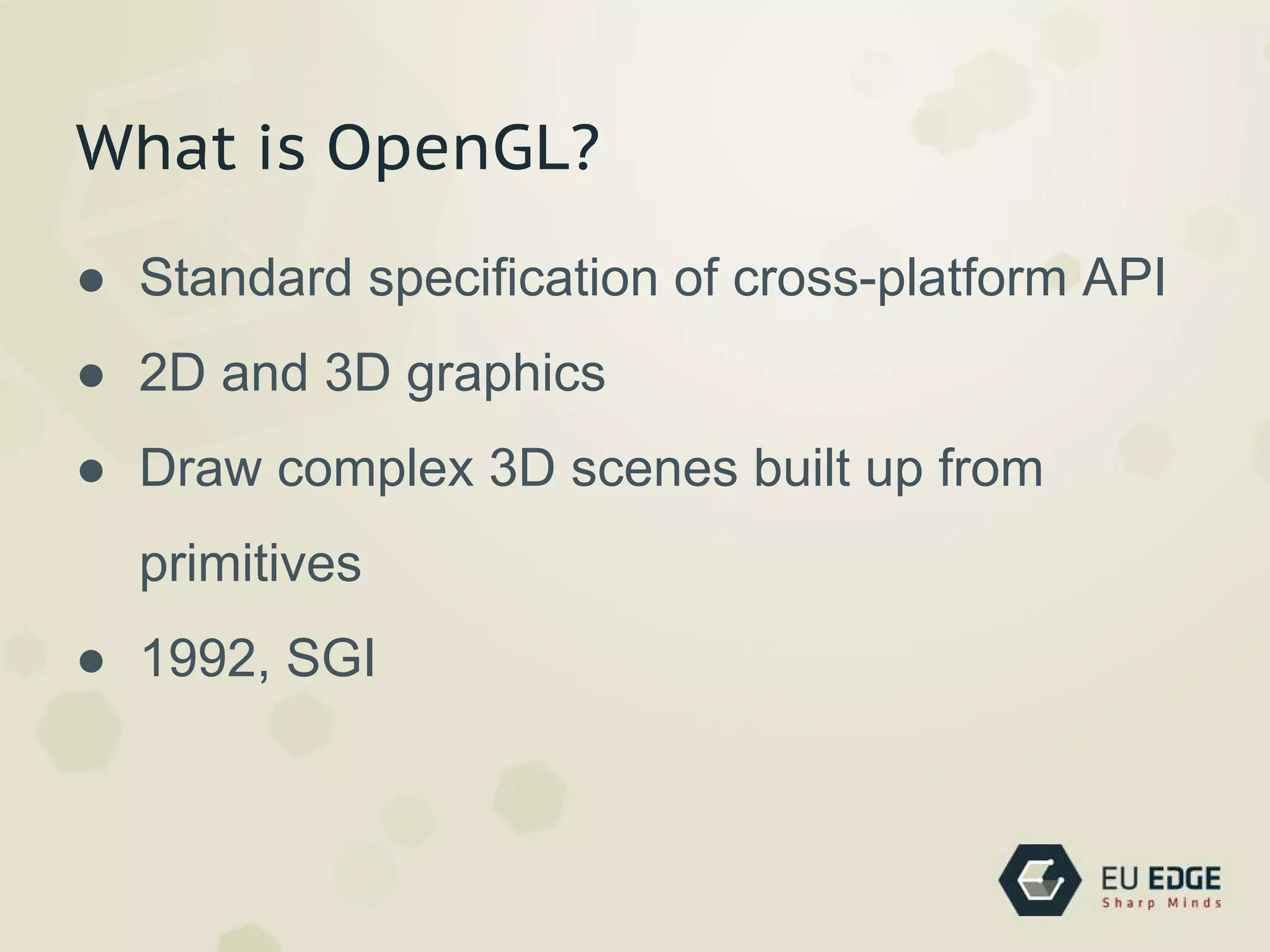
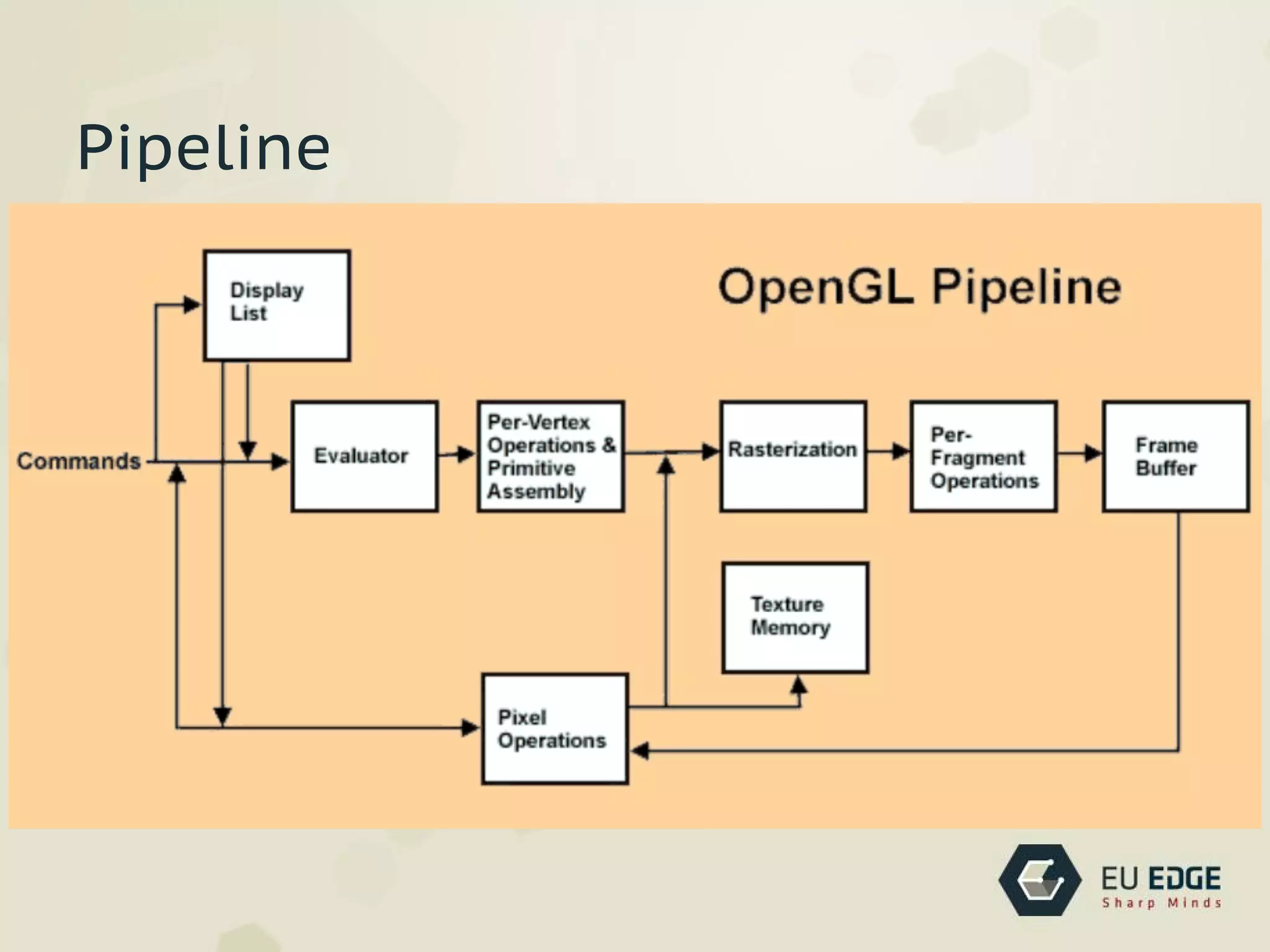
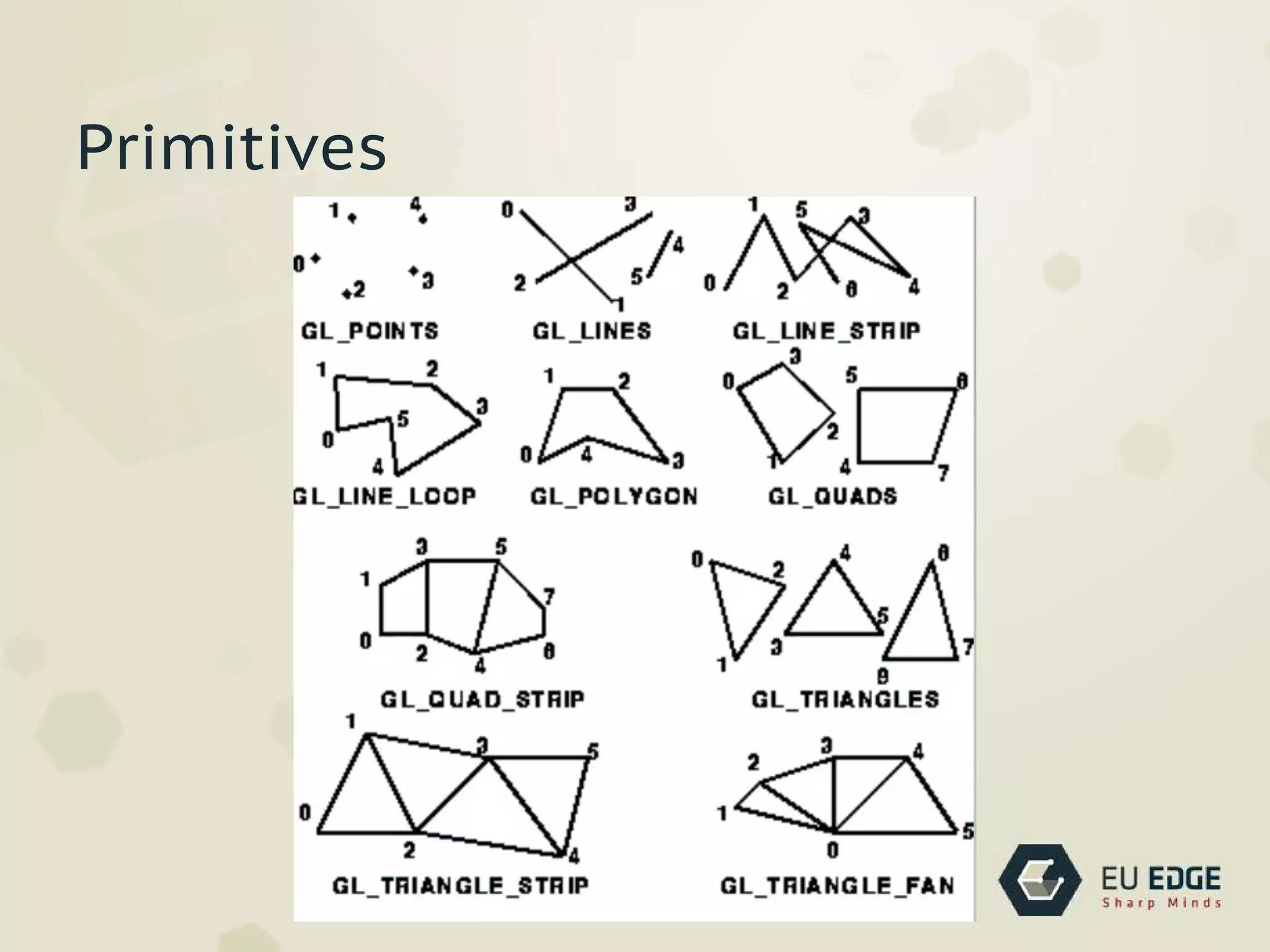
OpenGL is a cross-platform API for 2D and 3D graphics. It allows developers to draw complex 3D scenes using primitives. OpenGL was created in 1992 by SGI and has evolved over time. It uses a pipeline architecture where commands are evaluated to transform vertices and attributes before rasterization converts them to fragments for framebuffer operations. Developers can use shading languages like GLSL in vertex and fragment shaders to add lighting, textures, and other effects.










![#include <GL/gl.h>
#include <GL/glut.h>
#include <GL/glu.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
glutInit(&argc, argv);
glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_RGB | GLUT_DEPTH | GLUT_DOUBLE);
glutInitWindowSize(800,600);
glutCreateWindow("Hello World");
glutDisplayFunc(display);
glutMainLoop();
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opengl-140704091831-phpapp01/75/Open-gl-14-2048.jpg)









![int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
..
//
glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION);
gluPerspective(45, //view angle
1.0, //aspect ratio
10.0, //near clip
200.0);//far clip
glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW);
// enabe face culling function
glEnable(GL_CULL_FACE);
initCube();
glutMainLoop();
..
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opengl-140704091831-phpapp01/75/Open-gl-24-2048.jpg)
![void display()
{
...
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
glPushMatrix();
glTranslatef(0, 0, -50);
glRotatef(rotateBy, 1, 1, 0); //rotate by rotateBy degrees about the vector
(1,1,0)
...
glBegin(GL_QUADS);
for (b=0; b<4; b++)
{
currentVer = cube.quad[a].ver[b];
glColor3fv(cube.ver[ currentVer ].col);
glVertex3fv(cube.ver[ currentVer ].pos);
}
glEnd();
...
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opengl-140704091831-phpapp01/75/Open-gl-25-2048.jpg)


![const float texCoords[4][2]=
{
{0.0, 0.0},
{0.0, 1.0},
{1.0, 1.0},
{1.0, 0.0}
};
UV coordinates](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opengl-140704091831-phpapp01/75/Open-gl-28-2048.jpg)


![int display()
{
...
// draw cube
for (a=0; a<6; a++) //quads loop
{
glBegin(GL_QUADS);
for (b=0; b<4; b++) //points loop
{
currentVer = cube.quad[a].ver[b]; //sets the current vertex to
this point's vertex
// glColor3fv(cube.ver[ currentVer ].col); //changes the colour to the
current vertex's colour
glTexCoord2fv(texCoords[b]);
glVertex3fv(cube.ver[ currentVer ].pos); //draws a vertex at the current
vertex's position
}
glEnd();
}
...
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opengl-140704091831-phpapp01/75/Open-gl-31-2048.jpg)