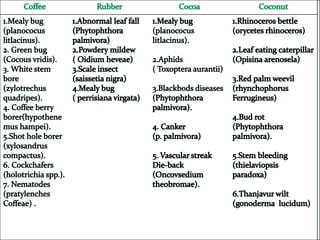
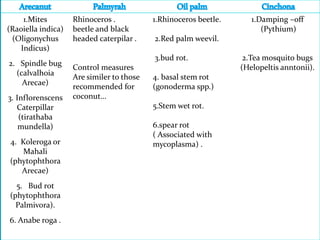
This document provides information on the botanical classification, origin, chromosome number, cultivation practices, varieties, and processing methods for 10 important plantation crops. Tea, coffee, rubber, cocoa, cashew, coconut, arecanut, palmyrah, and oil palm are described. Key details include native regions, climate requirements, propagation techniques, pruning and harvesting schedules, and economic uses of each crop and its products.