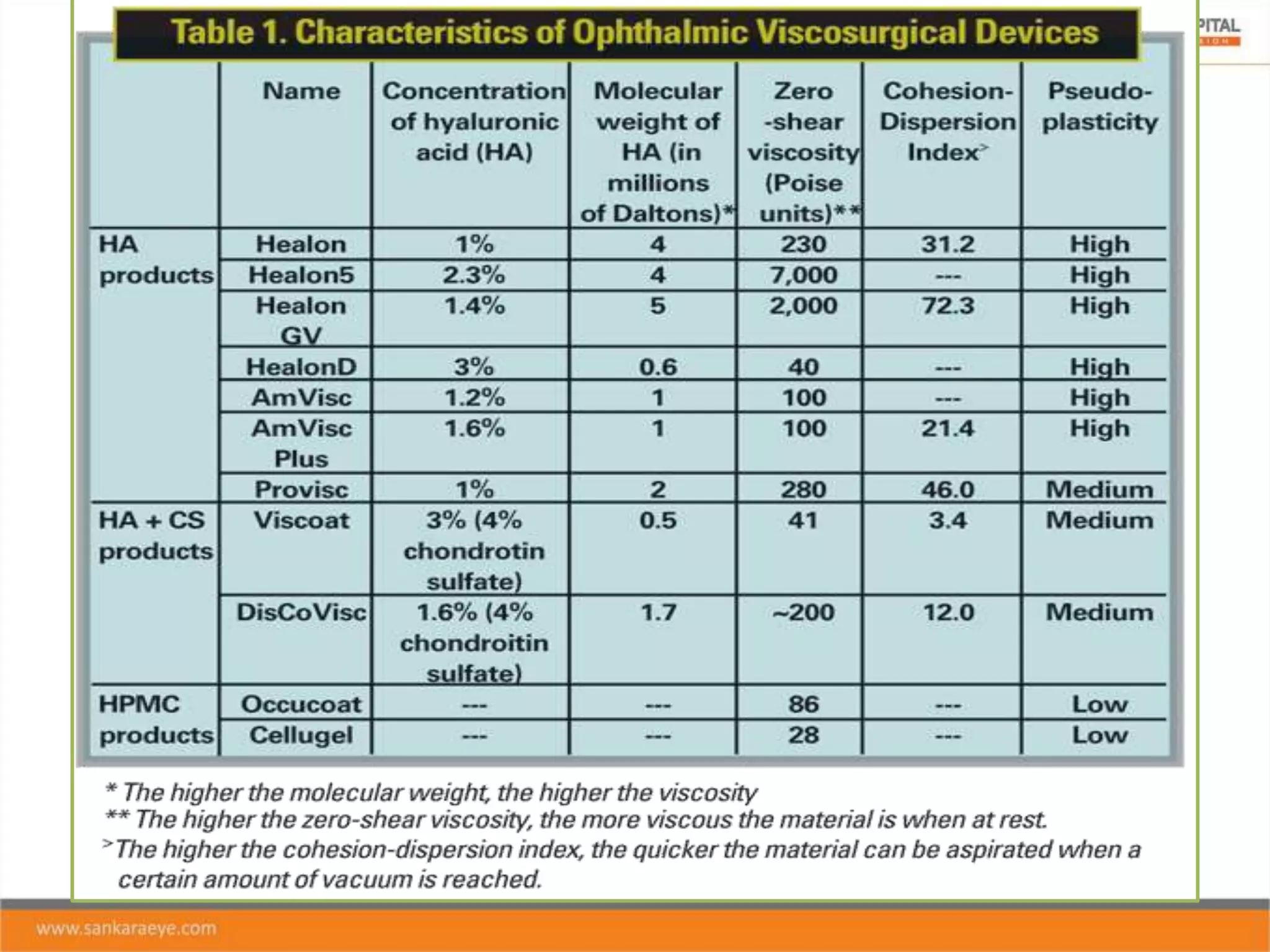
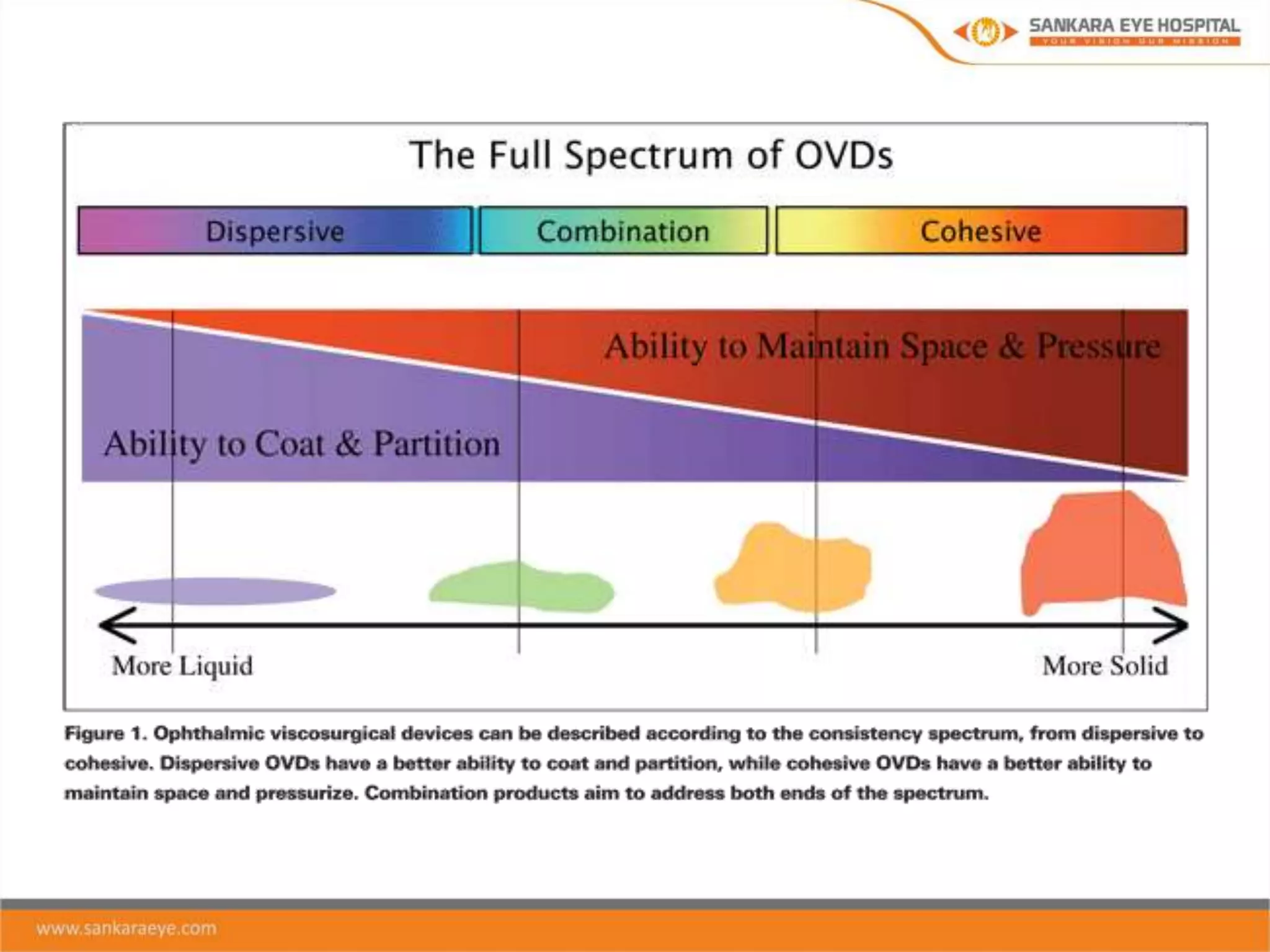
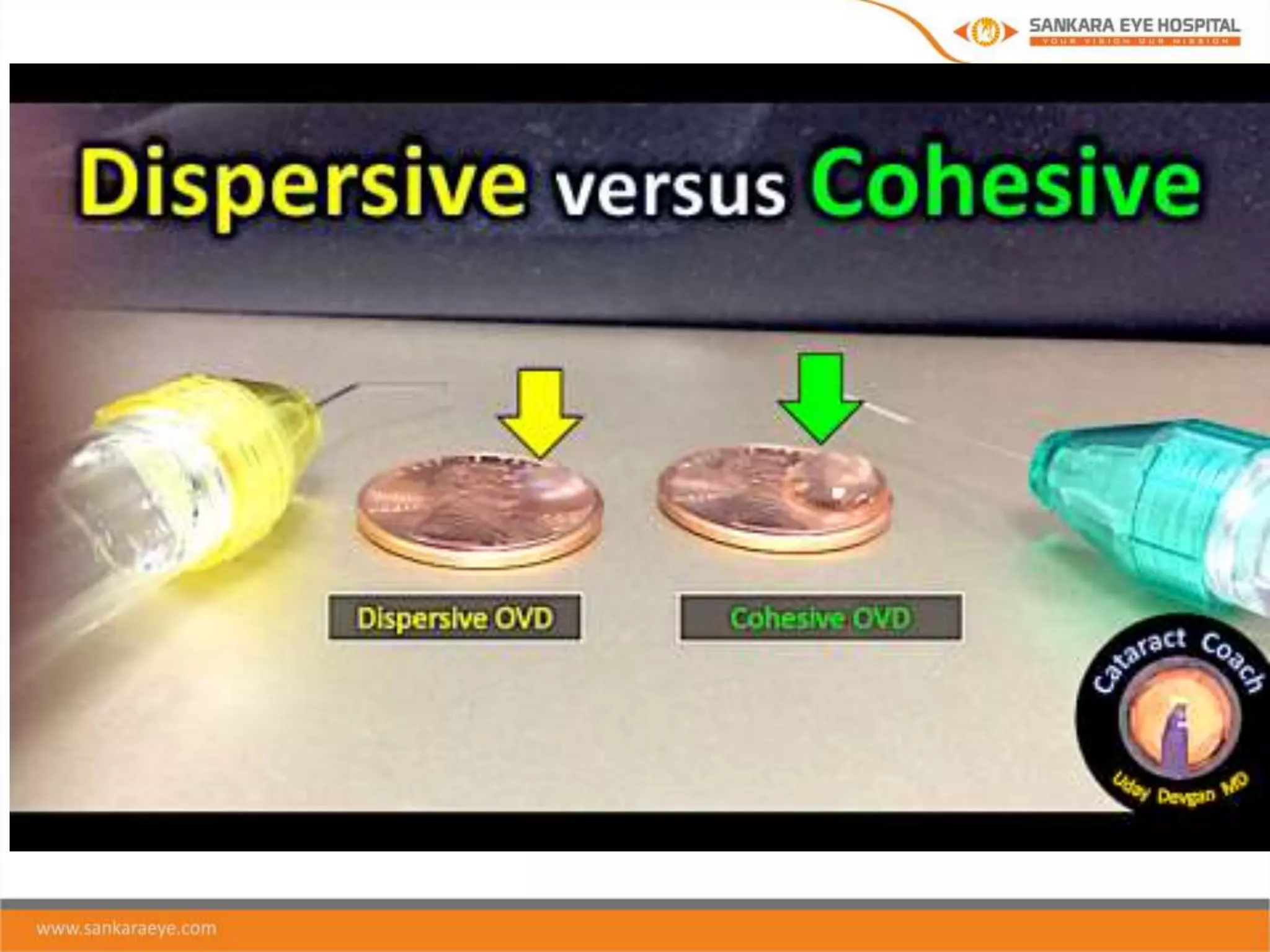
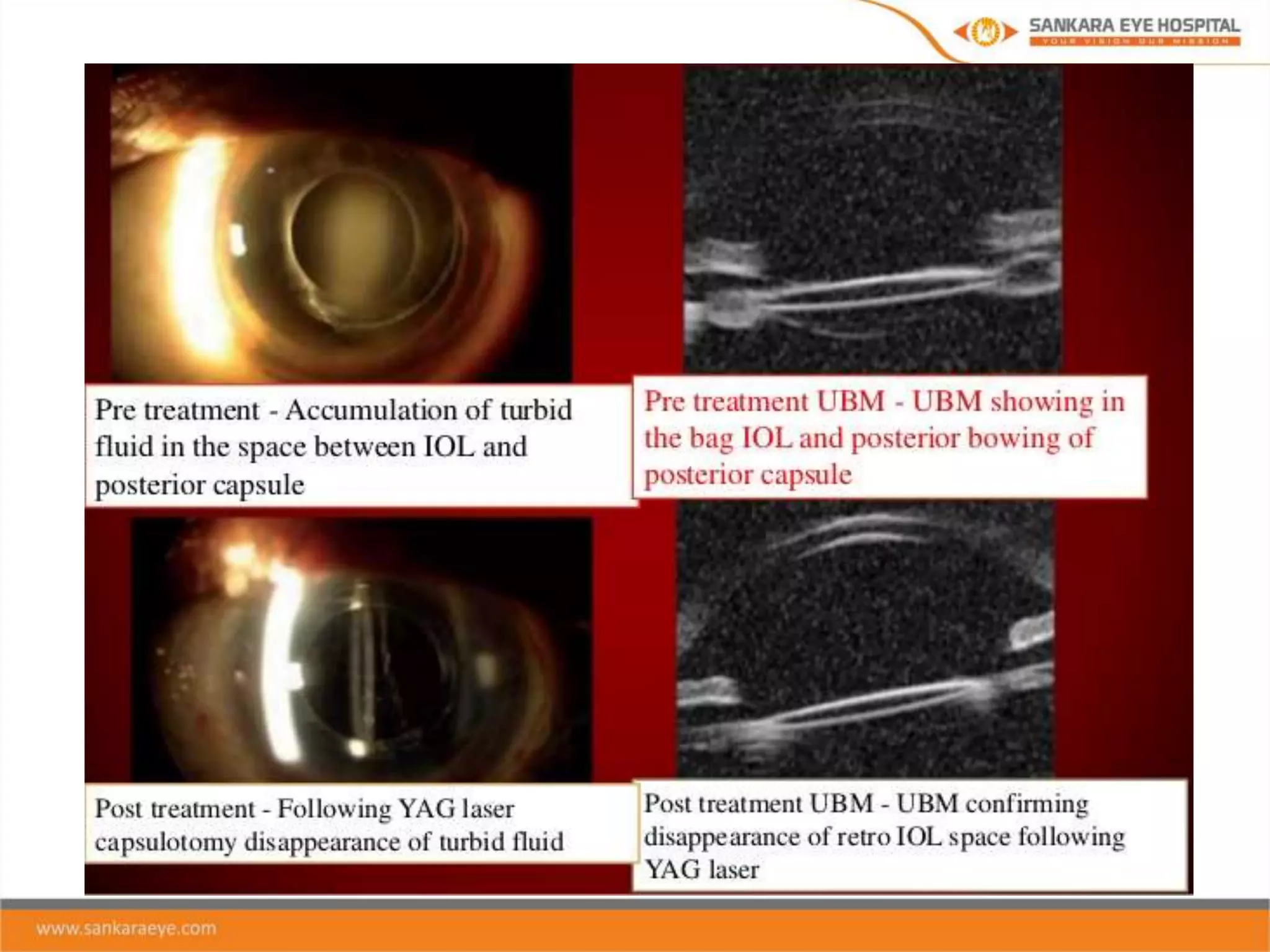
The presentation discusses ophthalmic viscosurgical devices (OVDs), covering their historical overview, characteristics, classifications, and clinical applications in ocular surgeries such as cataract and glaucoma surgery. It details the rheological properties of OVDs, including viscosity, elasticity, and cohesiveness, as well as the advantages and disadvantages of different types like cohesive, dispersive, and viscoadaptive OVDs. The document also highlights complications associated with OVD use, emphasizing the importance of selecting the appropriate OVD based on its properties and the surgical context.