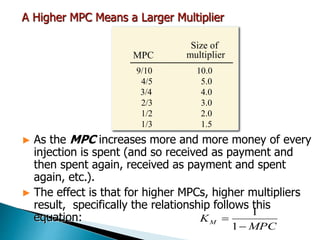
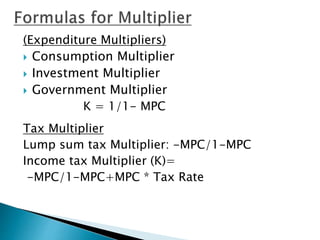
The document discusses the concept of the multiplier, which refers to the total change in aggregate income resulting from a change in autonomous expenditures. It provides examples to show how an initial $1 million injection is multiplied through subsequent rounds of spending, consumption, and savings. The multiplier depends on the marginal propensity to consume (MPC), with a higher MPC resulting in a larger multiplier. The document also discusses different types of multipliers, such as the investment, consumption, government and tax multipliers, and how they are calculated. It provides a practice question as an example.