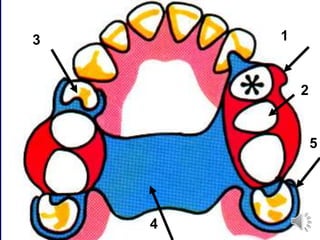
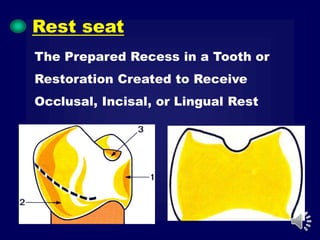
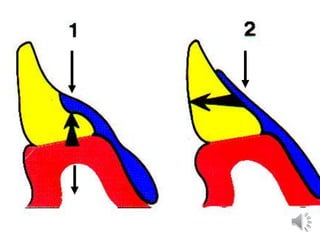
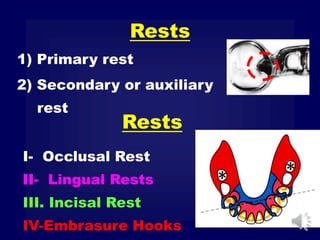
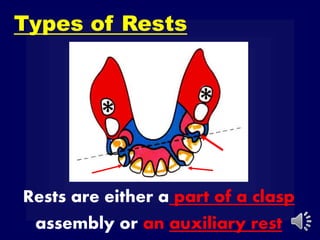
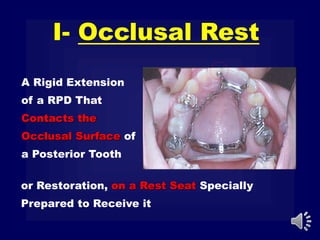
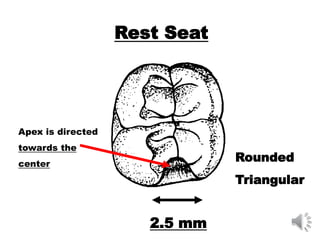
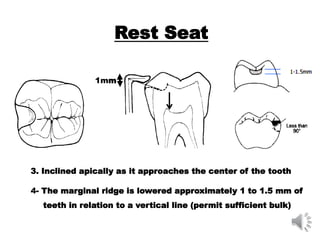
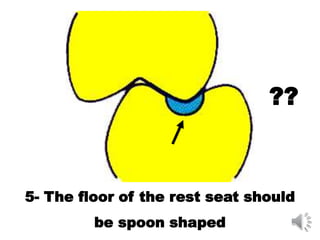
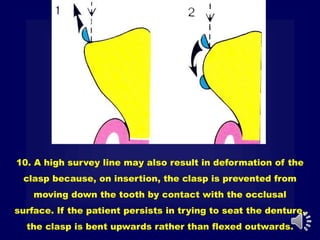
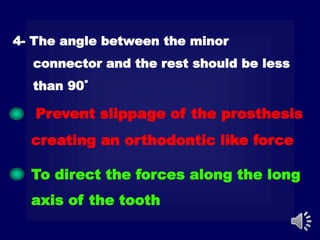
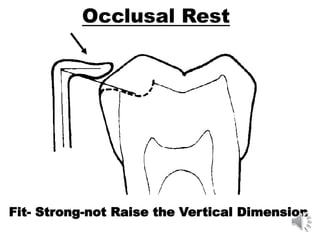
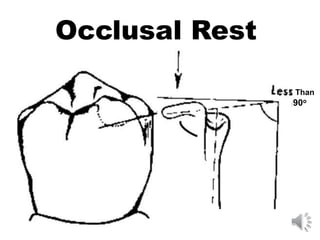
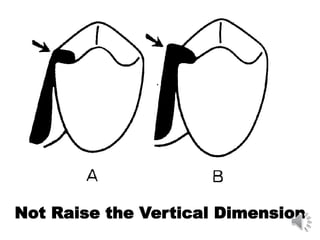
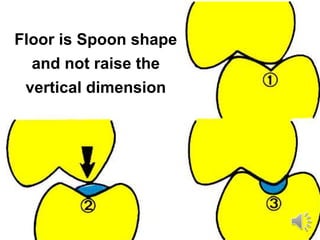
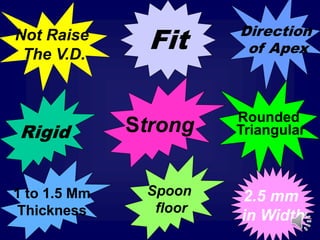
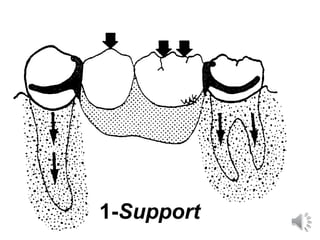
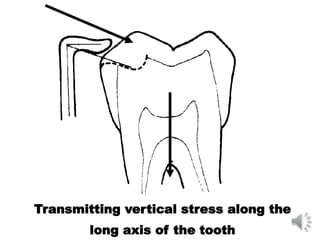
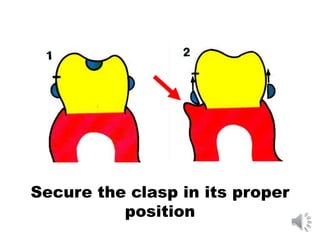
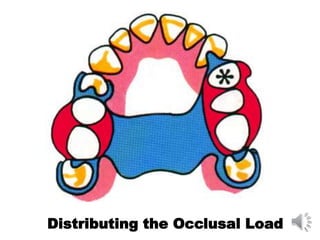
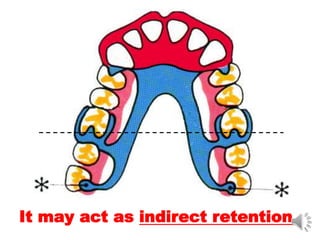
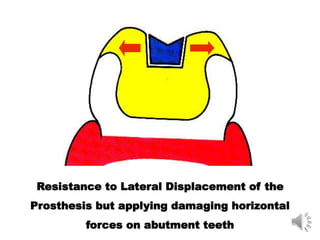
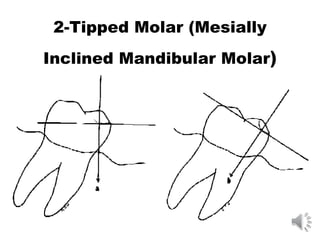
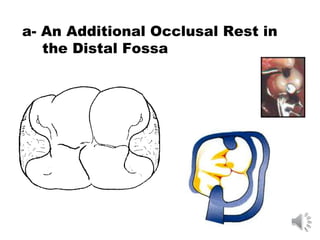
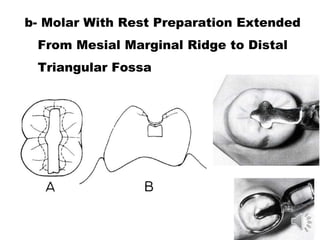
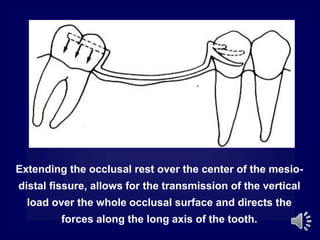
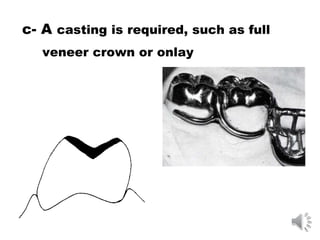
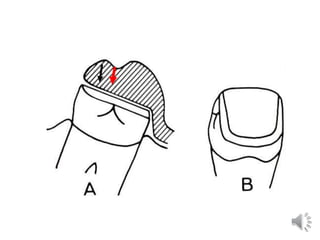
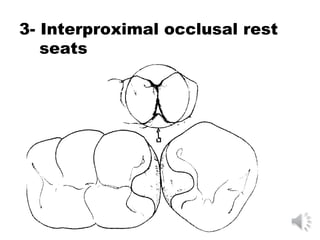
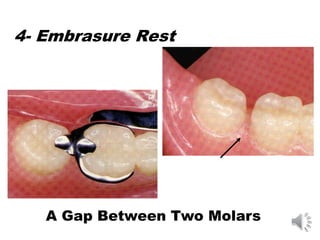
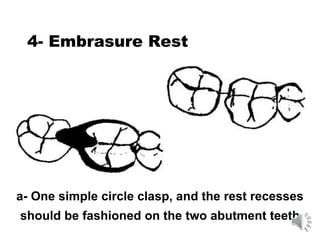
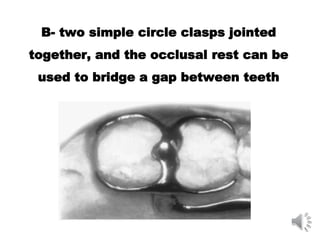
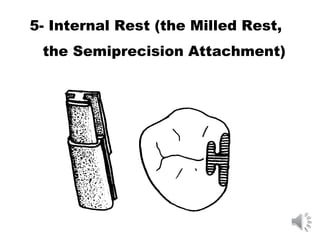
This document discusses different types of tooth rests used in partial dentures. There are four main types: 1) Occlusal rests, which contact the biting surface of posterior teeth. 2) Lingual rests, which contact the inside surface of teeth. 3) Incisal rests, which contact the front surface of anterior teeth. 4) Embrasure hooks, which span the gap between two teeth. Occlusal rests are the most common type and involve preparing the tooth with a rounded triangular rest seat for the denture to fit into. The preparation aims to direct forces along the tooth's long axis and not raise the vertical biting dimension.