Major connectors lec3 & 4
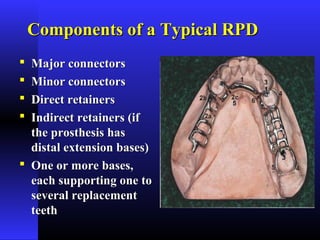
- 1. Components of a Typical RPDComponents of a Typical RPD Major connectorsMajor connectors Minor connectorsMinor connectors Direct retainersDirect retainers Indirect retainers (ifIndirect retainers (if the prosthesis hasthe prosthesis has distal extension bases)distal extension bases) One or more bases,One or more bases, each supporting one toeach supporting one to several replacementseveral replacement teethteeth
- 2. (a)(a) Major Connector:Major Connector: • TheThe Component of RPD that connects the parts ofof RPD that connects the parts of one side of the dental arch to those of the other side.one side of the dental arch to those of the other side. • Unit of partial denture to which All other parts are directly or indirectly attached.
- 4. (b)(b) Minor Connector:Minor Connector: A unit of a partial denture that connects otherA unit of a partial denture that connects other components (i.e. direct retainer, indirect retainer,components (i.e. direct retainer, indirect retainer, denture base, etc.) to the major connector.denture base, etc.) to the major connector.
- 5. (c)(c) Direct Retainer:Direct Retainer: A unit of a partial denture that provides retentionA unit of a partial denture that provides retention against dislodging forces.against dislodging forces. A direct retainer is commonly called a 'clasp' or 'claspA direct retainer is commonly called a 'clasp' or 'clasp unit' and is composed of four elements, a rest, aunit' and is composed of four elements, a rest, a retentive arm, a reciprocal arm and a minor connector.retentive arm, a reciprocal arm and a minor connector.
- 6. (d)(d) Indirect Retainer:Indirect Retainer: • A unit of a Class I or II partial denture that prevents or resistsA unit of a Class I or II partial denture that prevents or resists movement or rotation of the base(s) away from the residual ridge.movement or rotation of the base(s) away from the residual ridge. • The indirect retainer is usually composed of one component, aThe indirect retainer is usually composed of one component, a rest.rest. • It is functioned through lever action on the opposite side ofIt is functioned through lever action on the opposite side of fulcrum line when denture moves away from tissuefulcrum line when denture moves away from tissue
- 7. (e)(e) Denture Base:Denture Base: The unit of a partial denture that covers the residualThe unit of a partial denture that covers the residual ridges and supports the denture teeth and transferridges and supports the denture teeth and transfer occlusal forces to the supporting oral structures.occlusal forces to the supporting oral structures.
- 8. (f) rests:(f) rests: Any unit of partial denture that rests on a tooth surfaceAny unit of partial denture that rests on a tooth surface to provide vertical support.to provide vertical support.
- 9. (g) Stabilizing or(g) Stabilizing or reciprocal components:reciprocal components: When direct retainer comesWhen direct retainer comes into contact with abutment,into contact with abutment, the framework must bethe framework must be stabilized against horizontalstabilized against horizontal movement for the requiredmovement for the required clasp deformation to occur.clasp deformation to occur. Stabilization is derivedStabilization is derived from either cross-archfrom either cross-arch framework contacts orframework contacts or stabilizing or reciprocalstabilizing or reciprocal clasp in the same claspclasp in the same clasp assemblyassembly
- 10. Tissue stopperTissue stopper o Are integral parts of minor connectors designed forAre integral parts of minor connectors designed for retention of acrylic resin bases.retention of acrylic resin bases. o They provide stability to framework duringThey provide stability to framework during processing and prevent the possibility of theprocessing and prevent the possibility of the framework being pushed down ward as the acrylicframework being pushed down ward as the acrylic dough is packed into mold.dough is packed into mold. o They are useful in preventing distortion of theThey are useful in preventing distortion of the framework during acrylic resin processingframework during acrylic resin processing procedures.procedures. o Tissue stops can engage buccal and lingual slopesTissue stops can engage buccal and lingual slopes of residual ridge for stability.of residual ridge for stability.
- 13. Major connectors( bars or plates)Major connectors( bars or plates) LocationLocation 1- free of movable tissue1- free of movable tissue 2- avoid impingement of gingival tissue2- avoid impingement of gingival tissue 3-avoid prominent bone and soft tissues3-avoid prominent bone and soft tissues 4-relief under it ?4-relief under it ? 5- They should be located and/or relieved to5- They should be located and/or relieved to prevent impingement of tissue because the distalprevent impingement of tissue because the distal extension denture rotates in function.extension denture rotates in function.
- 14. Requirements of a Major ConnectorRequirements of a Major Connector • 1- made from alloy compatible with oral1- made from alloy compatible with oral tissuetissue
- 15. • 2- It is rigid and provides Cross-Arch2- It is rigid and provides Cross-Arch Stabilization (Counter leverage)Stabilization (Counter leverage) − Bracing elements on one side of the archBracing elements on one side of the arch providing stability to the otherproviding stability to the other
- 16. 3-Non-Interference With and is not3-Non-Interference With and is not irritating to the Tissues(tongue).irritating to the Tissues(tongue).
- 17. 4-does not alter the natural contour of lingual4-does not alter the natural contour of lingual surface of mandible or palatal vault ofsurface of mandible or palatal vault of maxillamaxilla 5- does not impinge on oral tissue when5- does not impinge on oral tissue when restoration is placed, removed, or rotates inrestoration is placed, removed, or rotates in function.function. 6- covers no more tissue than is absolutely6- covers no more tissue than is absolutely necessary.necessary.
- 18. 7-Minimize Food Impaction7-Minimize Food Impaction • Locate margins away from the FGMLocate margins away from the FGM • Eliminate "traps" or large concavitiesEliminate "traps" or large concavities where food can collectwhere food can collect
- 19. 8- support from other elements of the8- support from other elements of the framework to minimize rotationframework to minimize rotation 9-support the prosthesis.9-support the prosthesis.
- 20. Beading:-Beading:- is scribing a shallow groove on maxillary masteris scribing a shallow groove on maxillary master cast( when major connector exclusive to rugae areas) to:-cast( when major connector exclusive to rugae areas) to:- 1- transfer the major connector design to the investment1- transfer the major connector design to the investment castcast 2-provide visible finishing line for the casting2-provide visible finishing line for the casting 3- ensure intimate tissue contact of major connector with3- ensure intimate tissue contact of major connector with selected palatal tissueselected palatal tissue
- 21. Maxillary Major ConnectorsMaxillary Major Connectors • single Palatal Strapsingle Palatal Strap • Single palatal barSingle palatal bar • Anterior-Posterior Palatal StrapAnterior-Posterior Palatal Strap • Anterior-Posterior Palatal barAnterior-Posterior Palatal bar • Palatal platePalatal plate • U-shape palatal connectorU-shape palatal connector
- 22. Single Palatal Strap • Used to connect bilateral tooth-supported prosthesis, even those with short edentulous spaces, particularly when the edentulous areas are located posteriorly.
- 23. Palatal StrapPalatal Strap • It can be made rigid without objectionable bulkIt can be made rigid without objectionable bulk and interference with the tongue.and interference with the tongue. • Thin and wide anterior-posteriorly.Thin and wide anterior-posteriorly.
- 24. IndicationIndication •Class III or Class III modification I partiallyClass III or Class III modification I partially edentulous arch (short edentulous span).edentulous arch (short edentulous span). Contraindication :Contraindication : •Tooth-tissue supported partial dentures(Class ITooth-tissue supported partial dentures(Class I and class II).and class II). •Presence of palatal torusPresence of palatal torus •Extremely long tooth supported edentulous space.Extremely long tooth supported edentulous space.
- 25. Palatal BarPalatal Bar •Narrow antero-posteriorlyNarrow antero-posteriorly •Thick occluso-gingivallyThick occluso-gingivally •Palatal bar objectionable due to bulk.Palatal bar objectionable due to bulk.
- 26. Single palatal barSingle palatal bar -Palatal connector less than 8mm in width-Palatal connector less than 8mm in width -It must be rigid enough for cross- arch distribution,It must be rigid enough for cross- arch distribution, therefore:- it istherefore:- it is objectionable.objectionable. -It is indicated in tooth borne unilateral or bilateralIt is indicated in tooth borne unilateral or bilateral spacesspaces
- 27. Palatal Strap (or Bar)Palatal Strap (or Bar) • NeverNever use in cases involving distal extensions oruse in cases involving distal extensions or replacement of anterior teeth since it must bereplacement of anterior teeth since it must be made bulky for rigiditymade bulky for rigidity • Relief may be required over bony midlineRelief may be required over bony midline • Not used with torusNot used with torus
- 28. Combination Anterior and Posterior Palatal Strap-type Connector • Structurally a rigid major connector. • May be used in any maxillary partial denture design.
- 29. • Posterior palatal strap : Design- flat and minimum 8 mm wide. Location- as far posteriorly as possible to avoid interference with tongue but anterior to line of flexure formed by the junction of hard and soft palates.
- 30. • Anterior connector : Location: extended anteriorly to support anterior tooth replacements. Strength: lies in the fact that anterior and posterior components are joined together by longitudinal connectors on either side, forming a square or rectangular frame. Each component braces the others against possible torque and flexure. All maxillary major connectors should cross the midline at a right angle rather than on a diagonal.
- 31. Indications 1.Class III or Class III ,modification 1,Class II, modification 1 partially edentulous arch with long span edentulous space or spaces. 2. Class I and II arches in which excellent abutment and residual ridge support exists. 3. Class IV arches in which anterior teeth must be replaced with a removable partial denture. 4. In operable palatal tori.
- 32. . Contraindication •In inoperable maxillary torus that extends posteriorly to soft palate (a broad U-shaped major connector is used).
- 33. Anterior-Posterior Palatal BarAnterior-Posterior Palatal Bar • A narrow (A-P) variation of anterior-A narrow (A-P) variation of anterior- posterior palatal strapposterior palatal strap − Double palatal bar connectorDouble palatal bar connector − Requires greater bulk for rigidityRequires greater bulk for rigidity
- 34. Anterior-Posterior Palatal BarAnterior-Posterior Palatal Bar • More objectionable to the patientMore objectionable to the patient • Strap connectors provide greaterStrap connectors provide greater distribution of stressesdistribution of stresses • It may be used in any partial dentureIt may be used in any partial denture design.design.
- 35. Palatal Plate-type Connector • Thin, broad, contoured palatal coverage, covering one half or more of the hard palate. • Anatomic replica palatal castings have uniform thickness and strength because of their corrugated contours.
- 36. Palatal major connector covering two thirds of palate. Anterior border follows valleys between rugae and does not extend anterior to indirect retainers on first premolars. Posterior border is located at junction of hard and soft palates but does not extend onto soft palate.
- 37. • Anatomic replica palatal major connector has several advantages: Permits making of a uniformly thin metal plate that reproduces the anatomic contours of the patient’s own palate. The corrugation in the anatomic replica permits fabrication of a thinner casting with adequate rigidity.
- 38. Intentional surface irregularities maintain the original uniform thickness of the plastic pattern (only electrolytic polishing is needed). By virtue of intimate contact, interfacial surface tension between metal and tissue provides the prosthesis with greater retention. (to resist the pull of sticky foods, the forces of gravity, coughing, sneezing etc
- 39. Uses of palatal plate-type connector • May be used in one of three ways : as a plate of varying width that covers the area between two or more edentulous areas, as a complete or partial cast plate that extends posteriorly to the junction of hard and soft palates (figures A & B).
- 40. in the form of an anterior palatal connector with a provision for extending an acrylic resin denture base posteriorly (figures C & D).
- 41. INDICATIONS:INDICATIONS: •In class I (with 1-4 )premolars and some ofIn class I (with 1-4 )premolars and some of anterior teeth remaining.anterior teeth remaining. •Class II with large posterior modification spaceClass II with large posterior modification space and some missing anterior teeth.and some missing anterior teeth. •Class I with the last remaining abutment tooth onClass I with the last remaining abutment tooth on either side is the canine or 1either side is the canine or 1stst premolar tooth.premolar tooth.
- 42. • Class III with poor condition of remainingClass III with poor condition of remaining anterior teeth.anterior teeth. • Patient with cleft palate to close any air passagePatient with cleft palate to close any air passage between nasal and oral cavity.between nasal and oral cavity. • Absence of palatal torus.Absence of palatal torus.
- 43. Anterior Palatal PlateAnterior Palatal Plate (U-Shaped or "Horse-Shoe" Palatal Connector)(U-Shaped or "Horse-Shoe" Palatal Connector) • Poor connectorPoor connector • NeverNever use unless absolutely necessaryuse unless absolutely necessary • Requires bulk in the rugae area (where the tongueRequires bulk in the rugae area (where the tongue requires freedom) for rigidityrequires freedom) for rigidity
- 44. Anterior Palatal PlateAnterior Palatal Plate DisadvantagesDisadvantages •Lack of rigidityLack of rigidity •Fail to provide good support and thus permitFail to provide good support and thus permit impingement of underlying tissue when subjected toimpingement of underlying tissue when subjected to occlusal forcesocclusal forces •Bulk to enhance rigidity results in increased thicknessBulk to enhance rigidity results in increased thickness in areas are hindrance to the tonguein areas are hindrance to the tongue
- 45. indicationsindications 1- large inoperable torus1- large inoperable torus 2- several anterior teeth are to be2- several anterior teeth are to be replacedreplaced
- 46. Mandibular Major ConnectorsMandibular Major Connectors • Lingual Bar most widely usedLingual Bar most widely used • Lingual PlateLingual Plate • Sublingual BarSublingual Bar • Continuous BarContinuous Bar • Cingulum bar (continuous bar).Cingulum bar (continuous bar). • Labial BarLabial Bar
- 47. • Relief is provided for soft tissue under all portions of mandibular major connector and any location where the framework crosses the gingival margin. • The inferior border does not impinge on the tissue in the floor of the mouth during the normal activities. • Located as far inferiorly as possible to avoid interference with the resting tongue and trapping of food substances
- 48. Methods to determine the relative height of the floor of the mouth: 1- Measure the height of the floor of the mouth in relation to the lingual gingival margins of adjacent teeth with a periodontal probe.
- 49. 2-Use an impression material with an individualized impression tray having its lingual borders 3 mm short of the elevated floor of the mouth
- 50. Characteristics and location o Half-pear shaped with bulkiest portion inferiorly located. o Superior border tapered to soft tissue.
- 51. o Superior border located at least 4mm inferior to gingival margins. o Inferior border located at the ascertained height of the alveolar lingual sulcus when the patients tongue is slightly elevated o The inferior border of the lingual bar should be slightly round when the framework is polished.
- 52. Indications:Indications: 1-sufficient space between slightly elevated alveolar1-sufficient space between slightly elevated alveolar lingual sulcus and lingual gingival tissue (9-11mm).lingual sulcus and lingual gingival tissue (9-11mm). 2-2-sufficientsufficient indirect retention by clasp and indirectindirect retention by clasp and indirect retainer.retainer. 3-Future additions of prosthetic teeth to the framework3-Future additions of prosthetic teeth to the framework are not anticipatedare not anticipated 4- diastema or opened cervical embrasures.4- diastema or opened cervical embrasures. 5-over lapped anterior teeth5-over lapped anterior teeth
- 53. Mandibular Major ConnectorsMandibular Major Connectors • ContraindicationsContraindications 1- space not enough(less than 8mm).1- space not enough(less than 8mm). 2- only few anterior teeth remain2- only few anterior teeth remain 3-lingually inclined teeth3-lingually inclined teeth 4-lingual undercut in alveolar ridge4-lingual undercut in alveolar ridge 5- parallel or sloped anterior lingual alveolar5- parallel or sloped anterior lingual alveolar contour in a distal extension RPD because thecontour in a distal extension RPD because the bar may rotate into tissue as denture base movesbar may rotate into tissue as denture base moves toward residual ridgetoward residual ridge
- 55. Lingual Plate (Linguoplate)Lingual Plate (Linguoplate) • Lingual bar with extension over cingula ofLingual bar with extension over cingula of anterior teethanterior teeth • Should have rest at each end regardless theShould have rest at each end regardless the need of indirect retainer.need of indirect retainer.
- 56. • The upper border should follow the natural curvature of the supracingular surfaces of the teeth. • The half— pear shape of a lingual bar should still form the inferior border providing the greatest bulk and rigidity. • All gingival crevices and deep embrasures must be blocked out parallel to the path of placement to avoid gingival irritation and any wedging effect between the teeth.
- 57. • The linguoplate does not in itself serve as an indirect retainer. When indirect retention is required, definite rests must be pr‹›vided for this purpose
- 58. Lingual Plate IndicationsLingual Plate Indications − floor of the mouth space is limitedfloor of the mouth space is limited − Prominent lingual frenumProminent lingual frenum − Lingual tori can t removed surgicallyLingual tori can t removed surgically − Stabilizing periodontally weakenedStabilizing periodontally weakened teethteeth − Futural replacement of one or moreFutural replacement of one or more incisor teethincisor teeth − Only few remaining anterior teethOnly few remaining anterior teeth
- 59. Lingual PlateLingual Plate • Distal extension RPD with sloped lingual alveolarDistal extension RPD with sloped lingual alveolar ridge.ridge. • 8-8- Mandibular tori or exostosis. Relief isMandibular tori or exostosis. Relief is provided between the torus or exostosis and theprovided between the torus or exostosis and the framework.framework.
- 60. Lingual Plate contraindicationsLingual Plate contraindications • When lingual bar is usedWhen lingual bar is used • Overlapped anterior teethOverlapped anterior teeth • Lingually inclined teethLingually inclined teeth • Diastema unless it has slots.Diastema unless it has slots. ( disadvantages)( disadvantages) • Open cervical embrasuresOpen cervical embrasures
- 61. Continuous Bar RetainerContinuous Bar Retainer • Lingual bar with secondary bar aboveLingual bar with secondary bar above cingulacingula • Narrow 3mmmetal strapNarrow 3mmmetal strap • Originated from incisal, lingual orOriginated from incisal, lingual or occlusal rests of adjacent abutmentsocclusal rests of adjacent abutments
- 62. Continuous Bar RetainerContinuous Bar Retainer • Excellent IR.Excellent IR.
- 63. indications:indications: 1-lingual plate indicated but axial alignment1-lingual plate indicated but axial alignment of anterior teeth require excessive block outof anterior teeth require excessive block out of interproximal undercuts.of interproximal undercuts. 2-wide diastema2-wide diastema 3-when major connector must contact3-when major connector must contact natural teeth for bracing and IR with opennatural teeth for bracing and IR with open cervical embrasures.cervical embrasures.
- 64. Contra indications:Contra indications: 1-Where a lingual bar or lingual plate will suffice.1-Where a lingual bar or lingual plate will suffice. 2-Any contra indicatiDn for a lingual bar.2-Any contra indicatiDn for a lingual bar. 3-Any contra indication for a lingual3-Any contra indication for a lingualplateplate exceptexcept openopen cervical embrasures.cervical embrasures.
- 65. Sublingual barSublingual bar Useful when the height of the floor of theUseful when the height of the floor of the mouth not allow placement of bar 4 mmmouth not allow placement of bar 4 mm below the FGMbelow the FGM
- 66. indications:indications: 1- the height of floor of the mouth less than 6 mm1- the height of floor of the mouth less than 6 mm 2- used when it is desirable to keep FGM exposed2- used when it is desirable to keep FGM exposed and there is inadequate depth of floor of mouth toand there is inadequate depth of floor of mouth to place lingual bar.place lingual bar. 3-presence of anterior lingual undercut3-presence of anterior lingual undercut 4- bracing and IR can be provided4- bracing and IR can be provided 5- distal extension with sloped lingual alveolar5- distal extension with sloped lingual alveolar ridgeridge 6- diastema and opened cervical ebrasure.6- diastema and opened cervical ebrasure. 7- over lapped anterior teeth7- over lapped anterior teeth 8- intolerance to other types of major connectors8- intolerance to other types of major connectors
- 67. Contraindications:Contraindications: 1-lingual bar or lingual plate is sufficient1-lingual bar or lingual plate is sufficient 2-natural anterior teeth severely tilted2-natural anterior teeth severely tilted linguallylingually 3-interfering tori3-interfering tori 4-interferance with elevation of the floor of4-interferance with elevation of the floor of the mouththe mouth 5-future addition of teeth may be anticipated5-future addition of teeth may be anticipated
- 68. Indications: 1-Axial alignment of the anterior teeth is such that the excessive block out of interproximal undercuts would be required. 2-Lingual frenum and floor of the mouth at the same level as marginal gingiva. 3-lnoperable tori or exostosis at the same level as the marginal gingiva. 4-Severely undercut lingual alveolus. . 5-Considerable gingival recession.
- 69. Contra indications: 1-Anterior teeth severely tilted to the lingual. 2-When wide diastemata exist between the mandibular anterior teeth .
- 71. Labial BarLabial Bar -Bar on labial or buccal sulcus-Bar on labial or buccal sulcus -Superior border located 4mm inferior to-Superior border located 4mm inferior to labial gingival margin.labial gingival margin. -Inferior border at the junction betweenInferior border at the junction between attached and unattached mucosaattached and unattached mucosa -It must be relieved in canine eminence areaIt must be relieved in canine eminence area
- 72. Labial barLabial bar Indications:Indications: 1.When the mandibular teeth are so severely1.When the mandibular teeth are so severely inclined lingually as to prevent the use ofinclined lingually as to prevent the use of lingual major connector.lingual major connector. 2.When large lingual tori exist and their removal is2.When large lingual tori exist and their removal is contraindicated.contraindicated. 3-abnormal high lingual frenum3-abnormal high lingual frenum 4-severe lingual tissue undercuts.4-severe lingual tissue undercuts. 5- patient cant tolerate lingual bar.5- patient cant tolerate lingual bar.
- 74. contraindicationscontraindications 1- when lingual major connector may be used.1- when lingual major connector may be used. 2-labial tori2-labial tori 3-facial alveolar ridge has undercut3-facial alveolar ridge has undercut 4-high facial muscle attachment result in less4-high facial muscle attachment result in less than 4 mm of space between superior edgethan 4 mm of space between superior edge of labial bar and marginal gingiva of theof labial bar and marginal gingiva of the teethteeth
- 76. A modification to the linguoplate is the hinged continuous labial bar. consists of a labial or buccal bar that is connected to the major connector by a hinge on one end and a latch at the other end.
- 77. • Support is provided by multiple rests on the remaining natural teeth. • Stabilization and reciprocation are provided by a linguoplate contacting the remaining teeth and are supplemented by the labial bar with its retentive struts. • Retention is provided by a bar type of retentive clasp arms projecting from the labial or buccal bar and contacting the infrabulge areas on the labial surfaces of the teeth.
- 78. Indications: 1- Missing key abutments (such as canine). 2- Unfavorable tooth contours. 3- Unfavorable soft tissue contours.. 4- Teeth with questionable prognoses Contra indications: 1-Poor oral hygiene and lack of patient motivation. 2-Shallow buccal or labial vestibule. 3-High frenal attachment (labial or buccal frenum).