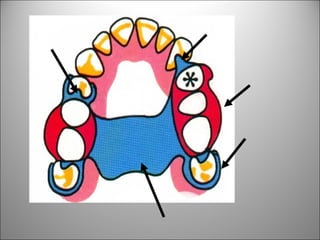
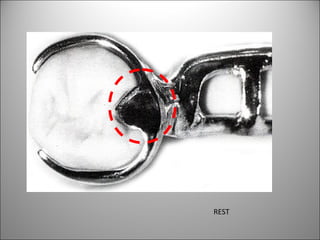
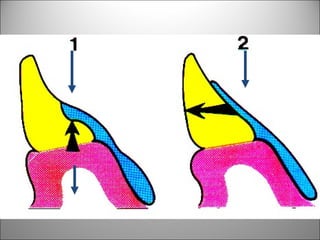
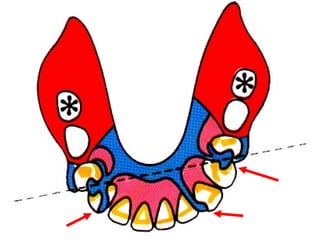
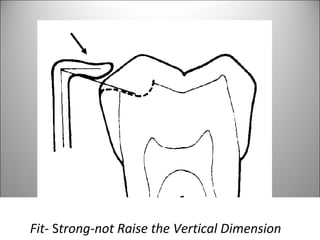
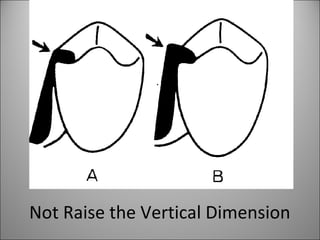
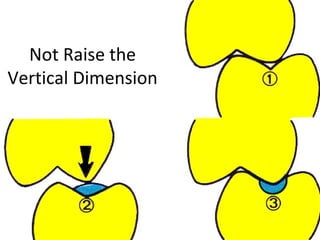
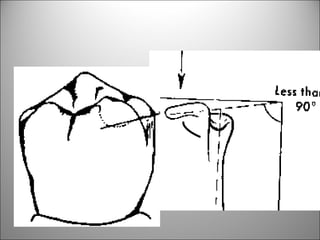
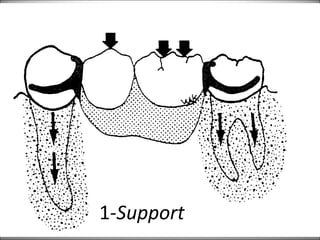
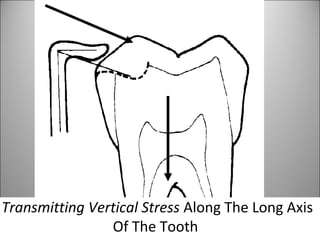
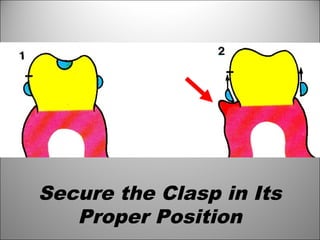
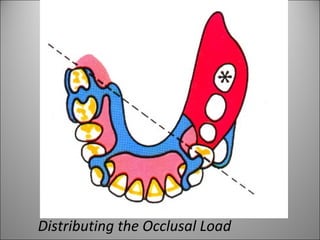
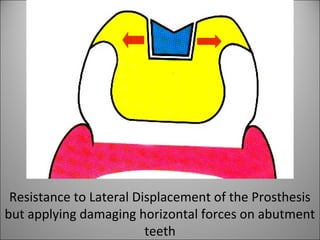
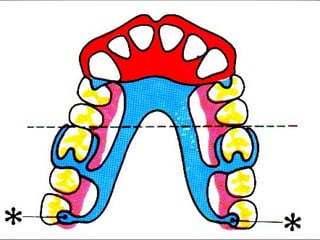
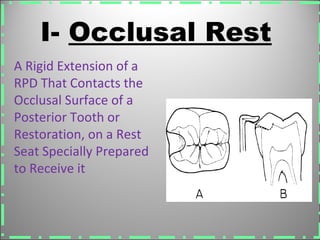
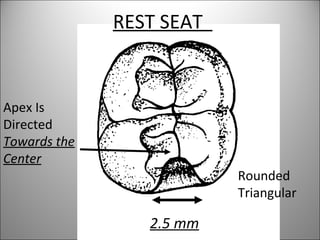
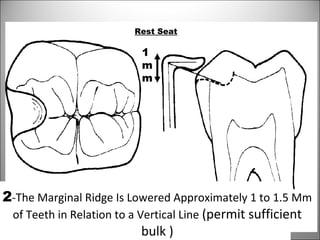
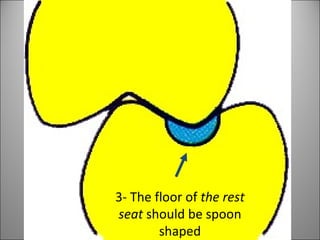
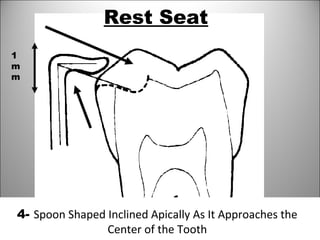
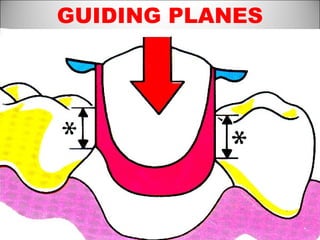
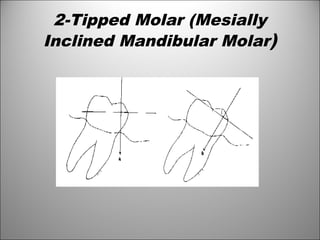
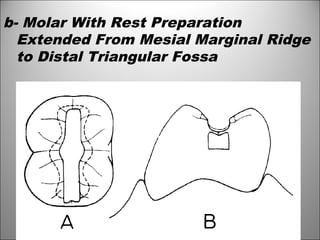
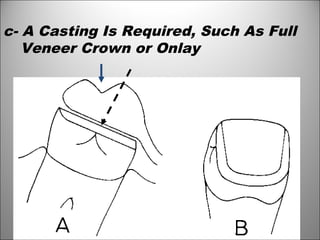
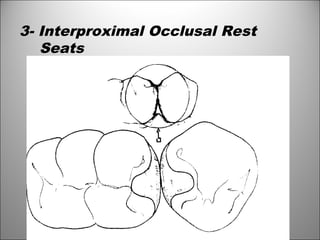
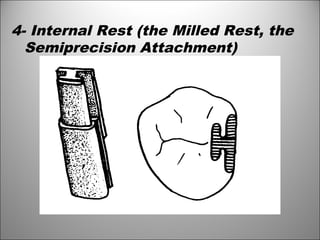
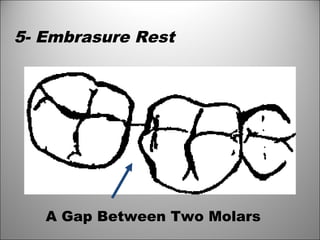
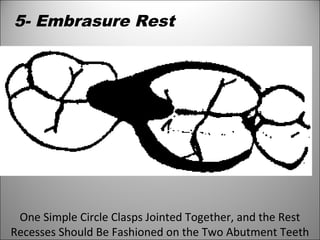
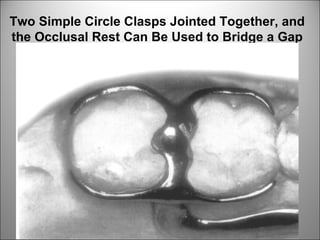
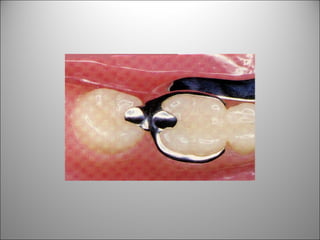
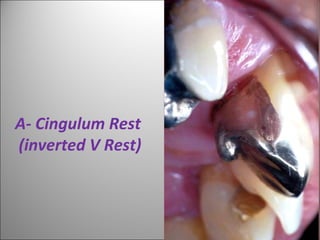
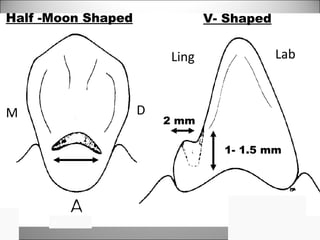
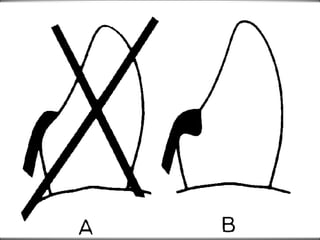
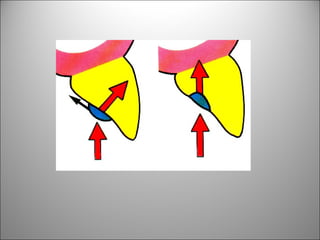
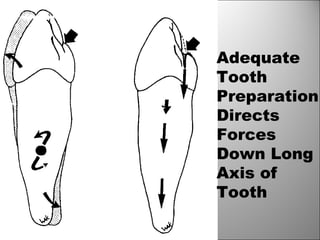
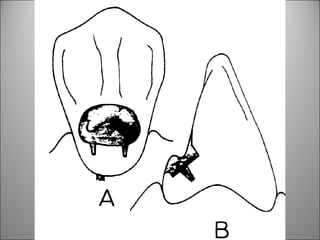
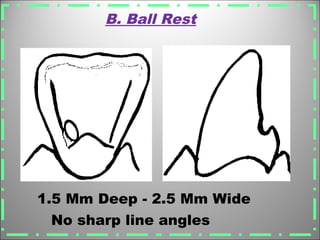
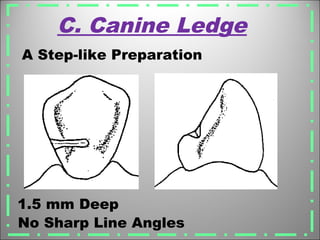
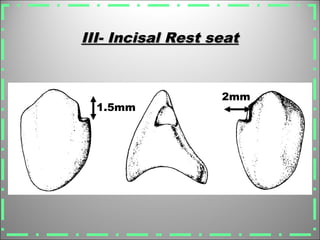
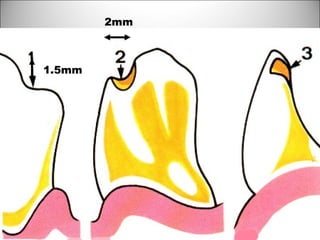
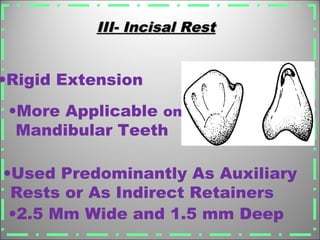
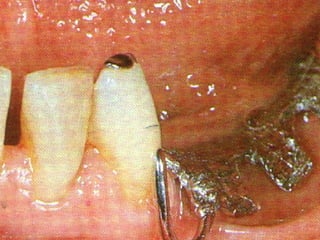
Rests are rigid extensions of a partial denture that are placed in specially prepared rest seats on teeth. They provide support to the partial denture. There are three main types of rests: occlusal, incisal, and lingual. Occlusal rests contact the chewing surface and are the most common type. Incisal rests are placed on the front surface of teeth. Lingual rests are on the inside surface of teeth. Rests must be properly fitted, strong, not raise the bite, transmit forces down the long axis of the tooth, and secure the clasp in the right position. Well-made rest seats help control stresses on teeth.