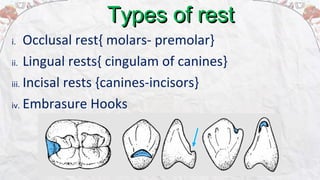
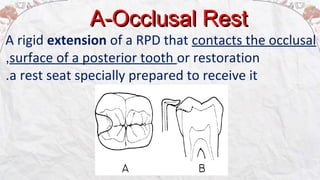
1) Rests are extensions of a partial denture that are placed in prepared rest seats on teeth. They provide support to the partial denture.
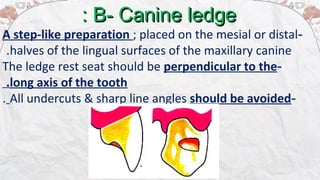
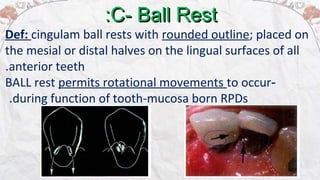
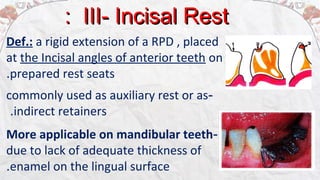
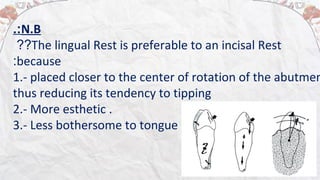
2) Common types of rests include occlusal rests, lingual rests, incisal rests, and embrasure hooks. Occlusal rests are most commonly placed on posterior teeth while lingual rests are used on anterior teeth.
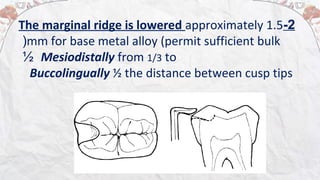
3) Rest seats are prepared to receive the rests. Requirements for an adequate rest seat include a rounded triangular shape, appropriate dimensions, and elimination of undercuts to allow for accurate seating of the rest.