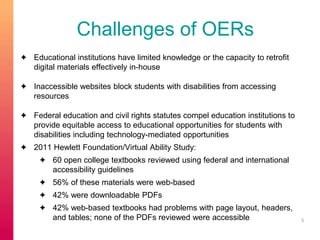
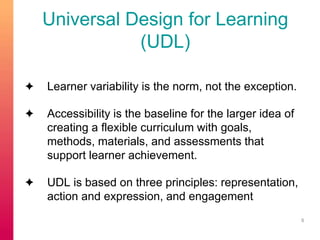
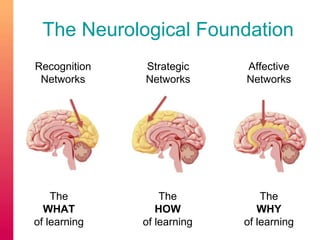
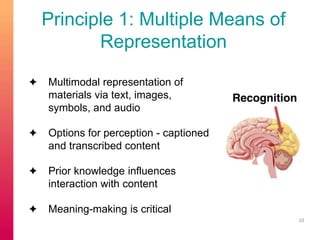
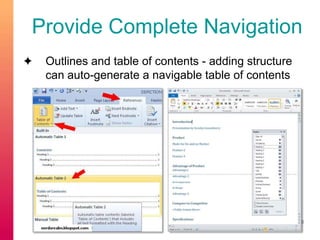
The document discusses selecting and creating open educational resources (OERs) that are accessible to all students. It defines OERs and the benefits they provide like reduced costs, though challenges exist around ensuring accessibility. The presentation emphasizes applying universal design for learning (UDL) principles to create flexible content that considers learner variability. Key recommendations include providing complete navigation, meaningful structure, and alternative access to media through tools like captions, transcripts and audio descriptions.