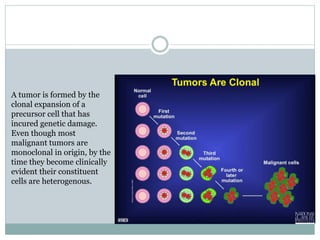
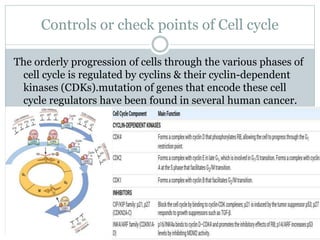
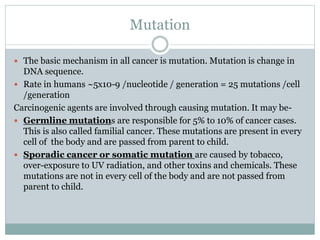
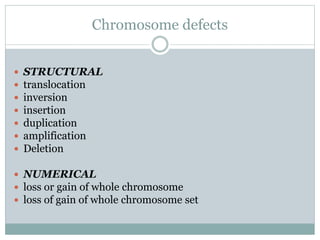
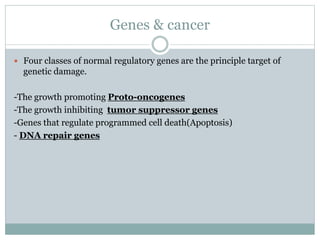
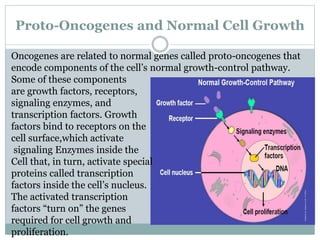
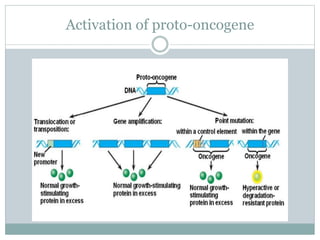
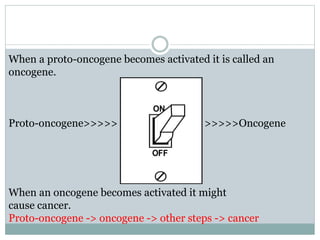
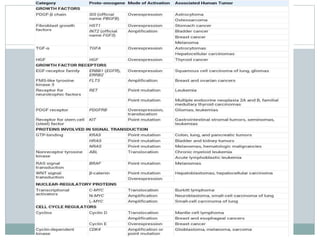
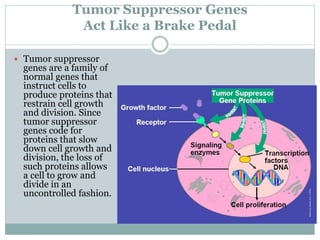
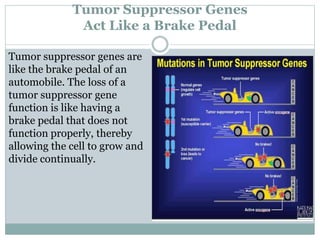
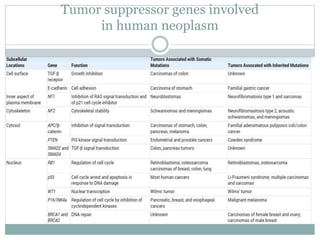
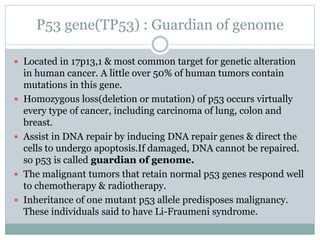
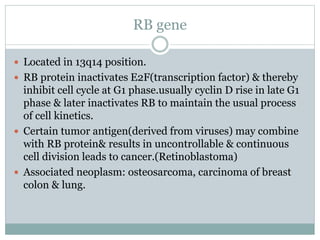
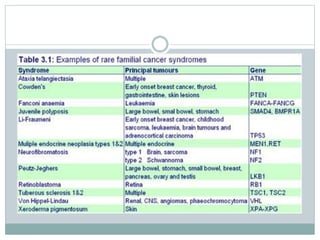
Genetic changes play a key role in cancer development. Cancer arises due to mutations in genes that regulate cell growth, such as oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes. Oncogenes promote cell growth when activated by mutations, while tumor suppressor genes normally inhibit cell growth but require two mutations to be inactivated. Many cancers are caused by the accumulation of both germline and somatic mutations in genes over time. Certain inherited genetic syndromes predispose individuals to specific cancer types if high-risk genes are mutated.