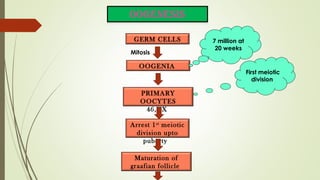
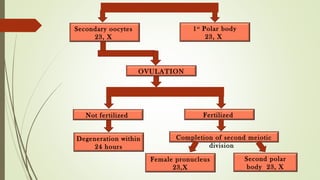
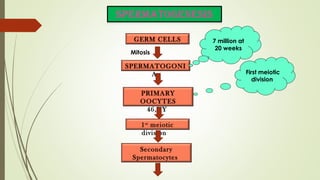
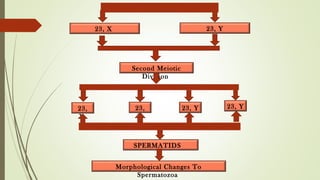
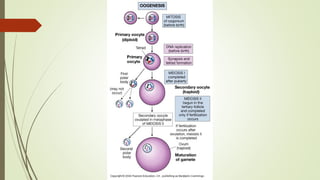
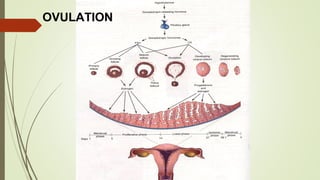
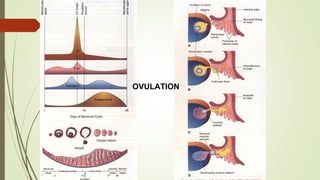
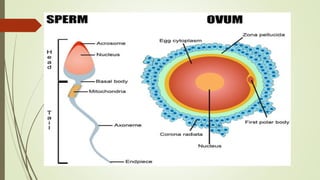
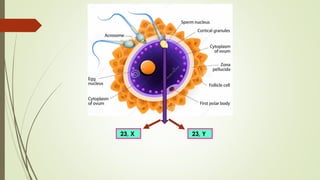
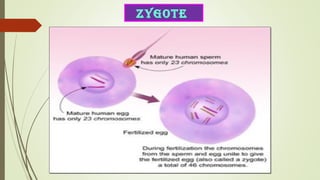
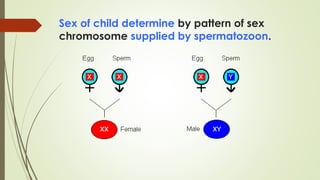
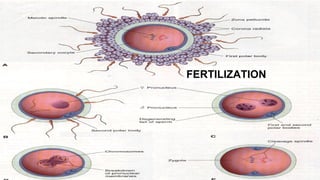
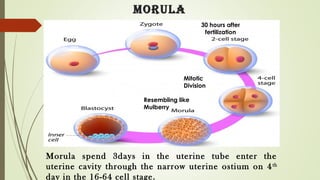
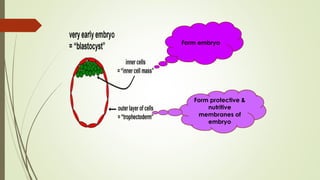
Gametogenesis is the process of developing mature gametes (eggs and sperm) through meiosis. Oogenesis involves the development of a primary oocyte into a secondary oocyte over many years in females. Spermatogenesis is the process where spermatogonia develop into spermatozoa in males. Fertilization occurs when a sperm penetrates an egg in the fallopian tube, and their genetic material combines to form a zygote, beginning the process of embryogenesis.