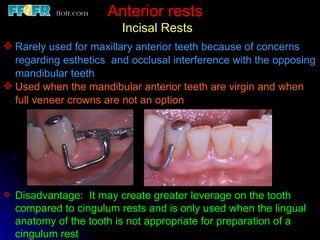
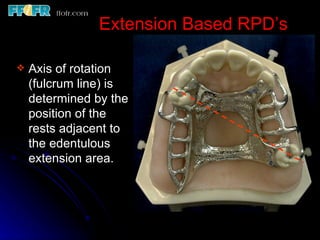
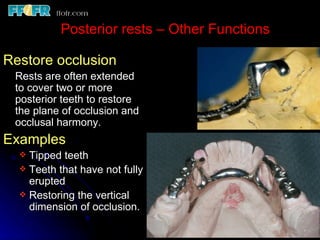
This document discusses partial denture rests and their role in supporting partial dentures. It describes the different types of rests used for anterior and posterior teeth. Anterior rests include crescent-shaped cingulum rests, circular concave rests, and incisal rests. Posterior rests are designed to direct forces along the tooth's long axis to preserve remaining structures. Continuous posterior rests can also stabilize periodontally compromised teeth. Proper rest design and tooth preparation are necessary to create positive, supportive engagement between the partial denture and abutment teeth.