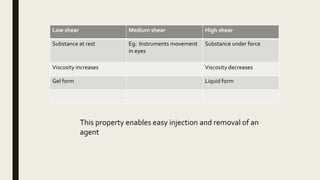
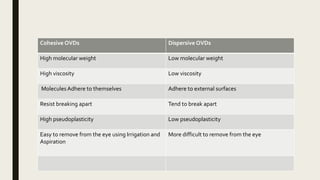
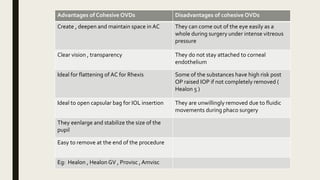
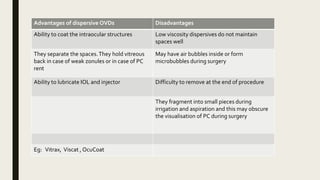
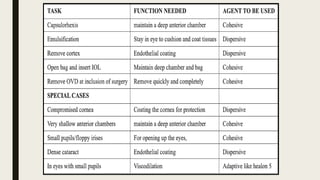
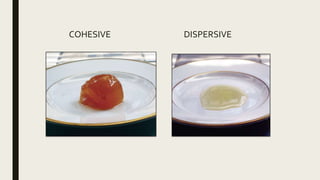
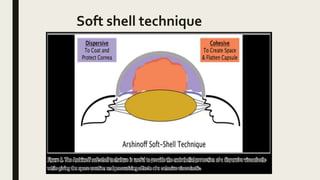
The document summarizes ocular viscosurgical devices used in ophthalmic procedures. It discusses the history and ideal properties of viscoelastic substances. Commonly used families include sodium hyaluronate, chondroitin sulfate, and hydroxypropyl methylcellulose. Physical properties like viscosity, pseudoplasticity, and coatability are described. Clinical applications involve cataract surgery, glaucoma surgery, and keratoplasty. Complications from use include increased intraocular pressure and capsular block syndrome.