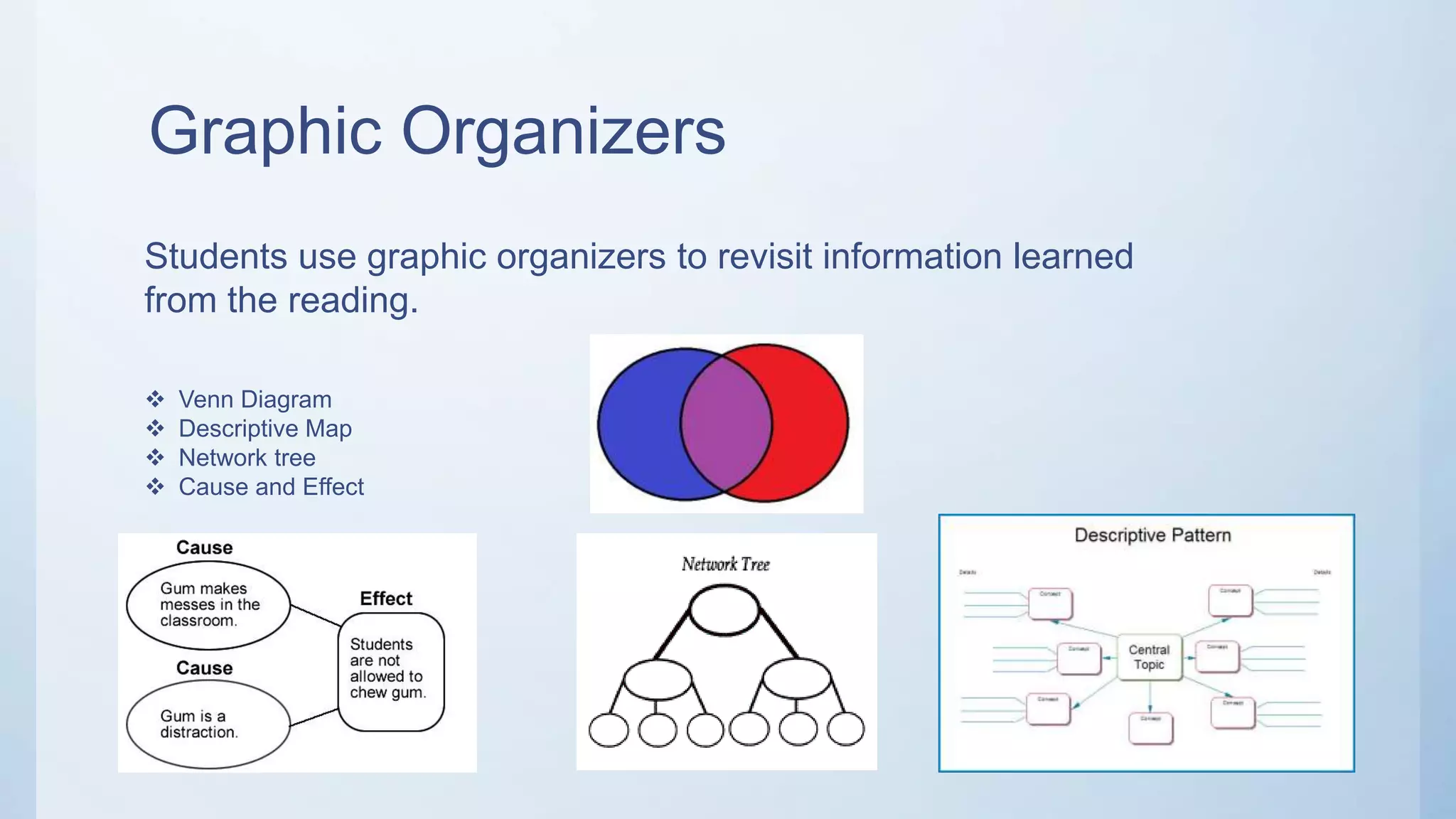
Before, during, and after reading strategies are used to help students comprehend texts. Before reading, teachers activate prior knowledge, pre-teach vocabulary, and set a purpose. During reading, teachers model metacognitive skills like predicting and questioning through reciprocal teaching. After reading, students review information through graphic organizers, discussions, summarizing and timelines to ensure understanding of main ideas. These strategies link the different comprehension stages to help students derive meaning from texts and develop problem solving abilities.