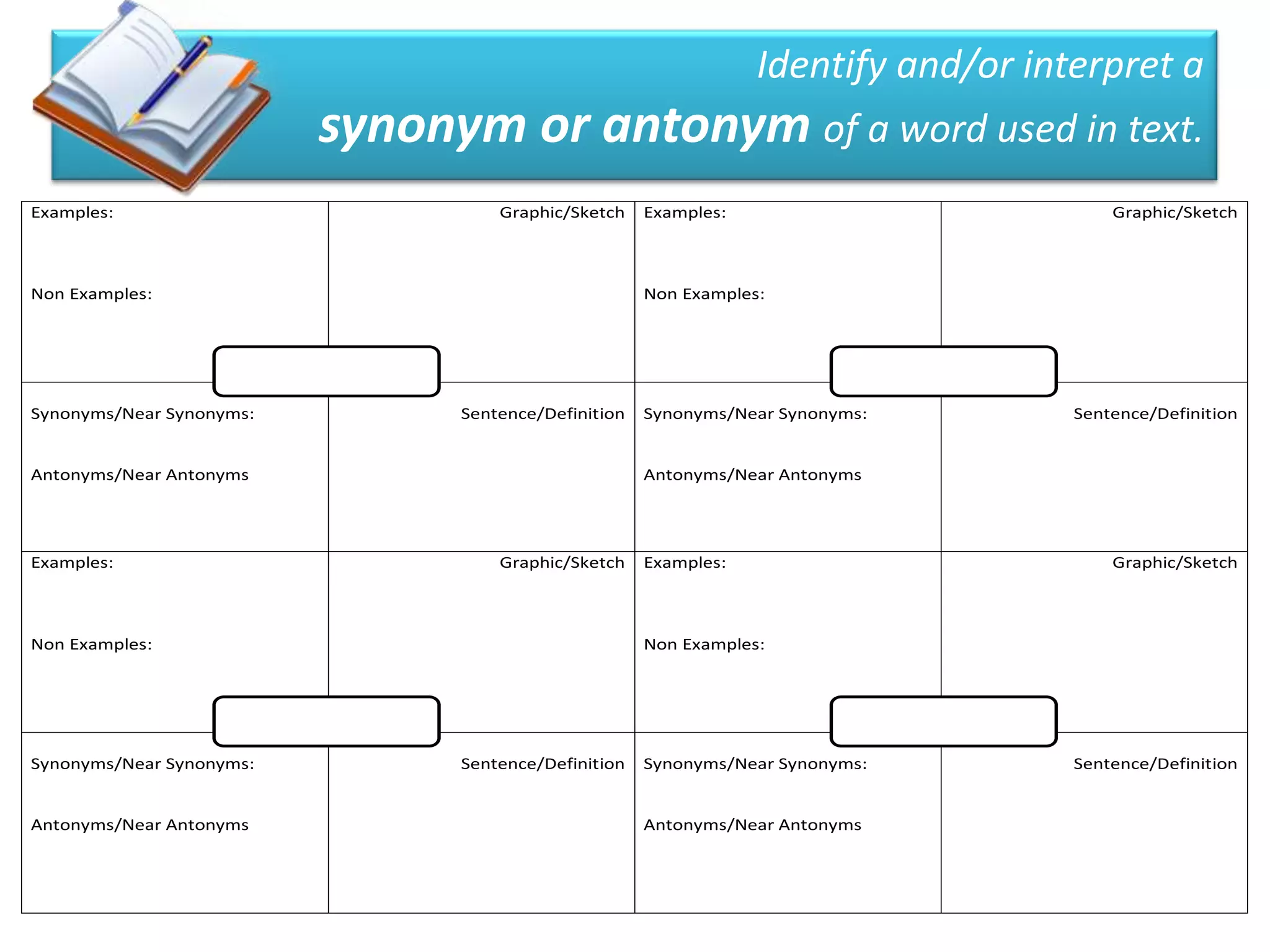
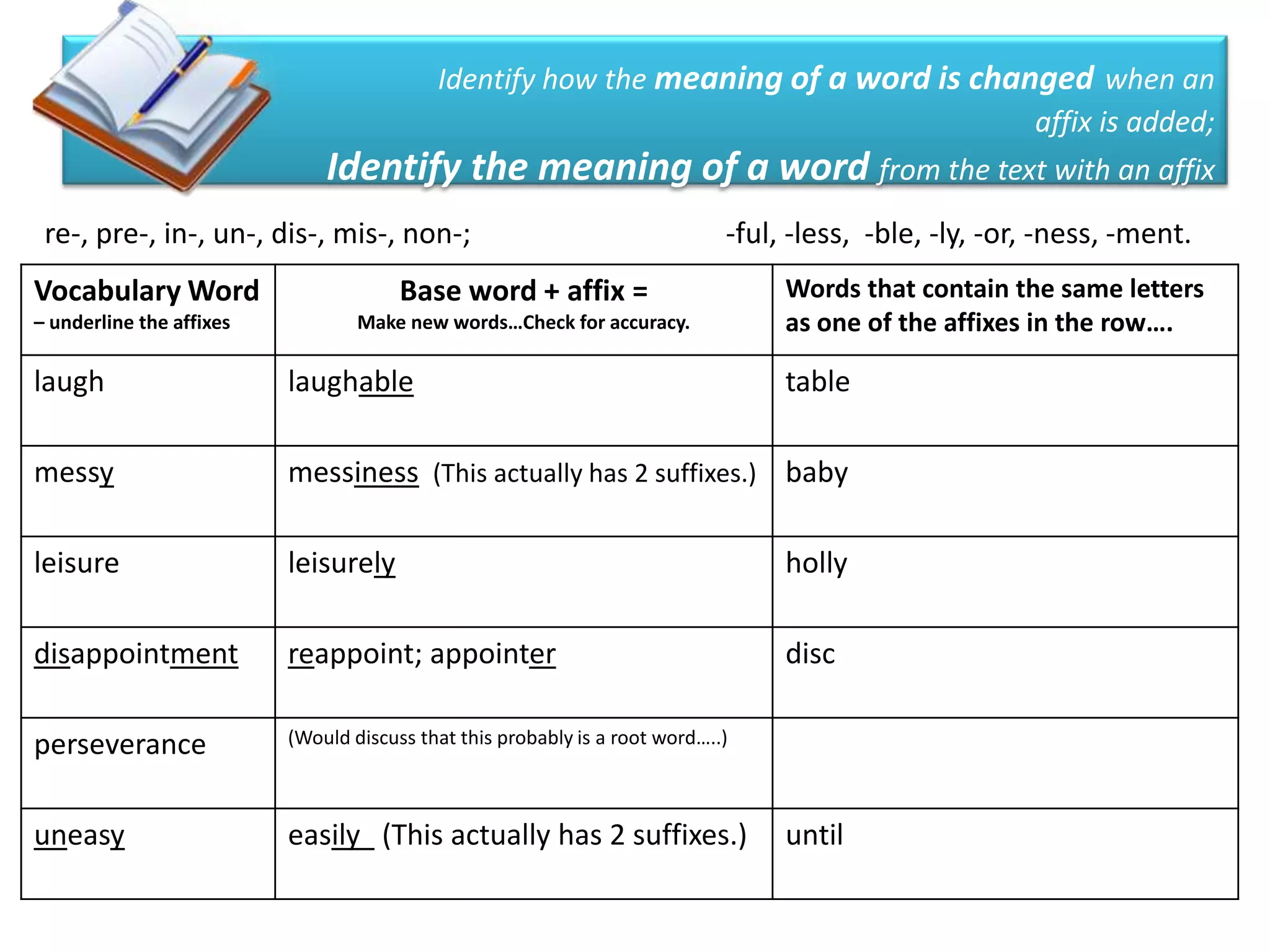
This document provides guidance for teachers on how to help more students become proficient readers through explicit instruction. It emphasizes explicitly modeling reading strategies and comprehension skills for students during mini-lessons. Teachers are advised to provide guided and independent practice opportunities aligned with the verbs in eligible content standards. Formative assessment methods like sticky notes are recommended to check students' understanding during reading. The document stresses balancing PSSA preparation with developing strategic readers through a reader's workshop approach and integrated repeated practice of skills.