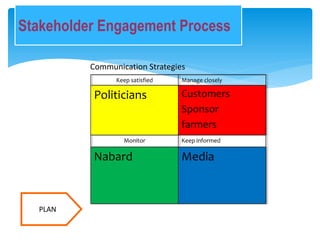
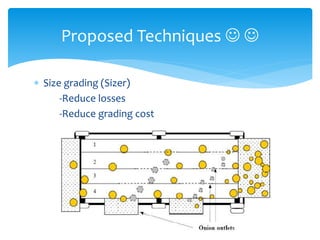
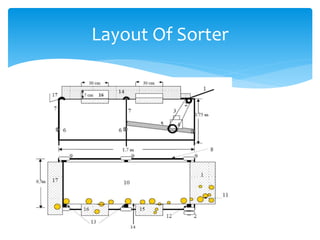
The document outlines a project for onion warehouse management aimed at reducing post-harvest losses and stabilizing onion prices, involving a cold storage unit and a distribution network. It highlights various objectives including training farmers and ensuring adequate supply chain management while excluding other agricultural products. Financial projections indicate expected profitability and future growth opportunities, alongside risk management strategies addressing potential challenges in implementation.






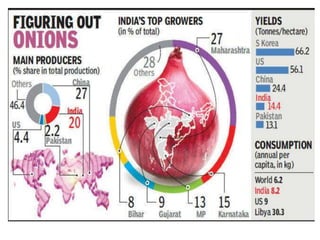
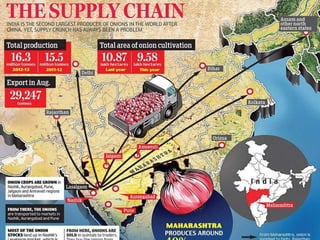


























![ In India, for instance, the main agency which is
authorized to export onion is the National
Agricultural Cooperative Marketing Federation of
India [NAFED].
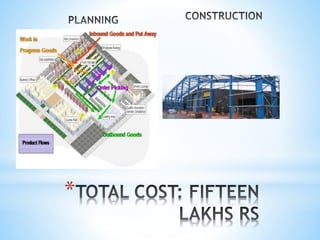
Proposed Procurement , we will buy onion at fixed
price for our warehouse store, sell in market at our
decided price. This will bring profit to farmer .
Contd…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/onionwarehousemanagement21-141217133721-conversion-gate02/85/Onion-warehouse-management-43-320.jpg)