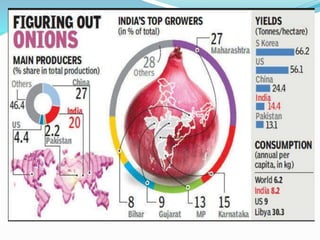
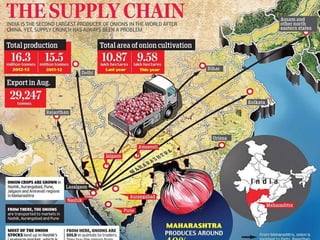
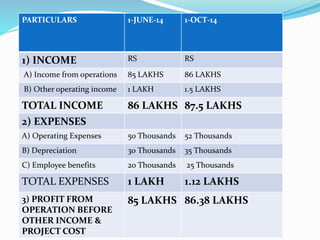
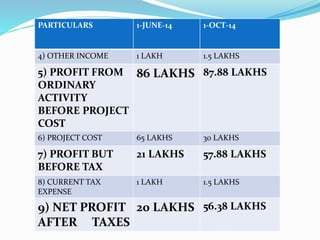
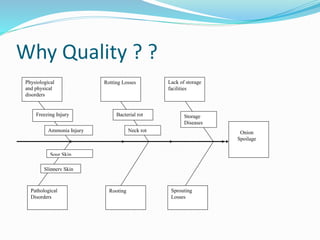
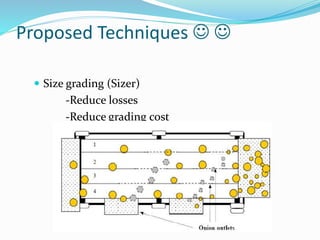
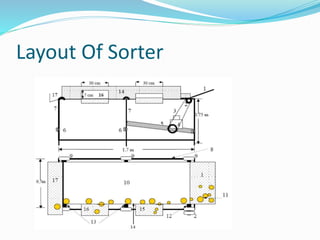
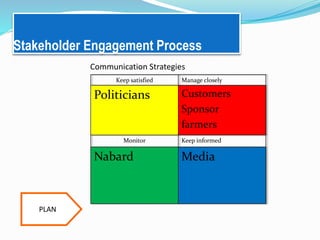
The document outlines a project aimed at improving onion warehousing and management to reduce post-harvest losses and stabilize prices for farmers. It includes various components such as training, equipment, and financial planning while detailing risks and stakeholder engagement. The project aims to address supply chain weaknesses and enhance the overall productivity of onion farming.